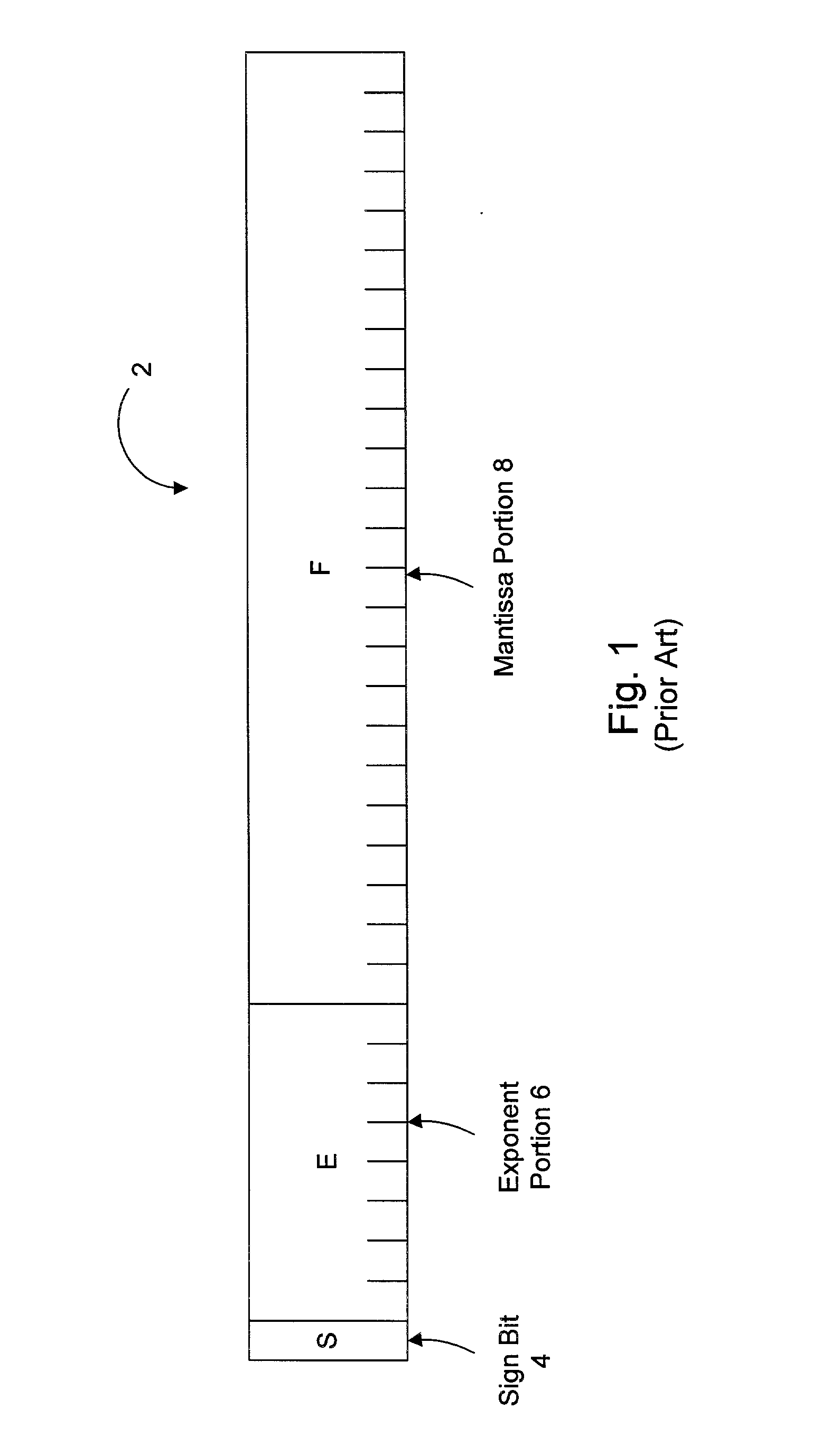
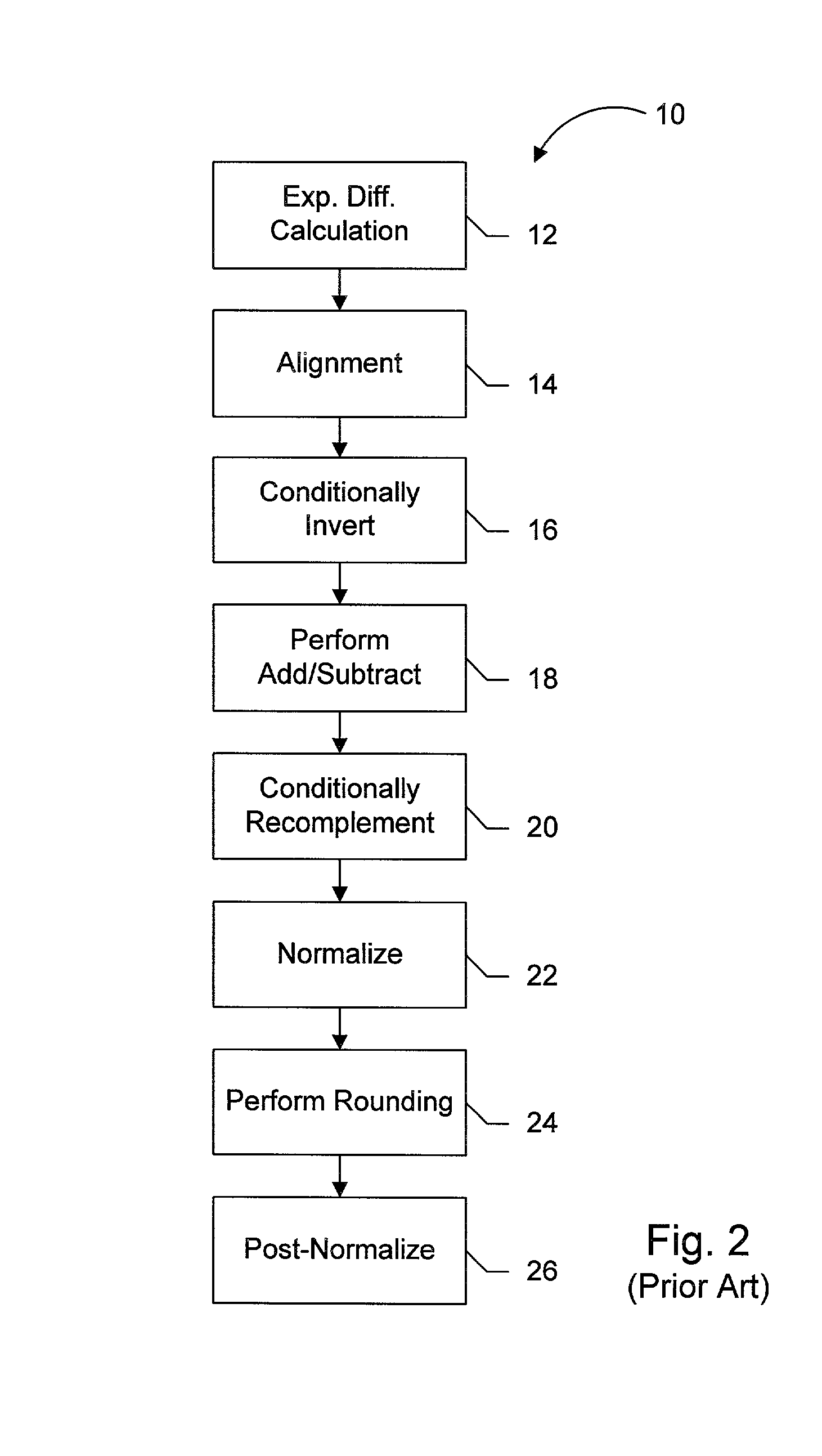
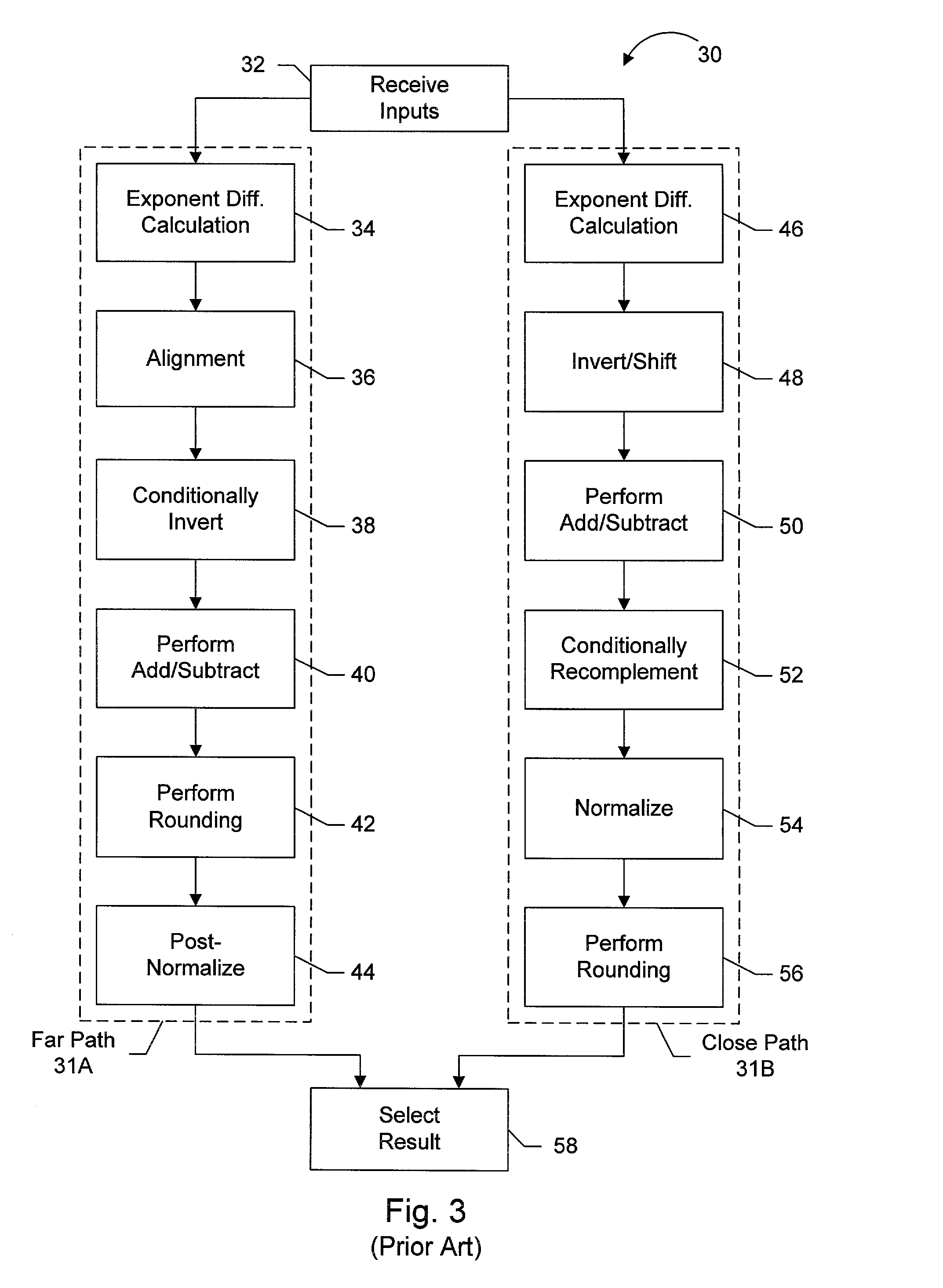
Floating point addition pipeline including extreme value, comparison and accumulate functions
a floating point addition and function technology, applied in the field of floating point arithmetic, can solve the problems of large precision, limiting format, and speculative output of close data paths
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
is representative of the close path case predicted by selection sub-block 950A, in which E.sub.A=E.sub.B and M.sub.A>M.sub.B. Because guard bit 714 is zero in this case, no borrowing is performed and the correction for one's complement addition is always needed. (This can be seen in the difference between actual result 1002A and computed result 1002B, which corresponds to adder output 722A). As a result, adder output 722B, or sum+1, is indicated by select signal 952A.
[0203] Turning now to FIG. 16B, an example 1000B of subtraction within close data path 240 is shown according to one embodiment of the invention. Example 1000B is representative of the close path case predicted by selection sub-block 950B, in which E.sub.A=E.sub.B and M.sub.B>M.sub.A. As with example 1000A, guard bit 714 is zero in this case, so borrowing is not performed. Because M.sub.B is larger than M.sub.A, however, the subtraction result is negative. It is noted that actual result 1004A is the bit-inverted (one's ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com