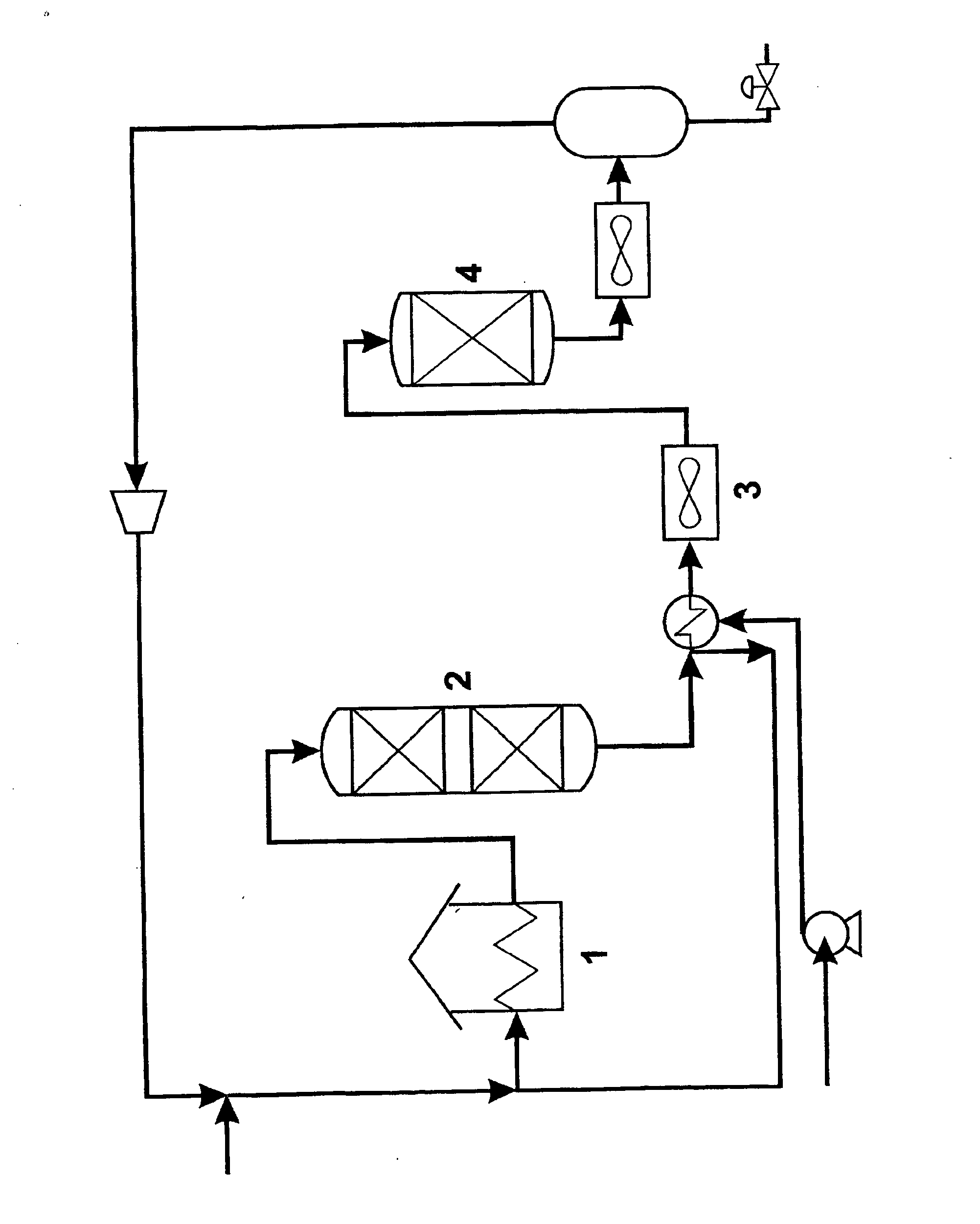
Process for reducing content of sulphur compounds and poly-aromatic hydrocarbons in a hydrocarbon feed
a technology of polyaromatic hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon feeds, which is applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oils, liquid carbonaceous fuels, metal/metal-oxide/metal-hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the propensity of catalyst coke making, reducing the yield of valuable products, and high cost, so as to reduce the amount of sulphur in the spent catalyst, reduce the amount of sulphur, and reduce the effect of sox emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031] Feedstock A (Table 1) was hydrotreated in a semi-adiabatic pilot plant unit running with an outlet temperature of 405° C.—a temperature, which normally is considered as end of run temperature (EOR) conditions and LHSV at 1 (hr−1). The pressure was 50 bar. Pure hydrogen was used as gas. Feedstock A is a mixture of 50% cooker gas oil and 50% straight run vacuum gas oil (SR VGO). Feedstock B (Table 1) was hydrotreated at typical FCC pretreatment conditions in a pilot plant unit at temperature at 400° C. (inlet)-420° C. (outlet) temperature, which normally is considered as end of run conditions at LHSV at 1.7 (h−1). The pressure was 50 bar. The feedstock was a pure cracked VGO.
TABLE 1Properties of feedstock used in the following Examples:PropertiesFeedstock AFeedstock BSG 60 / 600.92790.9924S (wt %)1.343.53N (wt ppm)26773594Aromatics (wt %)Mono-17.78.36Di-9.97.29Tri-11.436.5
[0032] Product properties from both of the tests are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2Properties of products in Ex...
example 2
[0035] Product A from Example 1 is further hydrotreated at lower temperatures at high LHSV. The pressure is 50 bar, which is identical to the pressure at which product A was obtained.
[0036] A Ni—Mo on alumina catalyst is used in this test. The results are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3Properties of products in Example 2:Tem-Di-Tri-pera-Naro-aro-tureLHSVSGS(wtmaticsmaticsPAH(° C.)(h−1)60 / 60(wt %)ppm)(wt %)(wt %)(wt %)32560.89140.00385054.65.09.635060.89110.00294684.94.99.5
[0037] As illustrated from the Table 3 there are a remarkable sulphur and nitrogen removal in this low temperature hydrotreatment, and further it is quite obvious that a large amount of the PAH can be removed at a relatively high LHSV during this low temperature posttreatment. Both the sulphur removal and the PAH removal is due to the shift in equilibrium.
example 3
[0038] Product B from Example 1 is further hydrotreated at lower temperatures at different LHSV and temperatures. The pressure is 50 bar, which is identical to the pressure at which product B was obtained. A Ni—Mo on alumina catalyst is also used in this test. The results are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4Properties of products in Example 3:Tem-Di-Tri-pera-Naro-aro-tureLHSVSGS(wtmaticsmaticsPAH(° C.)(h−1)60 / 60(wt %)ppm)(wt %)(wt %)(wt %)30020.93690.150020587.720.127.830040.93900.1588206710.221.331.530060.94060.161820809.921.431.635020.93350.104916576.617.023.635040.93650.131718709.218.127.335060.93780.144218779.619.328.9
[0039] Again it is clear that a large amount of the poly-aromatic compounds can be removed at low temperature (and the same pressure) due to the shift in equilibrium. Again there is a significant and important sulphur removal at this low-temperature hydrotreatment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com