Zinc comprising nanoparticles and related nanotechnology
a technology of nanoparticles and zinc, applied in the field of submicron and nanoscale powder manufacturing methods comprising zinc, to achieve the effect of high volum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-2
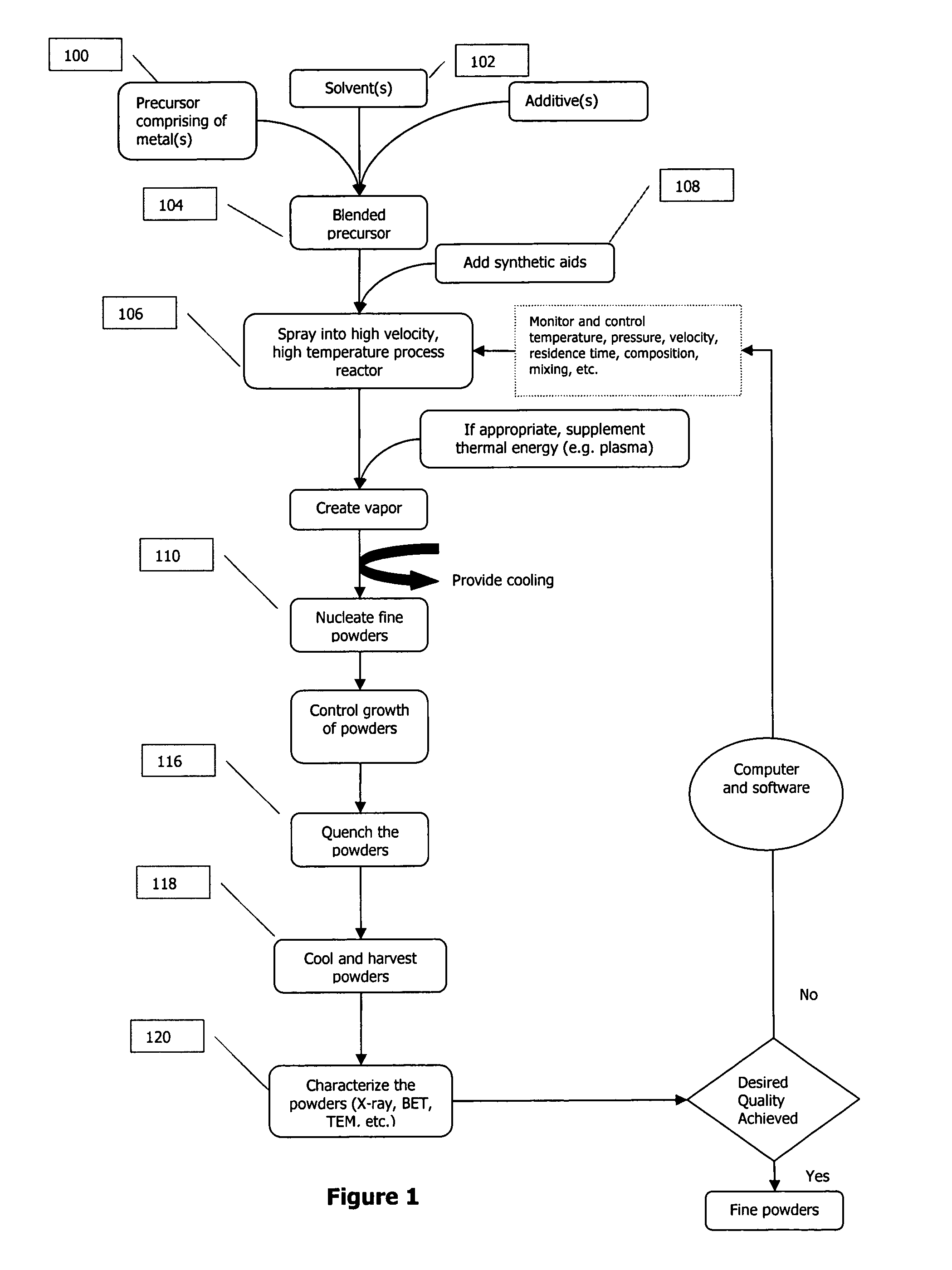
[0117] 99 weight % by metal pure zinc ethylhexanoate precursor was diluted with hexane until the viscosity of the precursor was less than 100 cP. This mix was sprayed into a thermal plasma reactor described above at a rate of about 50 ml / min using about 50 standard liters per minute oxygen. The peak temperature in the thermal plasma reactor was above 3000 K. The vapor was cooled to nucleate nanoparticles and then quenched by Joule-Thompson expansion. The powders collected were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (Warren-Averbach analysis) and BET. It was discovered that the powders had a crystallite size of less than 50 nm and a specific surface area of about 10 m2 / gm.
[0118] Next, in a separate run with the same process, the mix was sprayed at a rate of about 50 ml / min using about 65 standard liters per minute oxygen. The peak temperature in the thermal plasma reactor was above 3000 K. The vapor was cooled and then quenched by Joule-Thompson expansion. The powders c...
examples 3
[0120] A mixture of nickel, zinc, and iron organometallic (octoates, 1:1:2::Ni:Zn:Fe ratios) precursor was prepared. Using the process of Example 1, the mixture was processed at a peak temperature exceeding 2000 K, and the powder was collected. The powders were characterized using X-ray diffractometer and 10 point BET surface area analyzer. The powders were found to be nickel zinc ferrite nanoparticles. No independent peaks of zinc, nickel, or iron oxide were observed suggesting lattice level mixing of atoms. The powders were of a brown color, and had a mean crystallite size less than 15 nanometers and a surface area greater than 40 m2 / gm. The powders were found to be magnetic.
[0121] This example shows that color pigment nanoparticles can be prepared from zinc and that complex three metal oxide nanoparticles can be produced.
example 4
Aluminum doped Zinc Oxide Powders
[0122] A mixture of aluminum and zinc organometallic precursors were prepared. The ratio was adjusted between the two metal precursors to achieve 1.5 wt % aluminum oxide and 98.5 wt % zinc oxide. Using the process of Example 1, the mixture was processed at a peak temperature exceeding 2000 K, and the powder was collected. The powders were characterized using X-ray diffractometer and 10 point BET surface area analyzer. The powders were found to be doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. No independent peaks of zinc or aluminum oxide were observed suggesting lattice level mixing of atoms. The powders had a mean crystallite size of about 25 nanometers and a surface area of about 20 m2 / gm. Electrical conductivity of zinc oxide from Example 1 and aluminum-doped zinc oxide from this example were measured. It was discovered that the doped zinc oxide was over 10 times more conductive than the pure zinc oxide nanopowder.
[0123] This example shows that electrically c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com