System and method for locating and determining discontinuities and estimating loop loss in a communications medium using frequency domain
a communication medium and frequency domain technology, applied in the field of information communication system testing, can solve problems such as non-uniformities in telecommunications mediums, tdr implementation of twisted pair and similar dispersive channels, and progressively lost probe signal energy, so as to mitigate baseline effects of response signals and mitigate dispersion effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
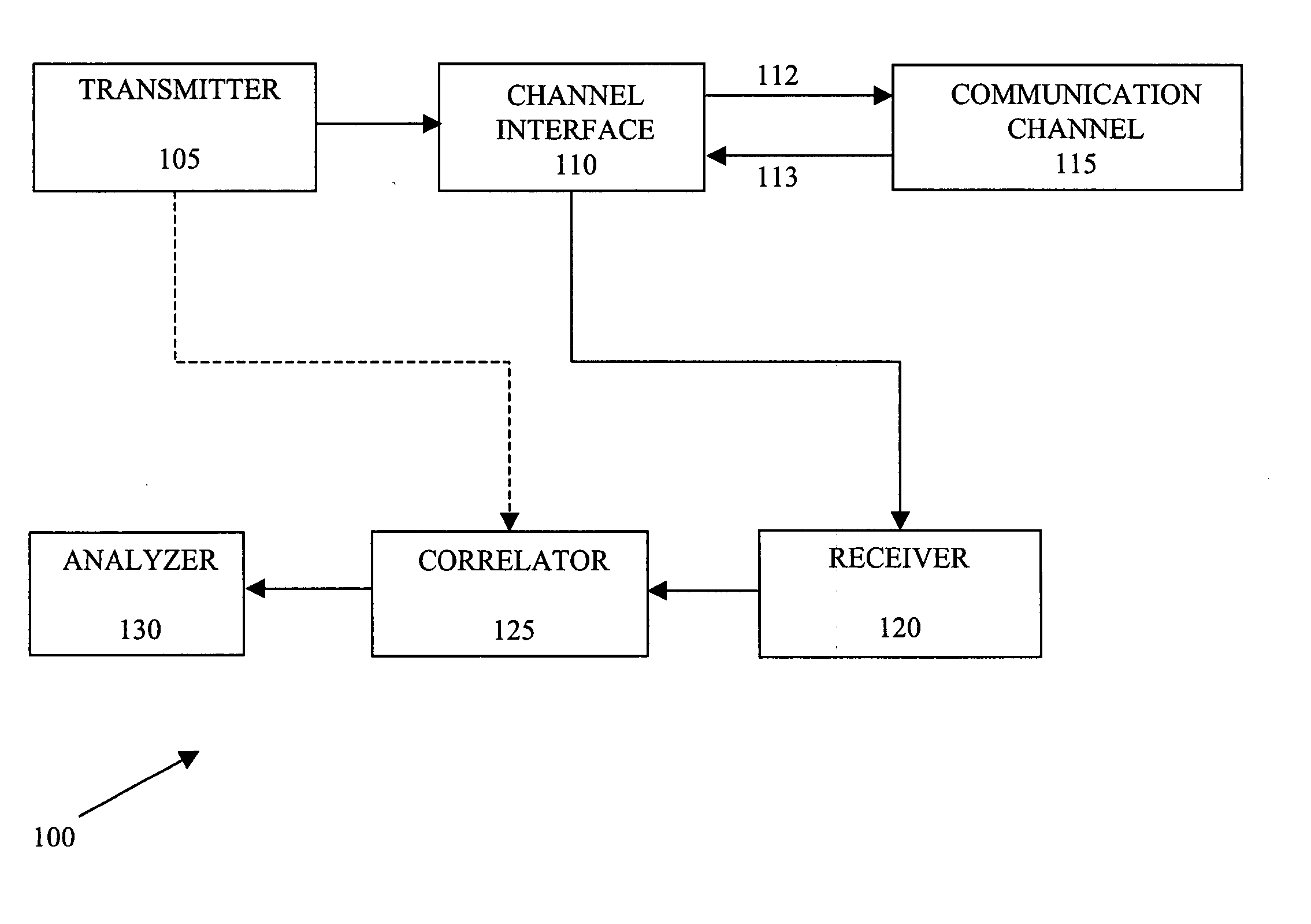
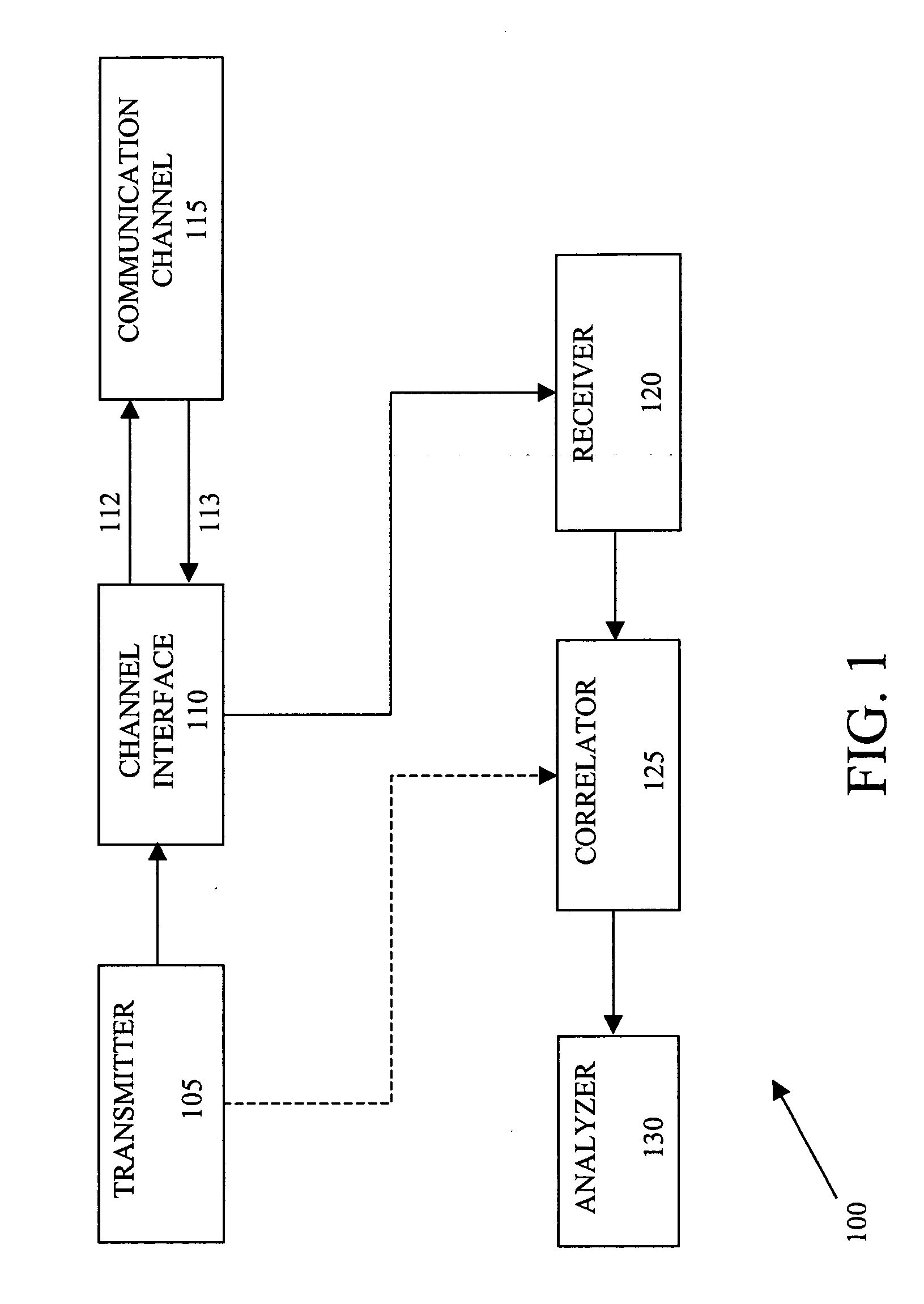
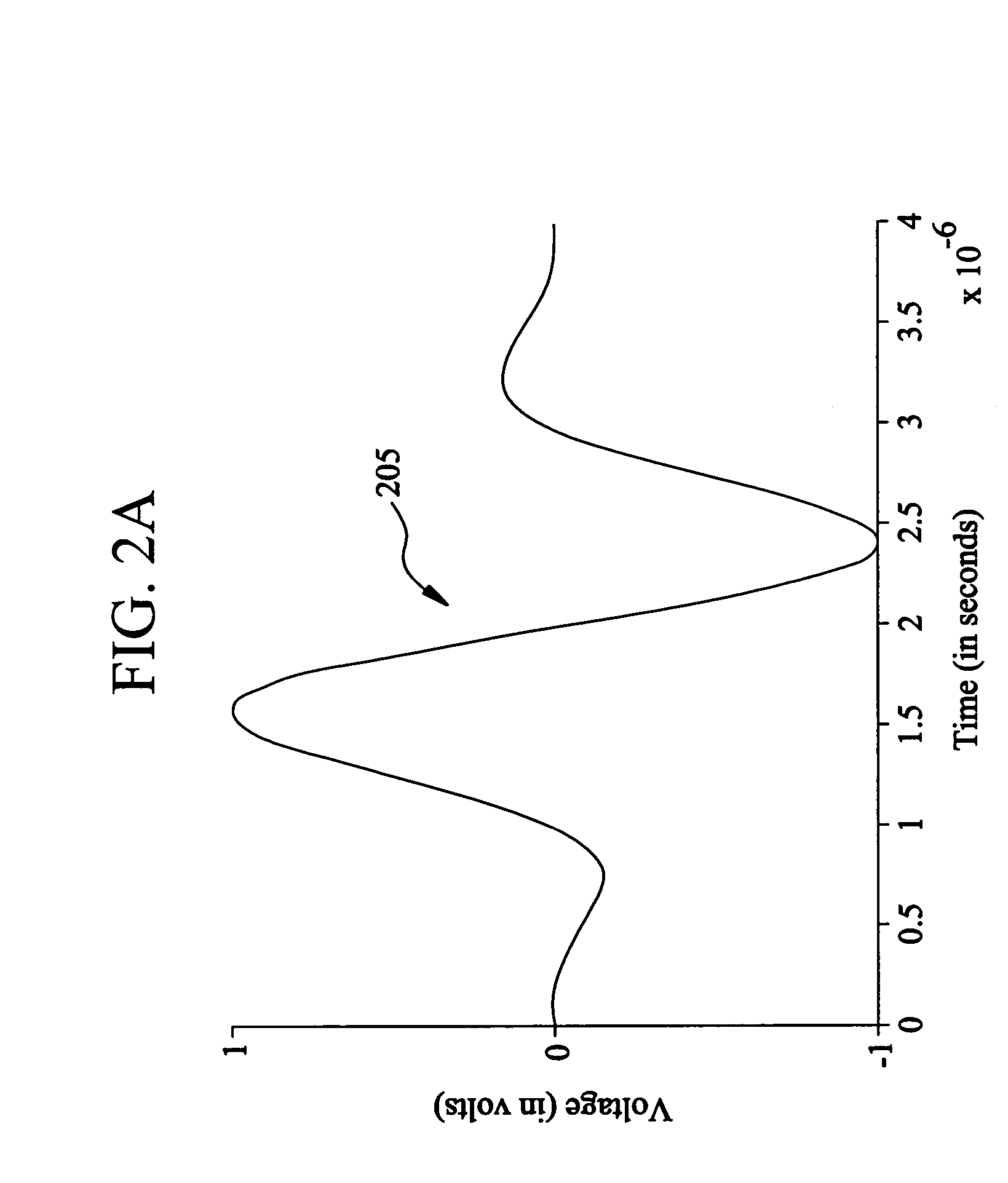
A system and method are disclosed for determining characteristics associated with a communication channel. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, Blackman-Harris windowed sine packets or other narrowband signals can be used as the stimulus for a time domain reflectometer (TDR) to address the dispersion of the communication channel. The stimulus is reflected back when it encounters discontinuities, such as an open, short, bridge tap or other discontinuities, in the communication channel. A frequency domain correlation routine can be applied to detect the location of these discontinuities. The frequency domain correlation routine can correlate Fourier transforms of the reflected signals with Fourier transforms of a series of time-delayed versions of the stimulus in the frequency domain, and then determine the location of the discontinuities by searching for the peaks of the magnitude of the frequency domain correlation results. The nature of the discontin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com