Network and method for access multimedia service to non-group mode mobile terminal
A technology for multimedia services and mobile terminals, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as the inability of mobile terminals to register, and achieve the effects of enriching multimedia services, reducing signaling detours, and increasing bandwidth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Embodiment 1: The case where there is an MGW.
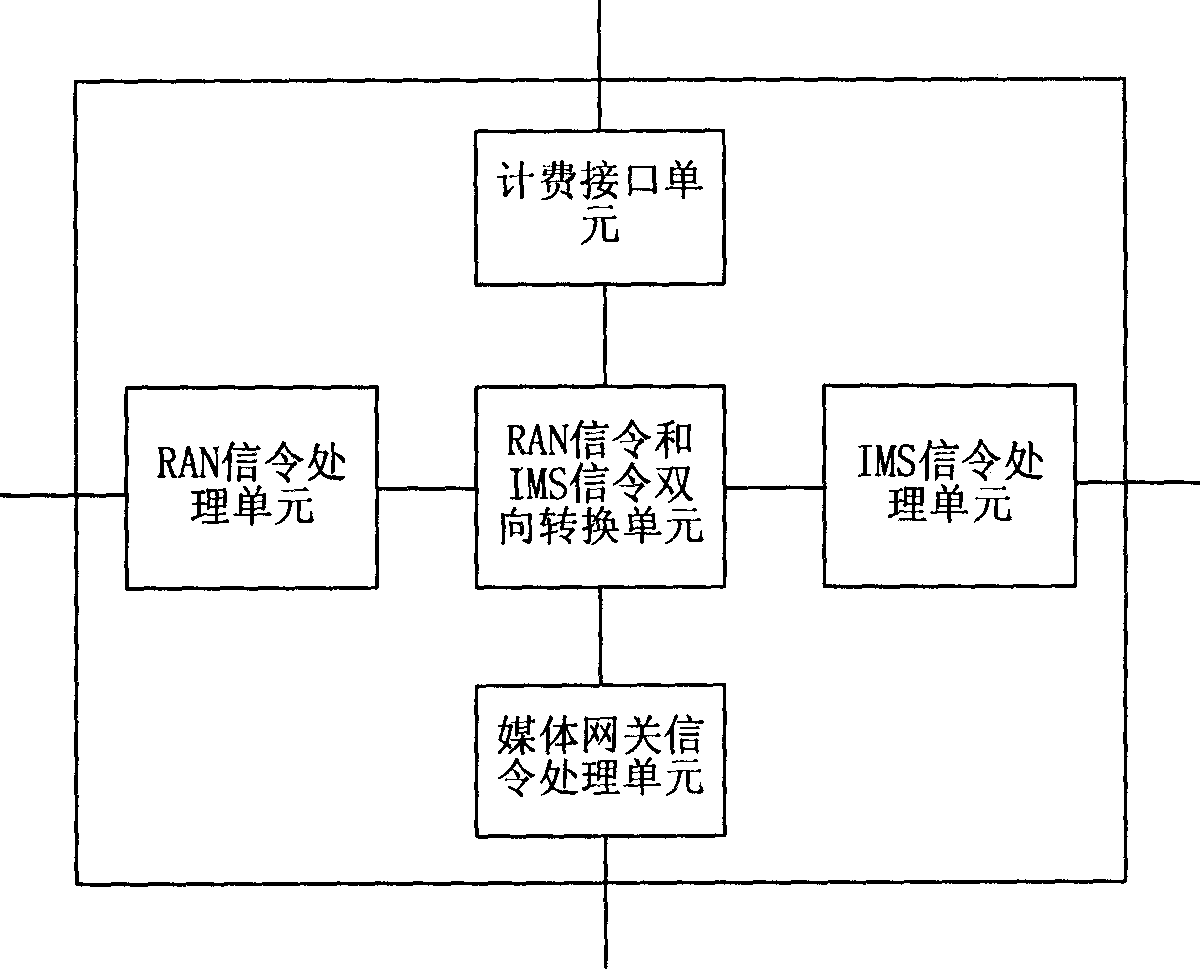
[0066] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the network structure of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In the network structure, an MGW is provided. It can be seen from the figure that the network for mobile users in non-packet mode to access multimedia services in the present invention mainly includes the following components:
[0067] RAN, for accessing the mobile user;
[0068] IMS, providing multimedia services for mobile users;
[0069] The MGW is used to control the conversion between the bearer in the circuit domain and the bearer in the IMS domain;
[0070] On the basis of the above content, the network adds a mobile user access agent unit (MAUA), which communicates with the RAN and MGW, accesses the mobile user to the IMS through the RAN, and manages the mobile user. Including registering, authenticating, initiating a session, accepting a session, etc. for the UE.
[0071] In this solu...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment 2: There is no MGW.
[0090] Such as Figure 4 as shown,
[0091] In this networking situation, the media stream is directly carried by the IP out of the BSC without passing through the A interface, and communicates through the IP network. At the same time, the network shall provide a Media Resource Function (MRF) entity to provide the playback resources required during the call.
[0092] The biggest difference between the solution of embodiment 2 and the solution of embodiment 1 is that the MGW network entity associated with each MAUA is canceled in the network, and the MRF entity shared by the whole network is used to replace its media resource capability (that is, to provide various playback, conference chip, etc.). Since the entity MGW is not needed, the MAUA does not need to provide the control capability of the MGW, that is, it does not need to support the H.248 protocol.
[0093] Such as Figure 4 Shown is a schematic diagram of the network struct...
example 1
[0120] Example 1. Registration process:
[0121] Such as Figure 6 As shown, under the network structure of the present invention, the signaling flow chart adopting the method of the present invention for initiating a location update request when the user terminal is turned on mainly includes the following steps:
[0122] S11, the user turns on the phone, and initiates a location update request; the request message contains a user identification parameter and an update type parameter; wherein the user identification is an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), and the update type is assigned as "user power on";
[0123] S12. The base station system (BS) sends a location update request to the MAUA;
[0124] S13. The MAUA maps the parameters in the location update request message to the header fields and parameters in the SIP registration message, constructs a SIP registration message, and sends it to the P-CSCF in the IMS domain;
[0125] S14. After receiving the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com