Light-emitting semiconductor device and method of fabrication
a technology of light-emitting semiconductors and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, basic electric elements, electrical appliances, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the manufacturing cost of light-emitting devices, increasing the cost of sapphire itself, and additional difficulties in connection with sapphire base plates, so as to reduce the power and voltage requirements of devices, improve the flatness of buffer layers and semiconductor regions, and reduce the resistance of buffer sublayers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
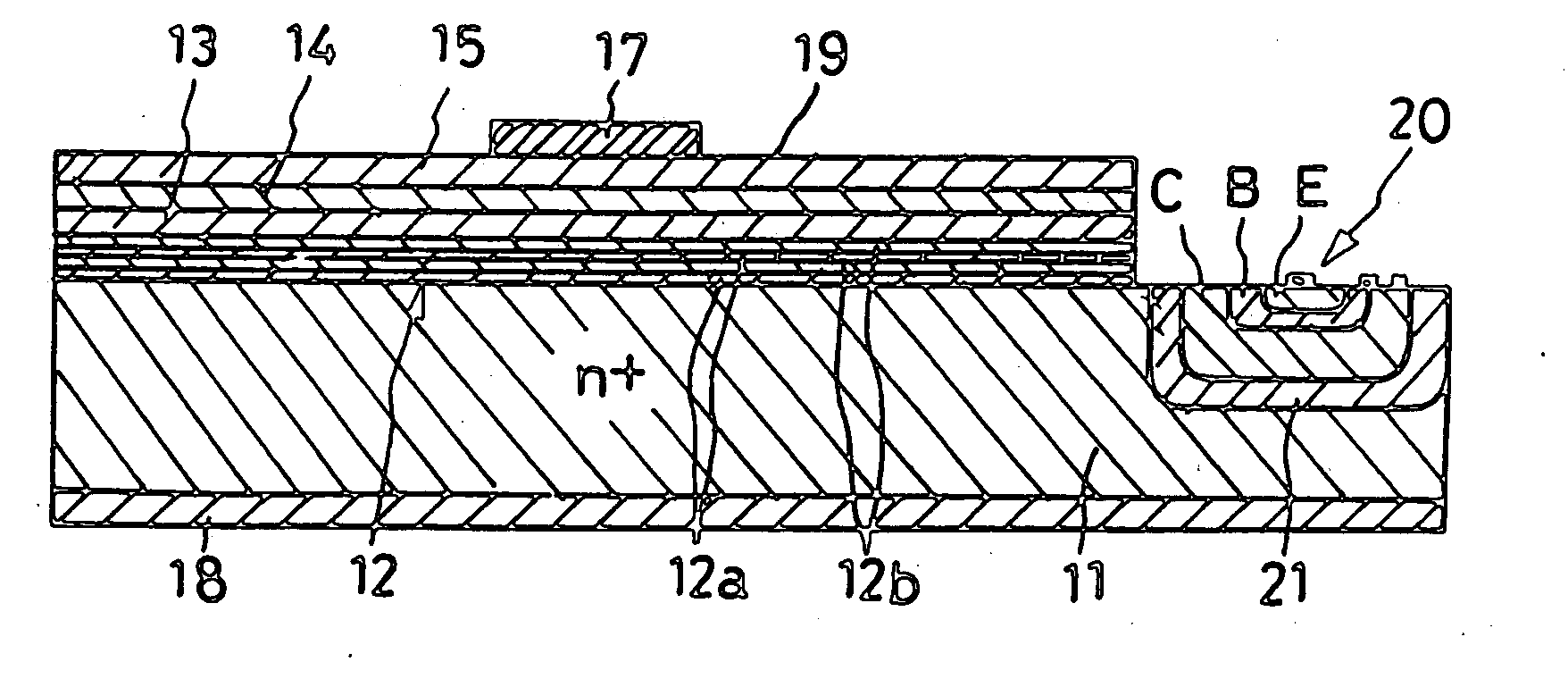
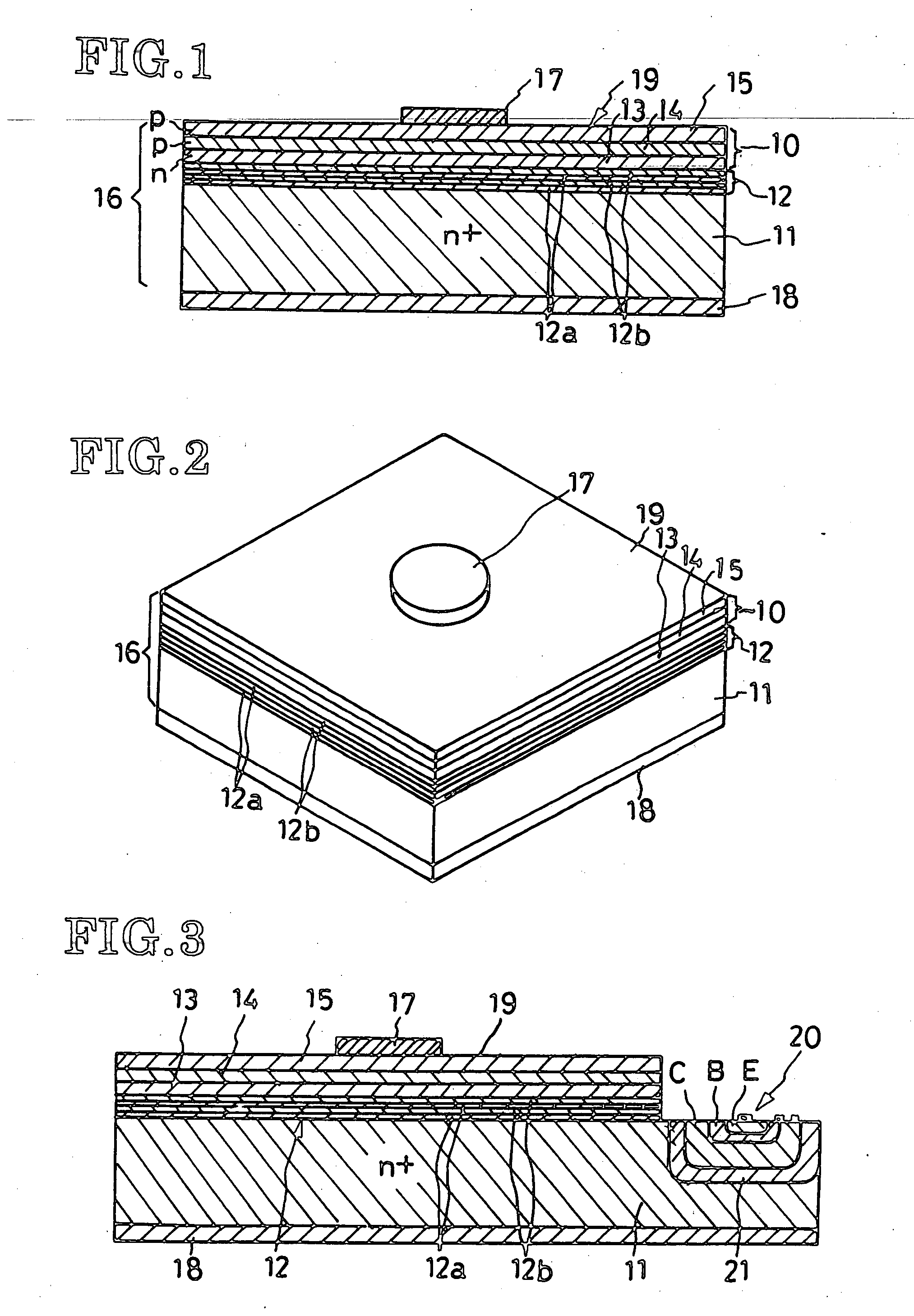
[0029] The light-emitting semiconductor device according to the invention will now be described in detail in terms of the blue-light-emitting GaN-based compound diode illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2. The exemplified blue LED comprises a semiconductor region 10 composed of a plurality of GaN-based compound semiconductor layers for emission of light, a substrate or baseplate 11 of a silicon semiconductor having a crystal plane (111), and a buffer layer 12. The light-emitting semiconductor region 10 comprises an n-type semiconductor region 13 composed of GaN, a p-type light-emitting or active layer 14 composed of InGaN, and a p-type semiconductor region 15 composed of GaN.
[0030] The lamination of the light-emitting semiconductor region 10, the baseplate 11 and the buffer layer 12 constitutes a substrate or base body 16. An anode 17 is formed on one of the two opposite major surfaces, or on the top as seen in the attached drawings, of the base body 16, or on the semiconductor region 15, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com