Apparatus and method for the processing of sectional images
A cross-sectional image and equipment technology, applied in image data processing, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of difficult quantitative scattering estimation, difficulty in finding low-contrast details, insufficient typical system geometry, etc., and achieves computational speed. quick effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
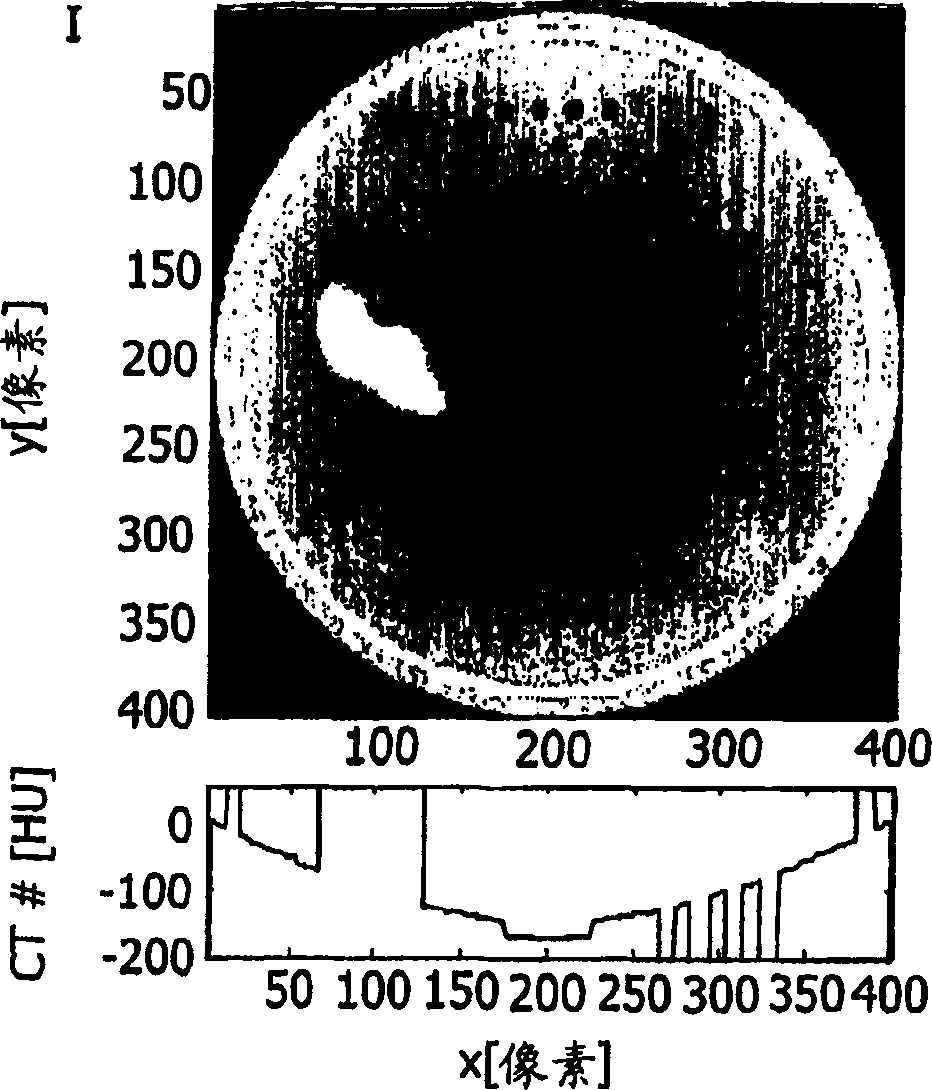
[0034] attached figure 2 Represents a simple cross-sectional image I through a cylindrical test body, including dark and light structures (representing air and bone in the human body, respectively) embedded in medium-gray-value "tissue". Moreover, there are also structural and spatially slowly varying inhomogeneities with relatively small contrast to the "tissue". in the attached figure 2 In the lower part of , a graph of the distribution of gray values along a horizontal line through the image (at y=200) is given. When applying a dense gray scale window to a slice of a reconstructed 3D image in order to find low contrast details, the inhomogeneity causes parts of the region of interest to be either below or above the edge of the applied window. It is therefore difficult to find low-contrast details in the presence of inhomogeneities.
[0035] The basic idea of the invention is to firstly find a spatially slowly varying 2D baseline within each slice of the 3D volume r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com