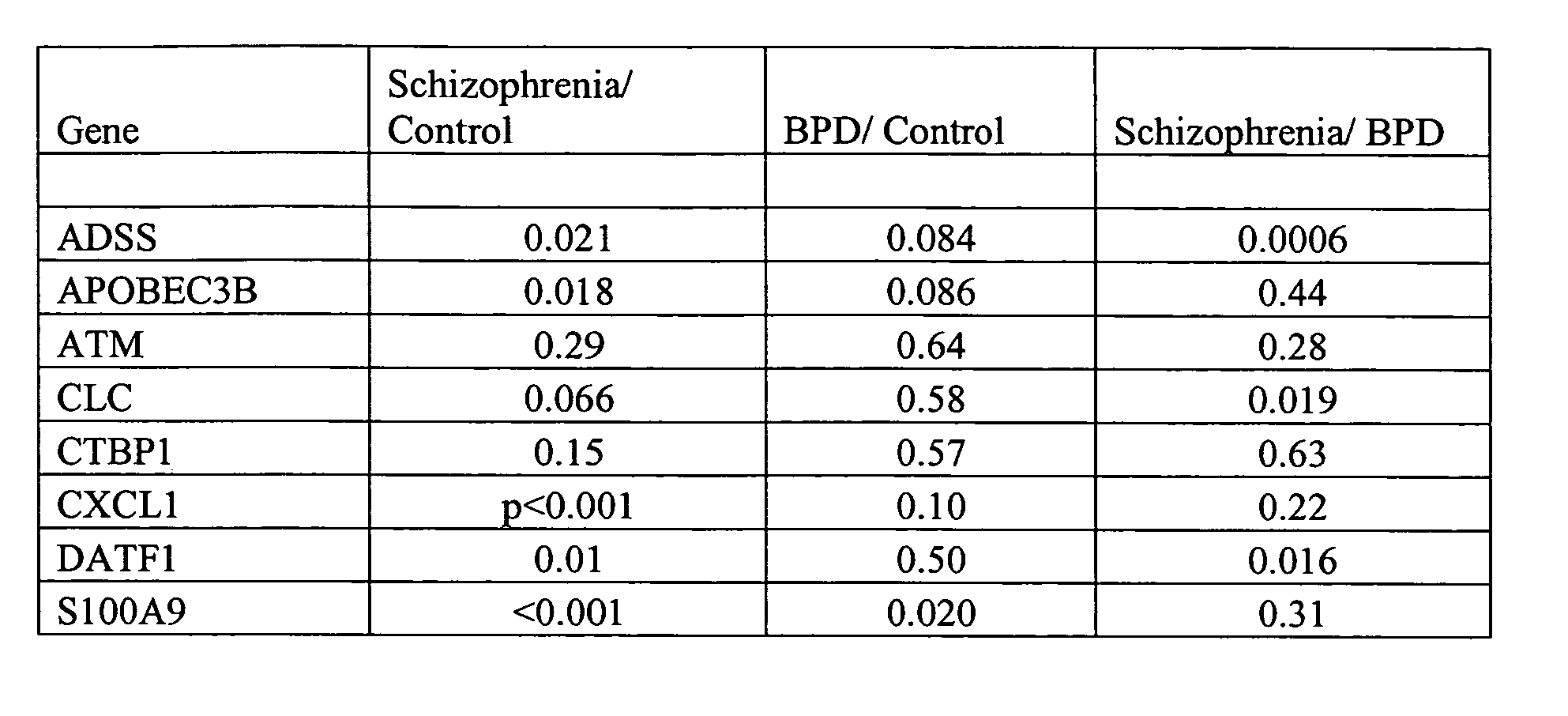
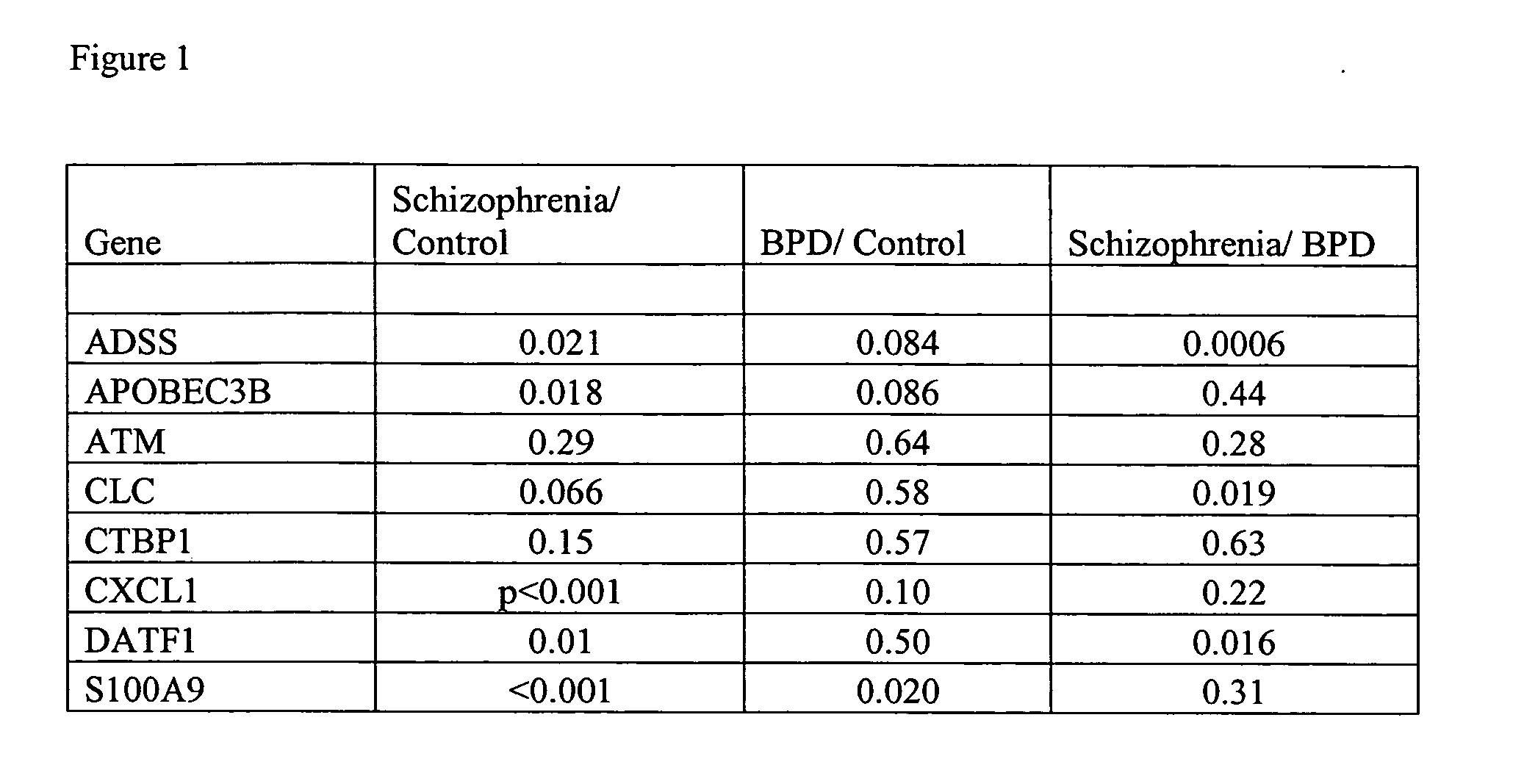
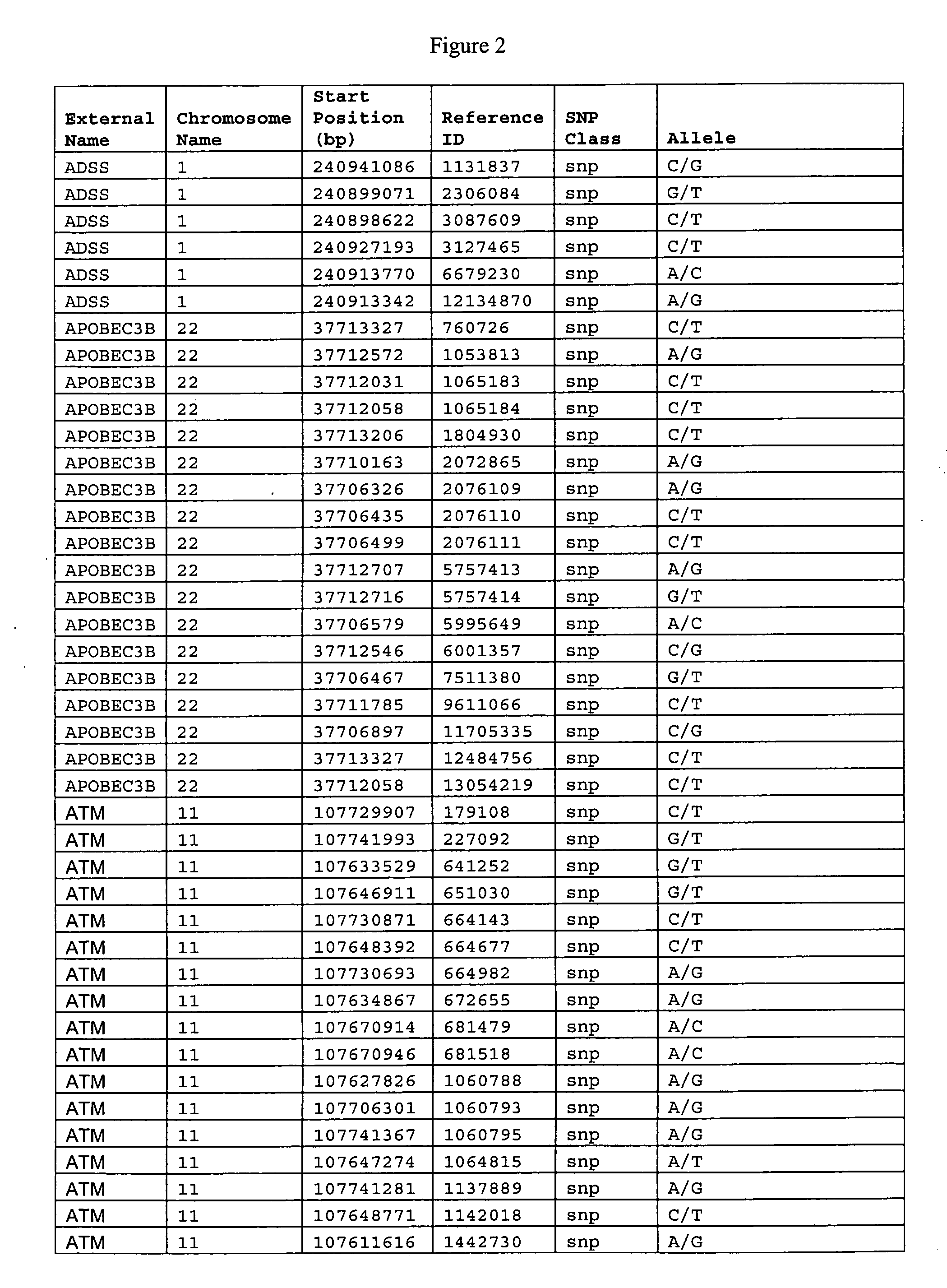
Biomarkers for diagnosing schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
a biomarker and schizophrenia technology, applied in the field of identification and selection of novel biomarkers, can solve the problems of difficult diagnosis of schizophrenia, inconvenience for patients, and increased difficulty in diagnosing schizophrenia, and achieve the effect of monitoring the efficacy of treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
RNA Isolation from Lysed Blood
[0547] 10 ml whole blood is obtained in a Vacutainer and spun at 2,000 rpm for 5 min at 4° C. and the plasma layer removed. Lysis Buffer is added to blood sample in a ratio of 3 parts Lysis Buffer to 1 part blood (Lysis Buffer (IL) 0.6 g EDTA; 1.0 g KHCO2, 8.2 g NH4Cl adjusted to pH 7.4 (using NaOH)). Sample is mixed and placed on ice for 5-10 minutes until transparent. Lysed sample is centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4° C., and supernatant is aspirated. Pellet is resuspended in 5 ml Lysis Buffer, and centrifuged again at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4° C. Pelleted cells are homogenized using TRIzol® (D (GIBCO / BRL) in a ratio of approximately 6 ml of TRIzol® for every 10 ml of the original blood sample and vortexed well. Samples are left for 5 minutes at room temperature. RNA is extracted using 1.2 ml of chloroform per 1 ml of TRIzol®. Sample is centrifuged at 12,000×g for 5 minutes at 4° C. and upper layer is collected. To upper layer, isoprop...
example 2
From Whole Blood
[0548] 100 ul whole blood is obtained in a microcentrifuge tube and spun at 2,000 rpm (800 g) for 5 min at 4° C. and the supernatant removed. Pelleted cells are homogenized using TRIzol (GIBCO / BRL) in a ratio of approximately 6 μl of TRIzol for every 10 μl of the original blood sample and vortexed well. Samples are left for 5 minutes at room temperature. RNA is extracted using 12 μl of chloroform per 10 μl of TRIzol. Sample is centrifuged at 12,000×g for 5 minutes at 4° C. and upper layer is collected. To upper layer, isopropanol is added in ratio of 5 μl per 10 μl of TRIzol. Sample is left overnight at −20° C. or for one hour at −20° C. RNA is pelleted in accordance with known methods, RNA pellet air dried, and pellet resuspended in DEPC treated ddH2O. RNA samples can also be stored in 75% ethanol where the samples are stable at room temperature for transportation.
From Centrifuged Lysed Blood
[0549] 10 ml whole blood is obtained in a Vacutainer and spun at 2,000...
example 3
Target Nucleic Acid Preparation and Hybridization
Preparation of Fluorescent DNA Probe from mRNA
[0551] Fluorescently labeled target nucleic acid samples of RNA are prepared for analysis with an array of the invention.
[0552] 1 μg Oligo-dT primers are annealed to 10 ug of total RNA isolated from blood from patient diagnosed with schizophrenia and / or bipolar disorder or suspected of having schizophrenia and / or bipolar disorder in a total volume of 10 ul, by heating to 70° C. for 10 min, and cooled on ice. The mRNA is reverse transcribed by incubating the sample at 42° C. for 40 min in a 25 ll volume containing a final concentration of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 75 mM KCl, 3 mM MgC12, 25 mM DTT, 25 mM unlabeled dNTPs, 400 units of Superscript II (200 U / uL, Gibco BRL), and 15 mM of Cy3 or Cy5 (Amersham). The reaction is stopped by the addition of 2.5 μl of 55500 mM EDTA and 5 μl of 1M NaOH, and incubation at 65° C. for 10 min. The reaction mixture is neutralized by addition of 12.5 μl ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Digital information | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com