Sediment interstitial water in-situ sampling method and apparatus
A technology for interstitial water and sediments, which is applied in the direction of sampling devices, etc., can solve the problems of differences in interstitial water, different results, and data deviations, and achieves the effect of simple structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The in-situ sampling method of sediment interstitial water of the present invention adopts the following method steps:
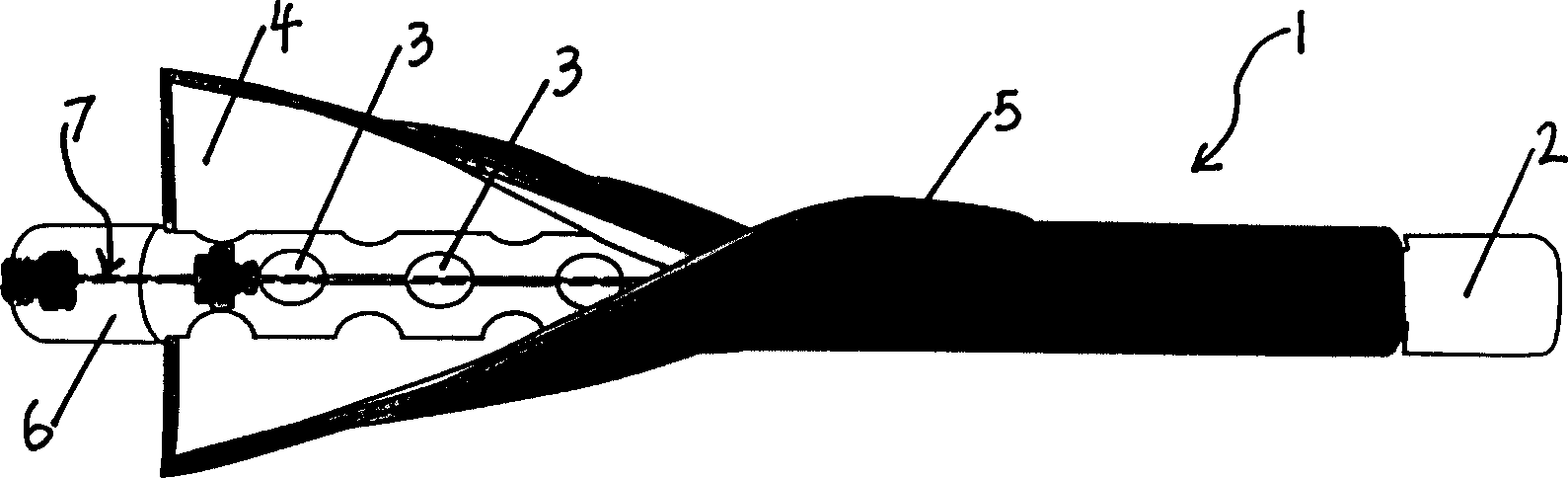
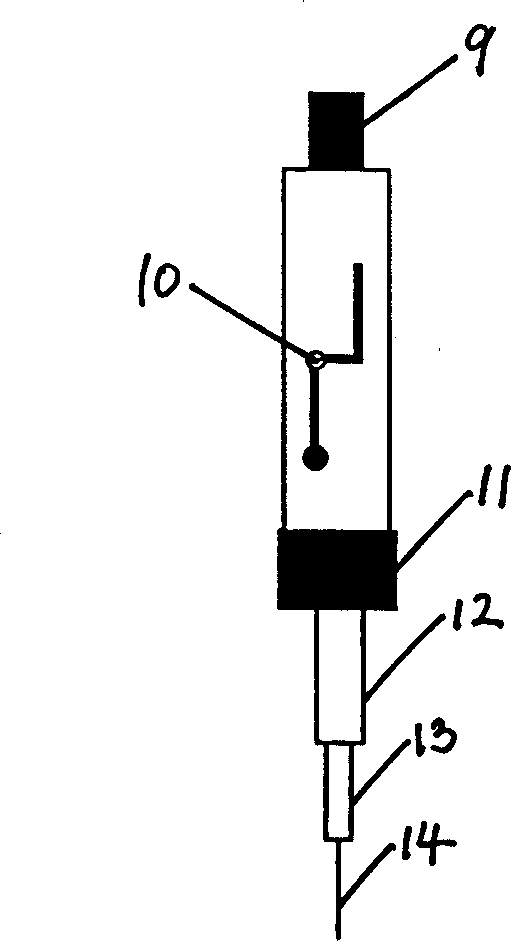
[0019] (1) Adopt a water exchange device 1, this water exchange device 1 comprises a copper pipe 2, has a plurality of through holes 3 on the pipe wall of the copper pipe 2, and a layer of glass fiber filter paper 4 and an outer layer of the pipe wall are wrapped outside the pipe wall. A layer of stainless steel mesh 5, which can well isolate particles and soil from entering, and water can freely enter and exit; the copper tube 2 plays a supporting role and ensures a certain space and prevents the growth of microorganisms; the stainless steel mesh 5 mainly protects the glass fiber filter Paper 4; one end of the copper tube 2 is closed, and the other end has a top cover 6, and the solid-phase microextraction device 7 in the copper tube 2 is fixed on the top cover 6 by matching the screw cap 16 with the threaded hole provided on the top cover.
[0020] ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] The in-situ sampling method of sediment interstitial water of the present invention adopts the following method steps:
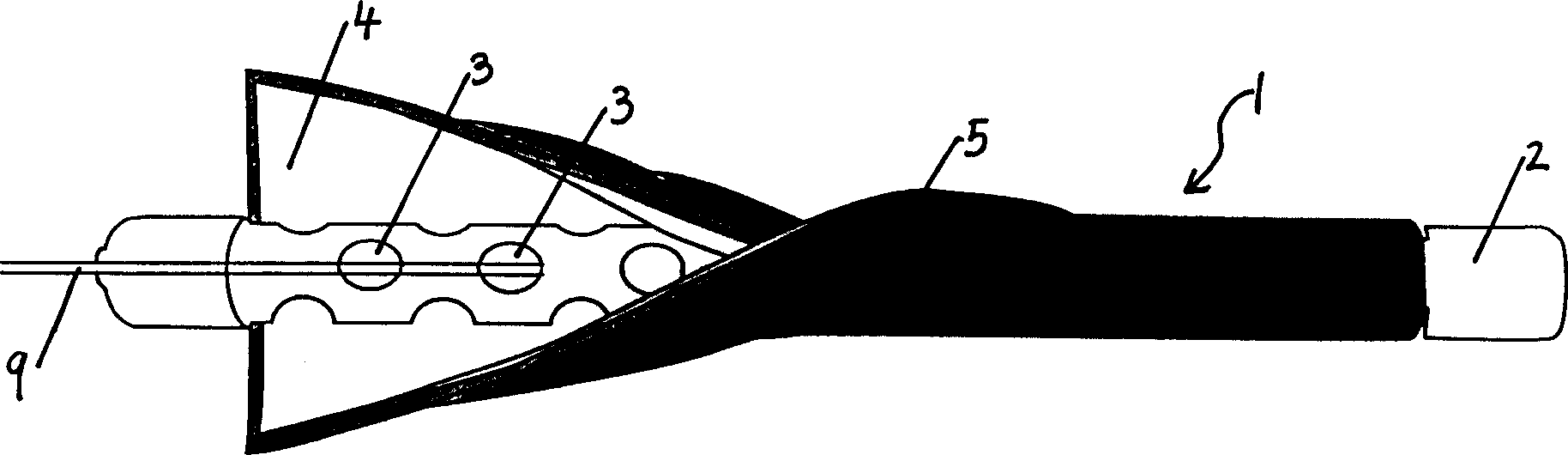
[0024] (1) Adopt a water exchange device 1, this water exchange device 1 comprises a copper pipe 2, has a plurality of through holes 3 on the pipe wall of the copper pipe 2, and a layer of glass fiber filter paper 4 and an outer layer of the pipe wall are wrapped outside the pipe wall. A layer of stainless steel mesh 5, which can well isolate particles and soil from entering, and water flows in and out freely; the copper pipe 2 plays a supporting role and ensures a certain space and prevents the growth of microorganisms; the stainless steel mesh 5 mainly protects the glass fiber filter Paper 4; one end of the copper pipe 2 is closed, and the other end has a top cover 6, the top cover 6 is sealed with a water pipe 8, and the water pipe 8 can communicate with the copper pipe 2 and can extend out of the ground surface.
[0025] (2) The above-mentioned wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com