Single molecular nucleic acid sequencing process for exonuclease-nanometer hole
A molecular nucleic acid and nanopore technology, which is applied in the field of exonuclease-nanopore single-molecule nucleic acid sequencing, can solve the problems of unusable sequencing, intolerance, and high error rate, and achieve high signal-to-noise ratio, improved accuracy, and high The effect of voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1: DNA Fragment Sequencing
[0018] ① Detection of dNMPs handwriting
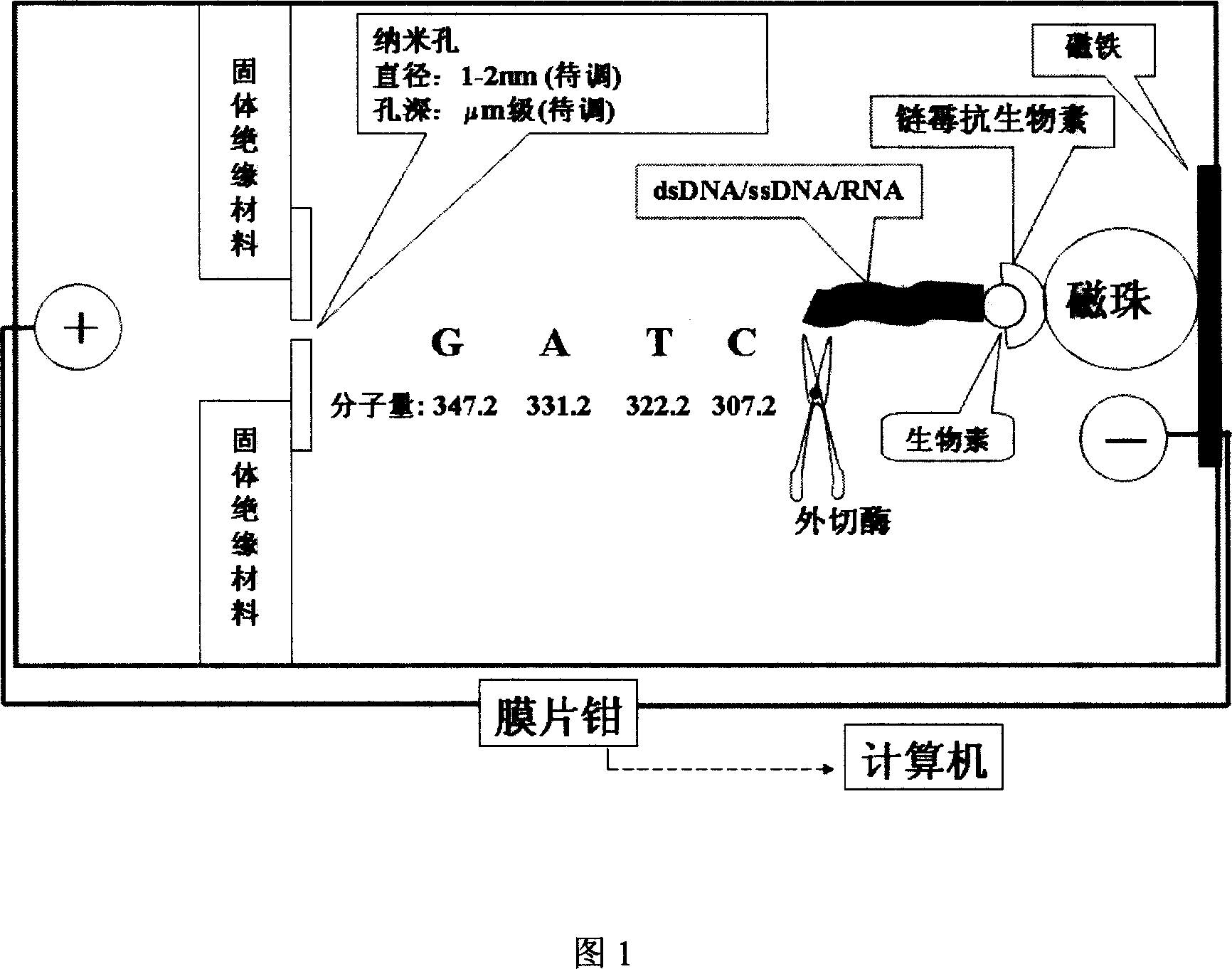
[0019] Add electrophoresis fluid to the two-stage electrophoresis tank connected to the patch clamp, separate the electrophoresis tank from the middle with nano-components with controllable diameter and hole depth, add only one kind of ultra-diluted nucleotide each time, turn on the power and record The electrical signal when a single nucleotide passes through the nanopore; in this way, the perforation electrical signal of various nucleotides is detected, and finally their specific handwriting is determined, a standard curve is established, and software is written.
[0020] ②Calculate the swimming speed of nucleotides, and find the farthest exonuclease action point of the base sequence;
[0021] When each of the above detections is over, the positive and negative electrodes are switched to each other, so that the nucleotides gathered on the original positive electrode migrate to the new posi...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Complete Chromosome Sequencing
[0033] ①Single-molecule operation: In this example, the nucleotide handwriting detection and the farthest point of action of the exonuclease are the same as in Example 1.
[0034] A single chromosome is extracted with the aid of a microscope, flow cytometer or other methods, and the chromosome is immobilized on magnetic beads according to the method in Example 1.
[0035]② Chromosome fixation: fix the magnetic beads with 1 complete chromosome on the magnet installed on the negative end of the electrophoresis tank of a sequencing unit. Each sequencing unit has a chromosome.
[0036] ③Sequence detection: Add exonuclease to the negative electrode of the electrophoresis tank. After a single enzyme molecule binds to DNA, add magnesium ions, turn on the power immediately, collect electrical signals, and use software to read the DNA sequence.
[0037] ④ Detection of complementary chain sequence: same as in Example 1.
[0038] Effe...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: RNA sequencing
[0040] ① The detection of rNMPs handwriting is the same as in Example 1, and a standard curve is established according to the specific electrical signals generated by them.
[0041] ②According to the method of Example 1, RNA single molecules were fixed to the negative electrode of the electrophoresis tank, nucleotides were degraded one by one with RNA exonuclease, the handwriting was recorded by patch clamp, and the electrical signal was converted into sequence information according to the standard curve.
[0042] ③ RNA can also be used as a template to synthesize cDNA (complementary DNA) by reverse transcriptase, and then obtain the sequence of RNA according to the steps in Example 1.
[0043] Implementation effect: suitable for the RNA / DNA exonuclease activity of the present invention at 1000nts / second, such as detection of mRNA sequence, according to the average length of mRNA of 1000nts, the array of 100×100, that is, 10000 mRNA or cDNA p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com