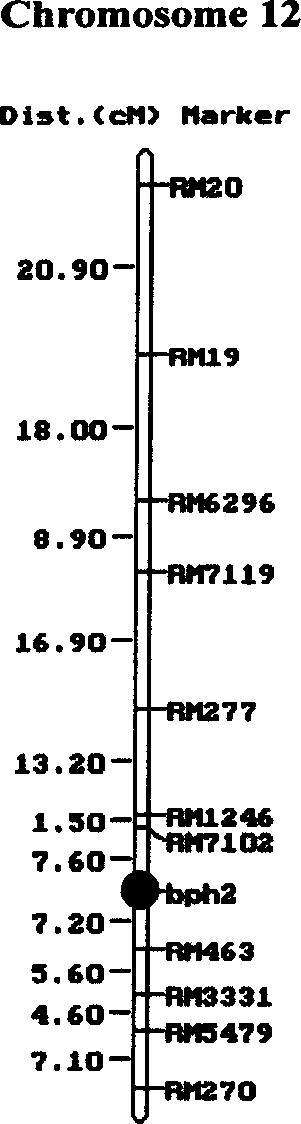
Main-gene bph2 molecular mark method for rice variety anti-brownspot gene site
A brown planthopper resistance and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve problems such as difficult aggregation of insect-resistant genes, and achieve the effects of convenient identification, clear location, and convenient and rapid detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The detailed description of the present invention is as follows:
[0031] Studies have shown that BPH resistance gene resources mainly exist in indica and wild rice species in Sri Lanka and India (Ikeda and Vaughau, 1991). Athwal et al. (1971) (Athwal D S, M D Pathak, E H Bacalangco, and C D Pura, Crop Sci.1971, 11: 747-750) reported that Mudgo, CO22 and MTU15 carry the same resistance gene Bph-1, and ASD7 carries a Recessive insect resistance gene bph-2. Athwal and Pathak (1972) reported that MGL2 contains the insect resistance gene Bph-1, and Ptb18 contains bph-2. Martinez and Khush (1974) reported that IR747B2-6 contained Bph-1 and that R1154-243 and IR4-93 contained bph-2. Lakshiminarayana and Khush (1977) reported that the Sri Lankan insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati is controlled by a dominant gene Bph-3 that segregates independently from Bph-1; while the variety Babawee is controlled by a recessive gene bph-4 that segregates independently from bph-2 . Si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com