Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1
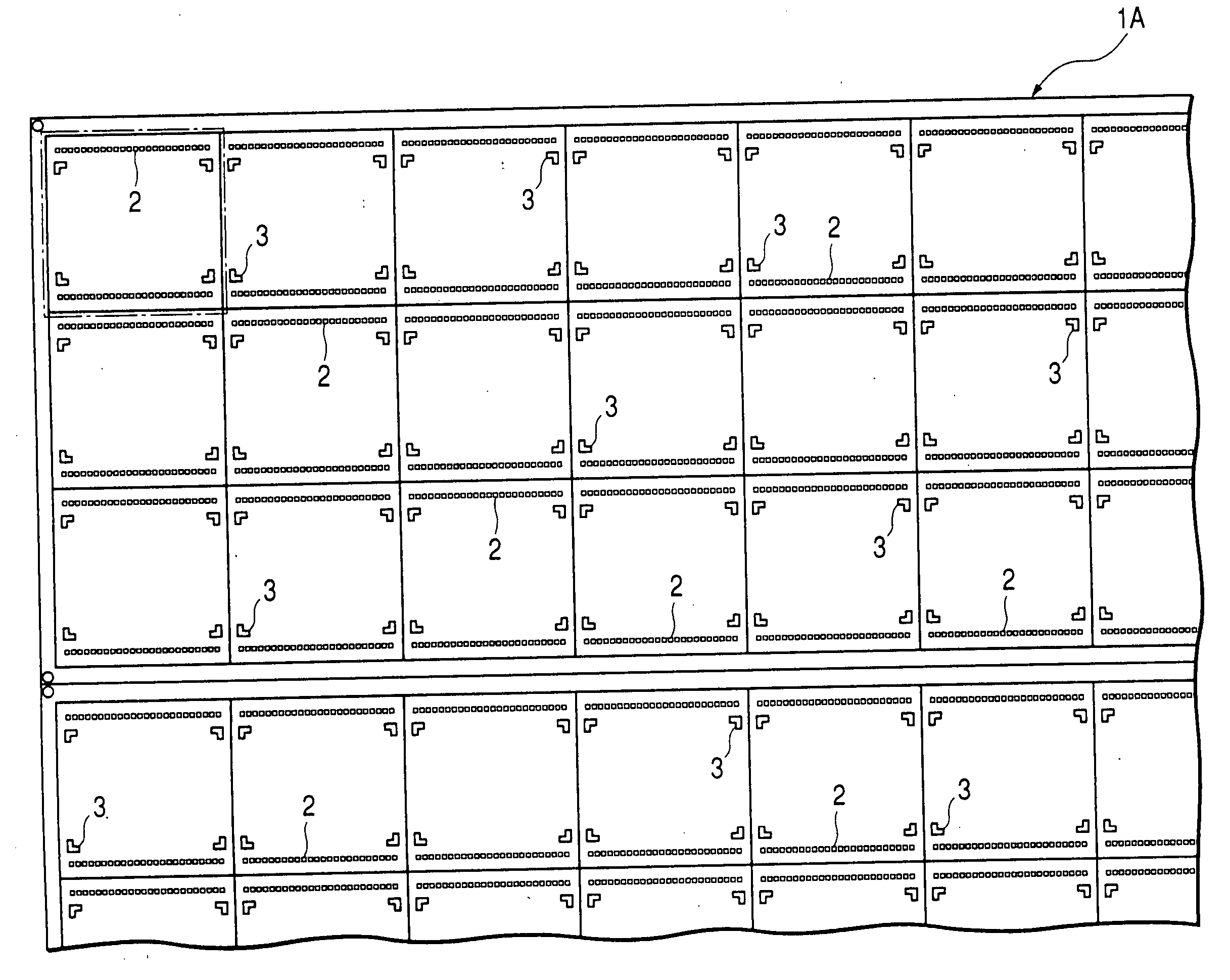
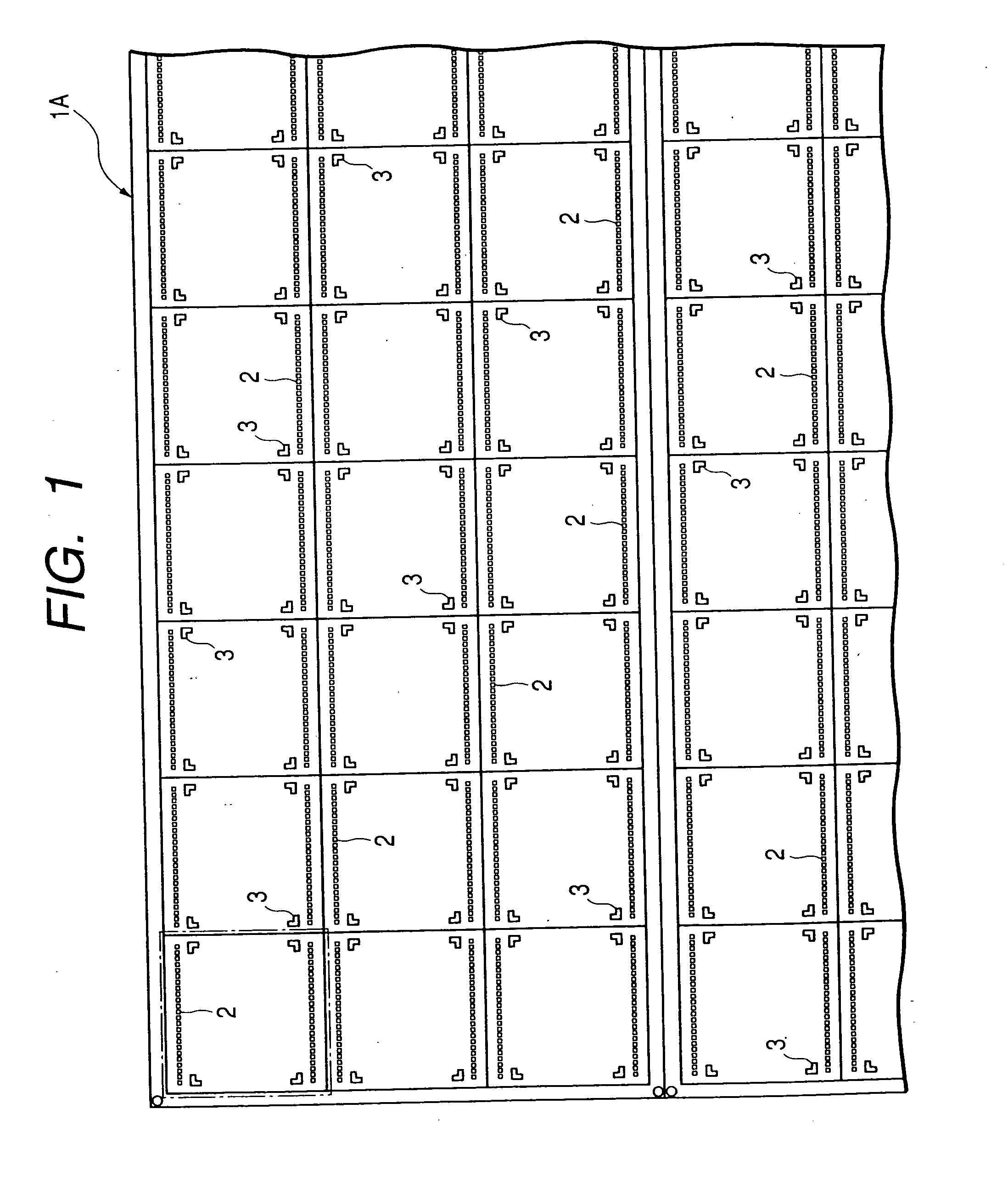
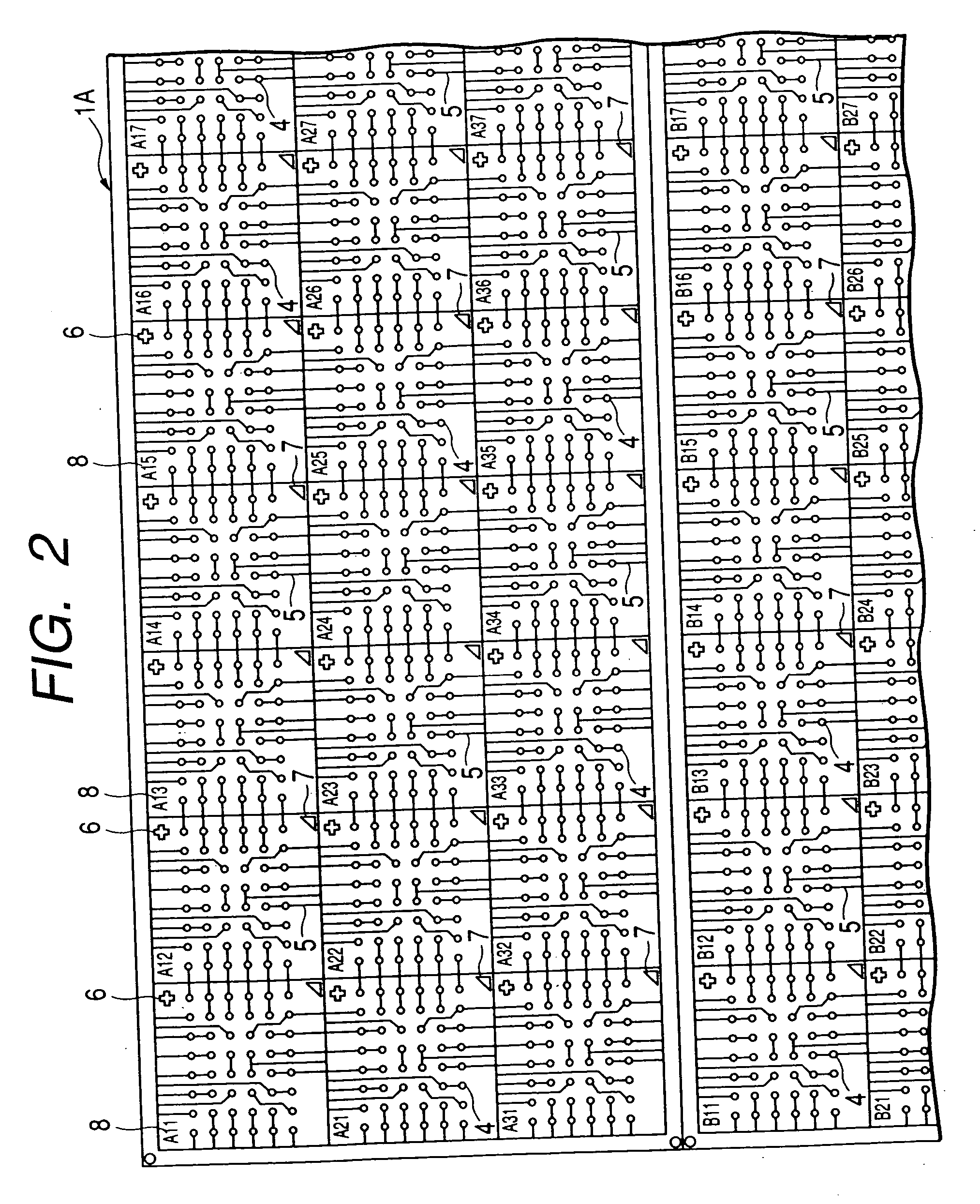
[0039]FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 show part of the matrix substrate which is used for the manufacturing of resin-molded semiconductor devices based on this embodiment. FIG. 1 shows the chip mounting surface (upper side), and FIG. 2 shows the packaging surface (rear side).
[0040] The matrix substrate 1A is a thin wiring substrate of resin having dimensions of 500 mm by 500 mm and 0.22 to 0.6 mm in thickness, for example, on the upper side of which are mounted a plurality of semiconductor chips in a matrix arrangement in the pellet putting process which will be explained later. The matrix-substrate 1A is made of a known material for wiring substrates, e.g., glass epoxy resin, BT resin or polyamide resin, and particularly it can be made of such an inexpensive material for wiring substrates as glass epoxy resin thereby to lower the manufacturing cost of resin-molded semiconductor devices. The matrix substrate 1A can also be made of a wiring substrate having flexibility such as ...
embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2
[0062] The address information patterns 8, which are formed by use of the wiring material on the packaging surface of the matrix substrate 1A in the preceding embodiment 1, can be formed in a different manner as follows.
[0063] Initially, a matrix substrate 1A as shown in FIG. 19 is prepared. This matrix substrate 1A has the same structure as the matrix substrate 1A of the preceding embodiment 1 except that it does not have the address information patterns 8.
[0064] Next, the processing steps of the preceding embodiment 1 shown in FIG. 6 through FIG. 11 are followed to implement the cutting out of matrix substrates 1B for molding, bonding of wires 13, and block molding of chips 12 with the resin mold 14. Finally, marks 19 of the product type, lot number, etc. are printed on the surface of the resin mold 14, and, at the same time in this embodiment, address information patterns 8 are printed on the surface of the resin mold 14 as shown in FIG. 20. The marks 19 and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com