Valve timing control device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0034] Hereafter, the present invention will be explained.
embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1
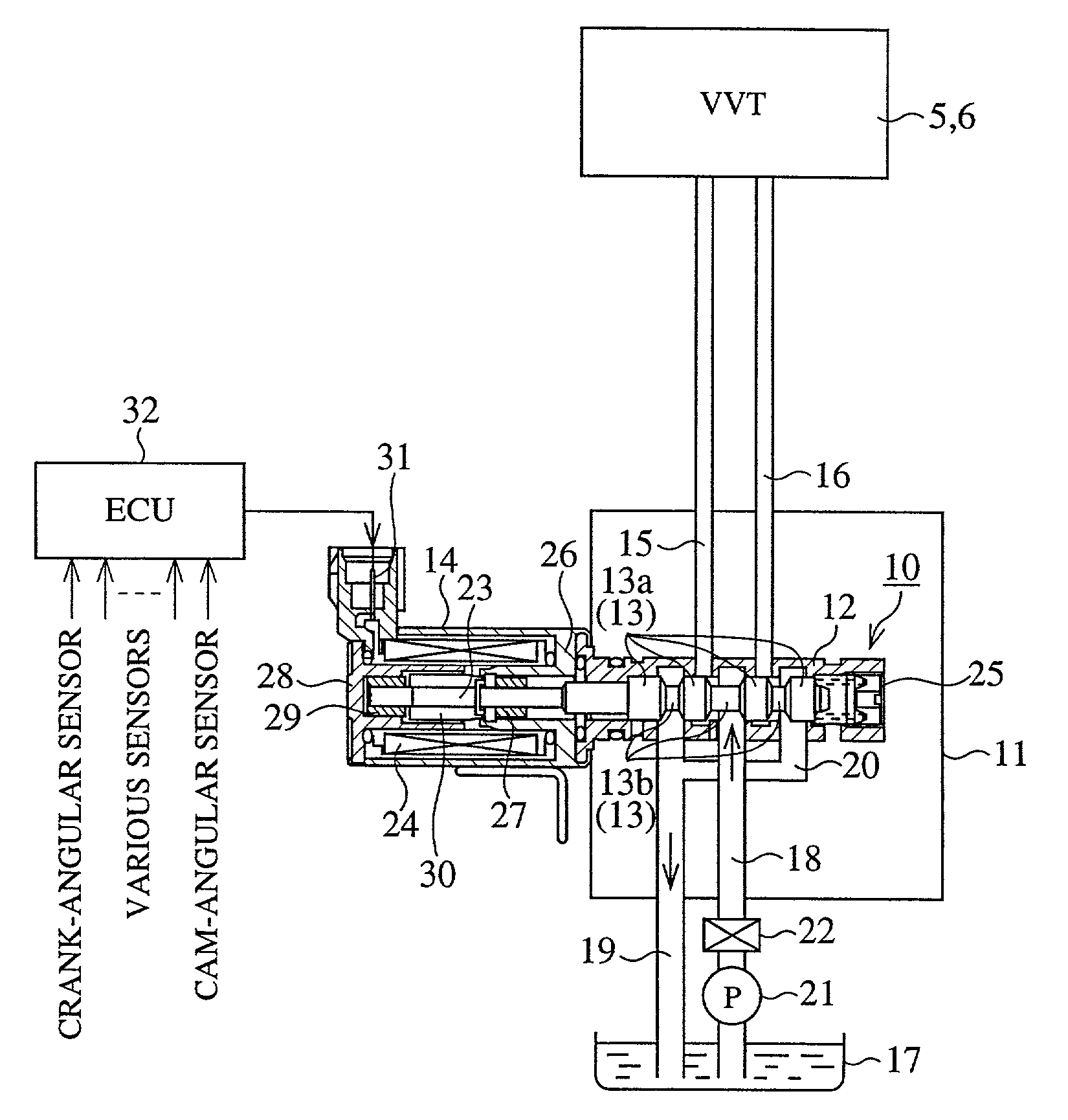
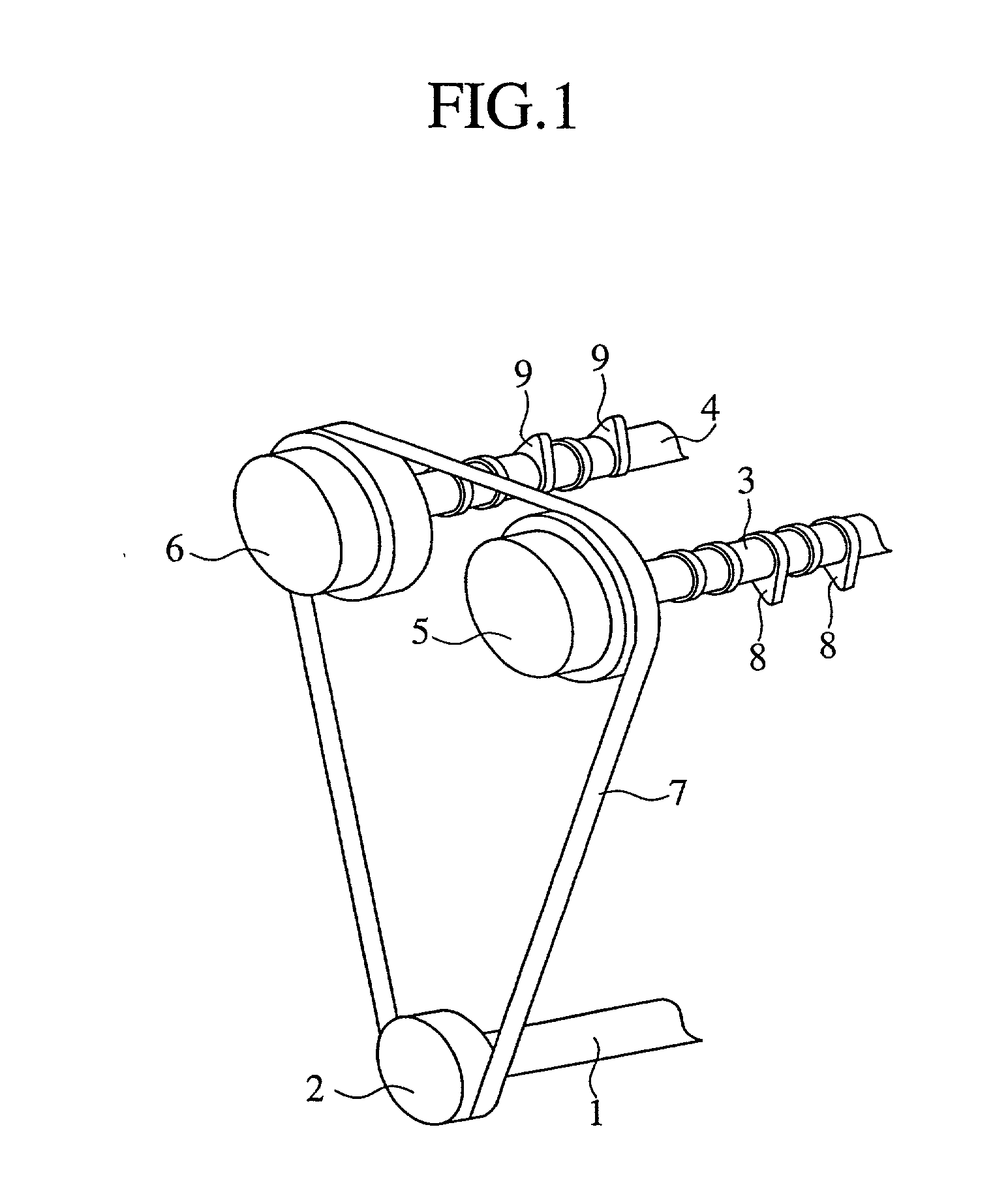
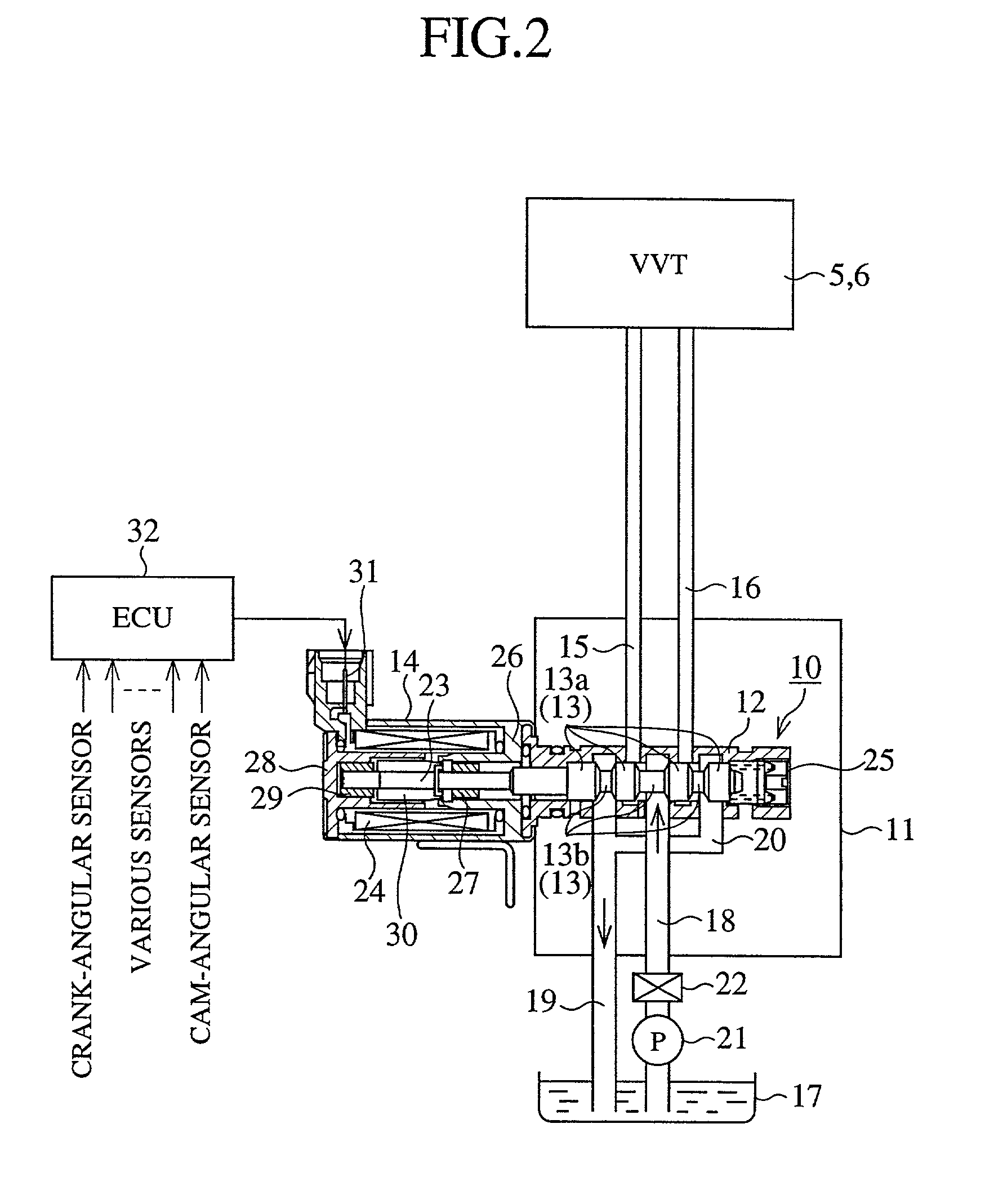
[0036] FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a valve system of the engine equipped with a valve timing control device according to the present invention. FIG. 2 is a partial cross sectional view of an internal construction of an oil control valve for supplying a hydraulic pressure to the valve timing control device shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a lateral cross sectional view of an internal construction of a valve timing control device as embodiment 1 according to the present invention. FIG. 4 is a cross sectional view taken along lines A-A of FIG.3. FIG. 5 is an enlarged cross sectional view of a main point B of FIG. 4. FIG. 6 is a graph showing a relation of a release hydraulic pressure and an operation of the lock member in the valve timing control device shown in FIG. 3, FIG. 4 and FIG. 5.
[0037] In FIG. 1, reference numeral 1 denotes a crankshaft of an engine (not shown) and numeral 2 denotes a chain sprocket fixed on an end of the crankshaft 1. Numeral 3 denotes an int...
embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2
[0069] FIG. 7 is a lateral cross sectional view of an internal construction of a valve timing control device as embodiment 2 according to the present invention. Components of the embodiment 2 of the present invention which are the same as those of the embodiment 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals and further description will be omitted.
[0070] In FIG. 7, a hydraulic pressure switch valve 54 includes a valve groove 54a, an approximately cylindrical-shaped valve body 54b, an advance side communication groove 54c and a retardation side communication groove 54d. The valve groove 54a is formed at an end face of the housing 40 close to the case 41 and has an about ellipse-shaped inner space. The valve body 54b is accommodated in the valve groove 54a. The advance side communication groove 54c is formed at the end face of the housing 40 close to the case 41 to communicate between the valve groove 54a and the advance side hydraulic pressure chamber 43. The retarda...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com