Transverse flux cylinder linear reluctance motor
A transverse flux, reluctance motor technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of eddy current loss, uneven distribution of the excitation magnetic field, etc., to reduce eddy current loss, improve material utilization and output thrust , the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
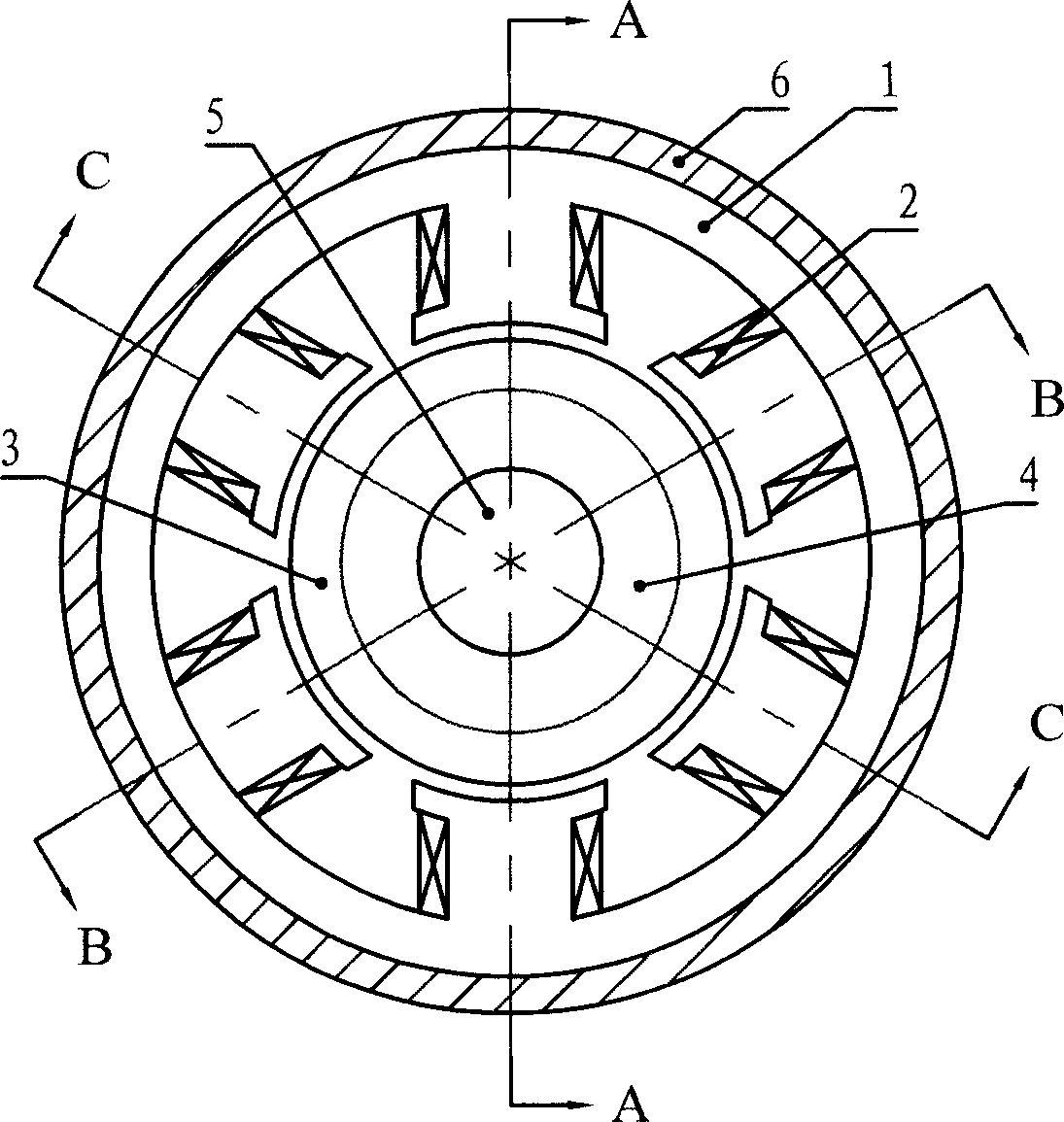
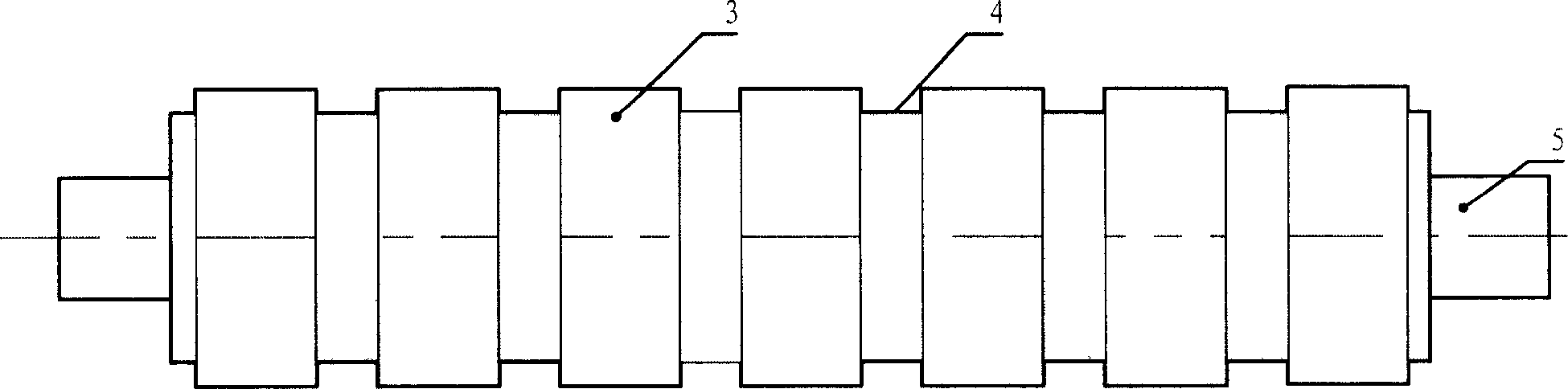
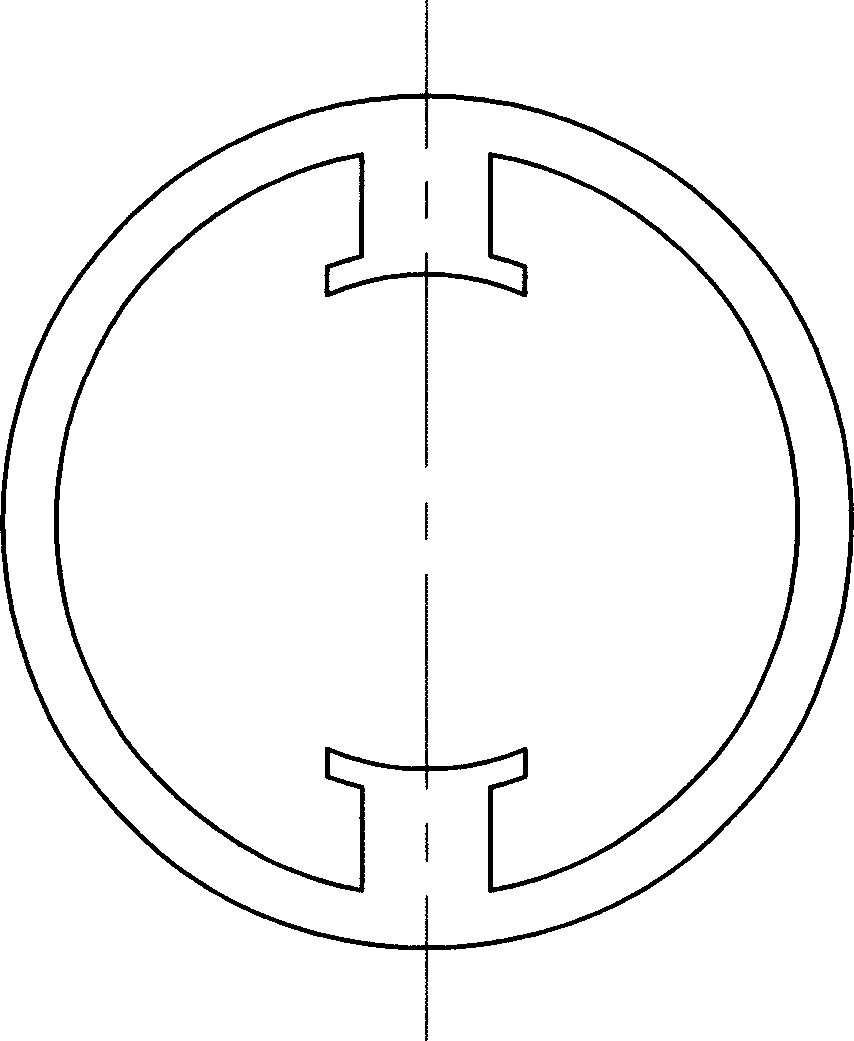
[0007] Specific embodiment one: see Figure 1 to Figure 8 , The transverse flux cylindrical linear reluctance motor of this embodiment is composed of a housing 6, an armature core 1, an armature winding 2, a mover tooth 3, a spacer ring 4, and a shaft 5. Each phase armature core 1 is fixed close to the inner wall of the casing 6, the spacer ring 4 and the mover teeth 3 are arranged alternately and fixedly sleeved on the shaft 5. There are 2n teeth on the armature core 1 of each phase, and n is a natural number; The armature core 1 is staggered in the circumferential direction by an angle of 360° / 2mn, where m is the number of phases of the motor; the coils of the armature winding 2 on the adjacent teeth of the armature core 1 of each phase have opposite winding directions, and the armature winding 2 of the same phase All the coils are connected in series.
[0008] This embodiment selects a three-phase motor, each phase armature core has 2 teeth, namely m=3, n=1, calculated accord...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Embodiment 2: The difference between the transverse flux cylindrical linear reluctance motor of this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that both the armature core 1 and the mover teeth 3 are made of silicon steel sheets.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0012] Specific embodiment 3: The transverse flux cylindrical linear reluctance motor of this embodiment is different from specific embodiments 1 or 2 in that the spacer ring 4 is made of magnetic material, and the outer diameter of the spacer ring 4 is smaller than that of the mover tooth 3. The outer diameter prevents the magnetic flux flowing out of the armature teeth from entering the spacer ring 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com