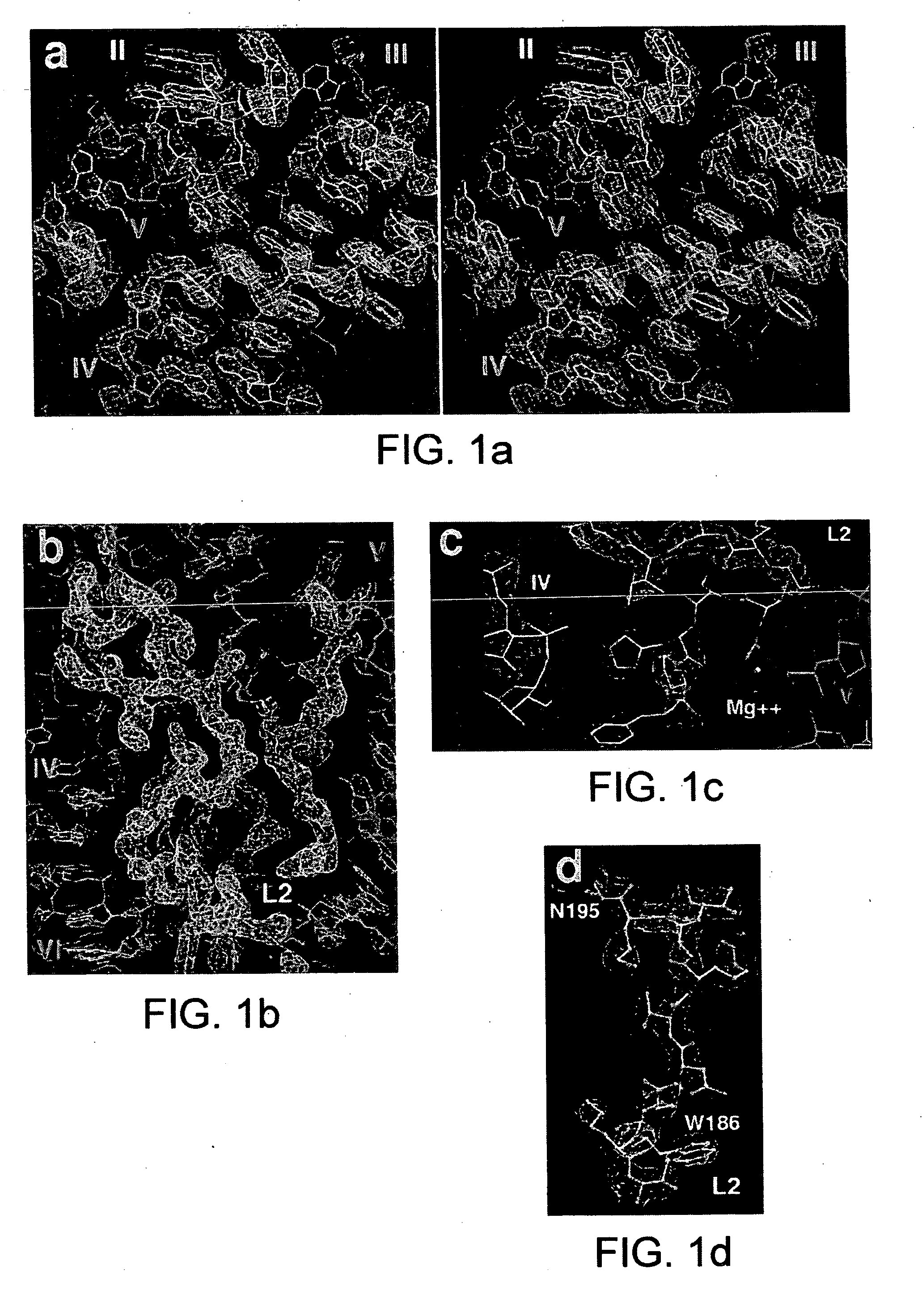
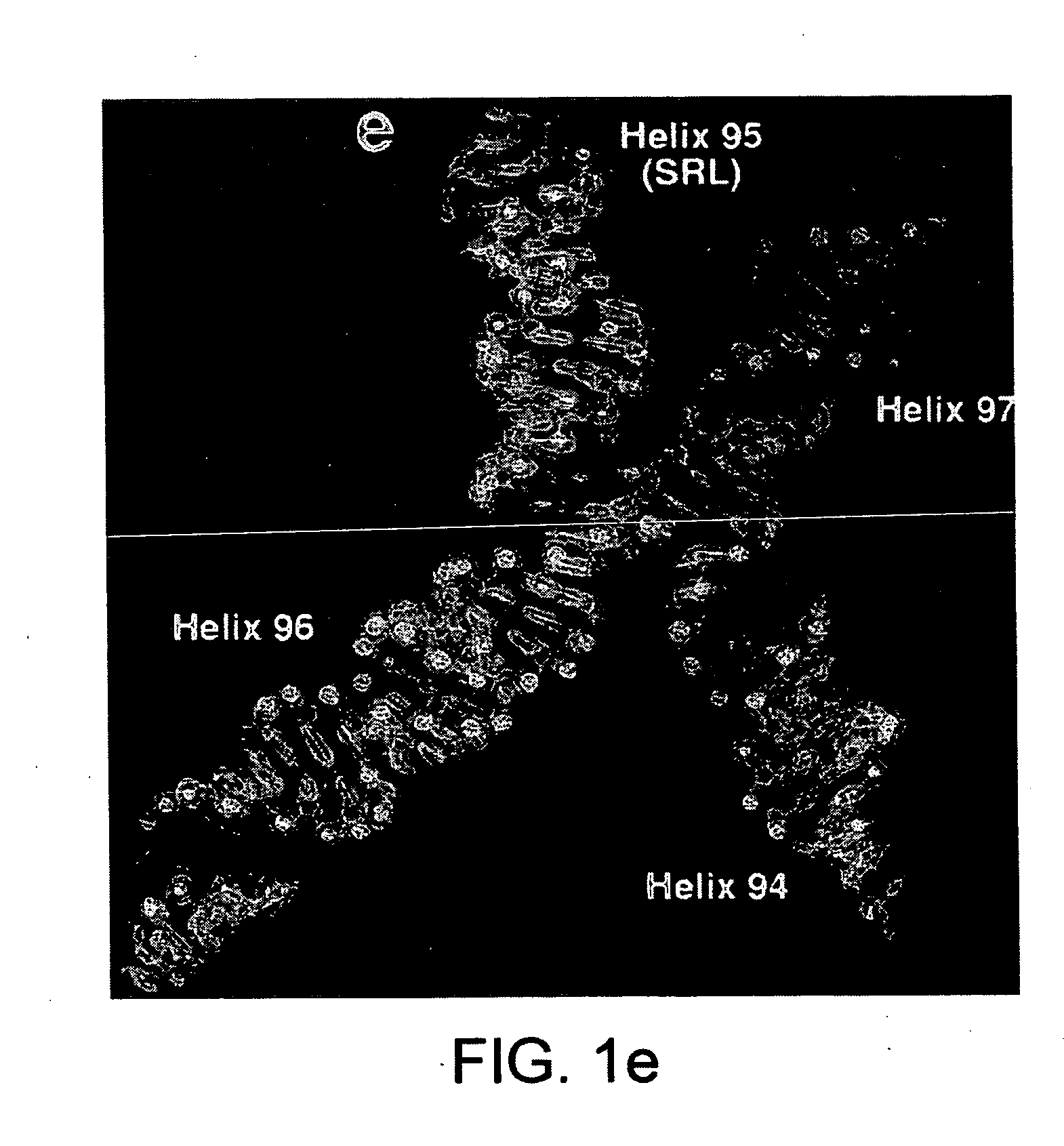
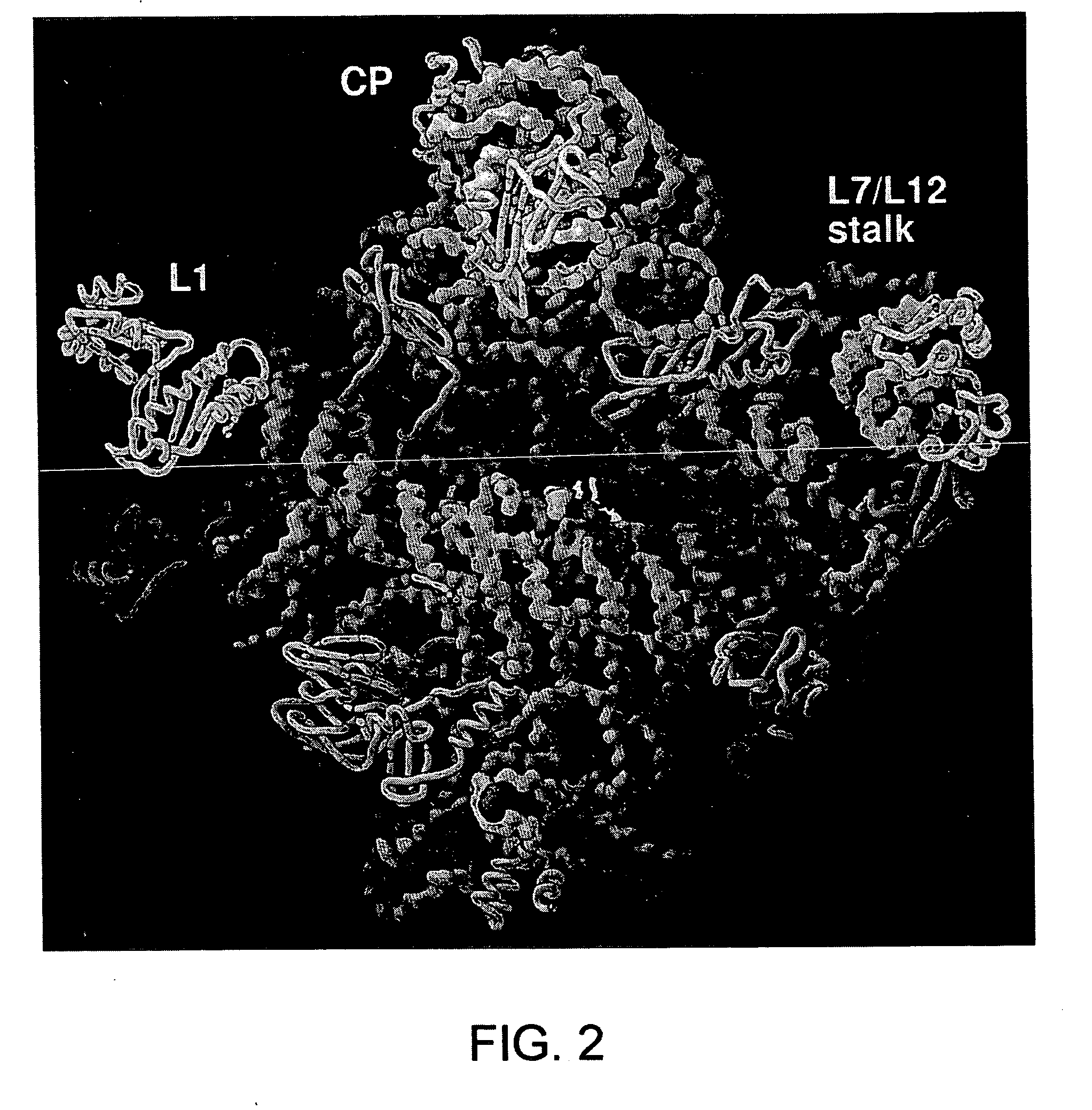
Ribosome structure and protein synthesis inhibitors
a ribosome and protein synthesis technology, applied in the field of protein biosynthesis and modulators, can solve the problems of low resolution electron density maps that are spurious, atomic scattering interferes constructively, and it is not possible to produce active particles that are completely protein-free, so as to achieve the effect of ready-to-test design and testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A. Example 1
Preparation of 50S Ribosomal Subunit Crystals
[0437]H. marismortui (ATCC 43049) was grown as described previously (Ban et al. (1998) supra) on a slightly modified version of ATCC culture medium 1230, which was supplemented with 4.3 g of yeast extract, 5.1 g of Tris, and 3.4 g of glucose per liter. Bacteria were grown at 37° C. to an OD550 nm between 1.0 and 2.2. They were harvested by centrifugation, and stored at −80° C. Cells were ruptured using a French press. Ribosomes were prepared from lysates by centrifugation, and subunits were isolated on sucrose gradients (Shevack et al. (1985) FEBS Lett. 184: 68-71).
[0438] 1. Reverse Extraction
[0439] (1) Take 1 mg of subunits from a concentrated 50S ribosomal subunit stock (30 mg / ml in 1.2 M KCl, 0.5 M NH4Cl, 20 mM MgCl2, Tris 10 mM, CdCl2 1 mM, Tris 5 mM, pH 7.5) and mix with ½ vol. of 30% PEG6000 (300g PEG, 700 ml H2O to make 1 liter of 30% PEG; filter through 0.2 μm filter). Leave on ice for 1 to 2 hr.
[0440] (2) Spin dow...
example 2
B. Example 2
Determination of the Crystal Structure of the 50S Ribosomal Subunit, With the Initial Refinement
[0458] All data, except the two native data sets, were collected at the National Synchrotron Light Source (Brookhaven) from crystals frozen at 100 K, using beamlines X12b and X25 and recorded using a 345 mm MAR imaging plate. For each heavy atom derivative, anomalous diffraction data were collected at the wavelength corresponding to the peak anomalous scattering. The beam size was 100×100 μm for most data collections at X25 and 200×200 μm at beamline X12b. The crystals were aligned along the long axis of the unit cell (570 Å) so that 1.0° oscillations could be used to collect reflections out to a maximum of 2.7 Å resolution at the edge of the MAR detector. At beamline X12b the crystal to detector distances varied between 450.0 mm and 550.0 mm depending on wavelength, crystal quality and beam divergence, and it was chosen so that maximum resolution data could be collected whil...
example 3
C. Example 3
Preparation of Crystals of 50S Ribosomal Subunit / Puromycin Complex and Collection of X-ray Diffraction Data
[0460] Crystals of 50S ribosomal subunits were grown and stabilized as described earlier. CCdA-p-puromycin (see FIG. 9A) was a generous gift from Michael Yarus (Welch, et al. (1995) supra). Oligonucleotides from amino-N-acylated minihelices (see FIG. 9B) were synthesized by Dharmacon. Following deprotection, the oligonucleotides were heated briefly to 100° C. and snap-cooled on ice to reanneal. Ribosomal 50S subunit crystals were stabilized and then soaked for 24 hours in stabilization buffer plus 100 μM CCdA-p-puromycin or amino-N-acylated mini-helices prior to cryovitrification in liquid propane and X-ray diffraction data collection. Phases were calculated by density modification (CNS) beginning with the best experimental phases using 2Fo(analogue)-Fo(native) for amplitudes, from 60.0 to 3.2 Å. (Native amplitudes were from the most isomorphous native 1 data set, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com