Device and method for processing a signal with a sequence of discrete values
A discrete value and sequence technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as rounding errors and difficult coding, and achieve the effects of improved decoding performance, fast signal processing, and reduced number of bits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
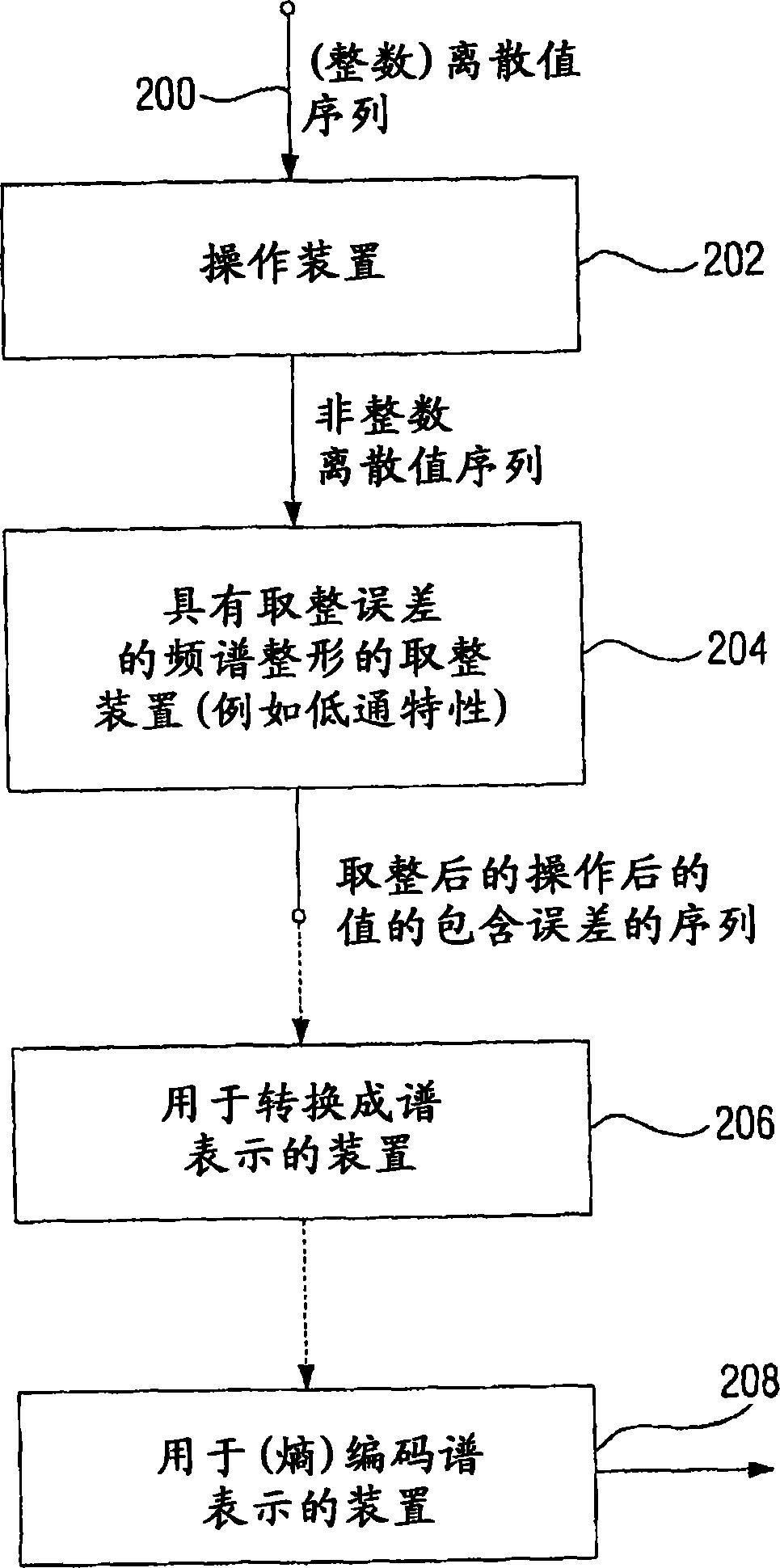
[0102] figure 1 A device is shown for processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values which is fed via a signal input 200 to an operating device 202 . A signal is typically constructed so as to have a first frequency range in which the signal has high energy and a second frequency range in which the signal has relatively low energy. If the first signal is an audio signal, it has high energy in the first frequency range, ie in the low frequency range, and low energy in the high frequency range. However, if the signal is a video signal, it also has high energy in the low frequency range and low energy in the high frequency range. In contrast to audio signals, the frequency range of a video signal is a spatial frequency range, unless successive video frames are considered, where there are also temporal frequencies relating to eg selected image regions in successive frames.
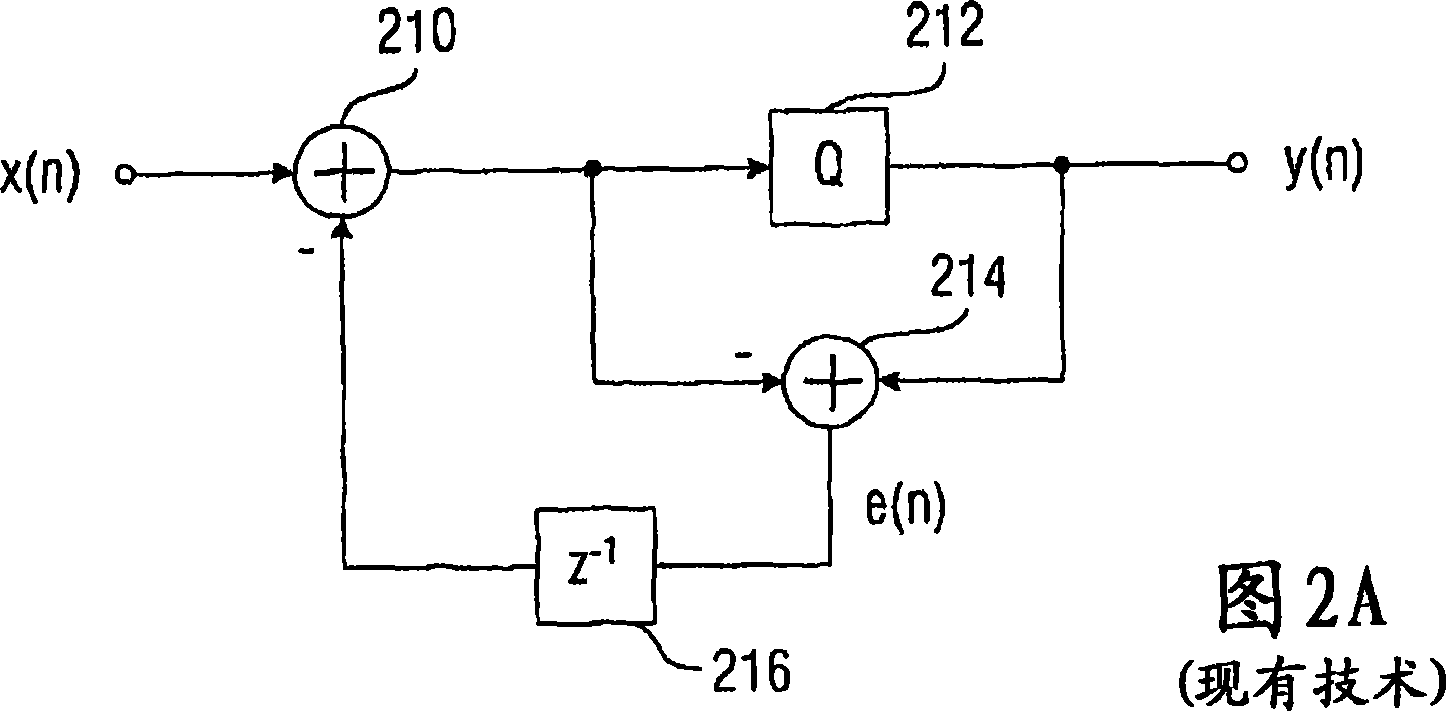
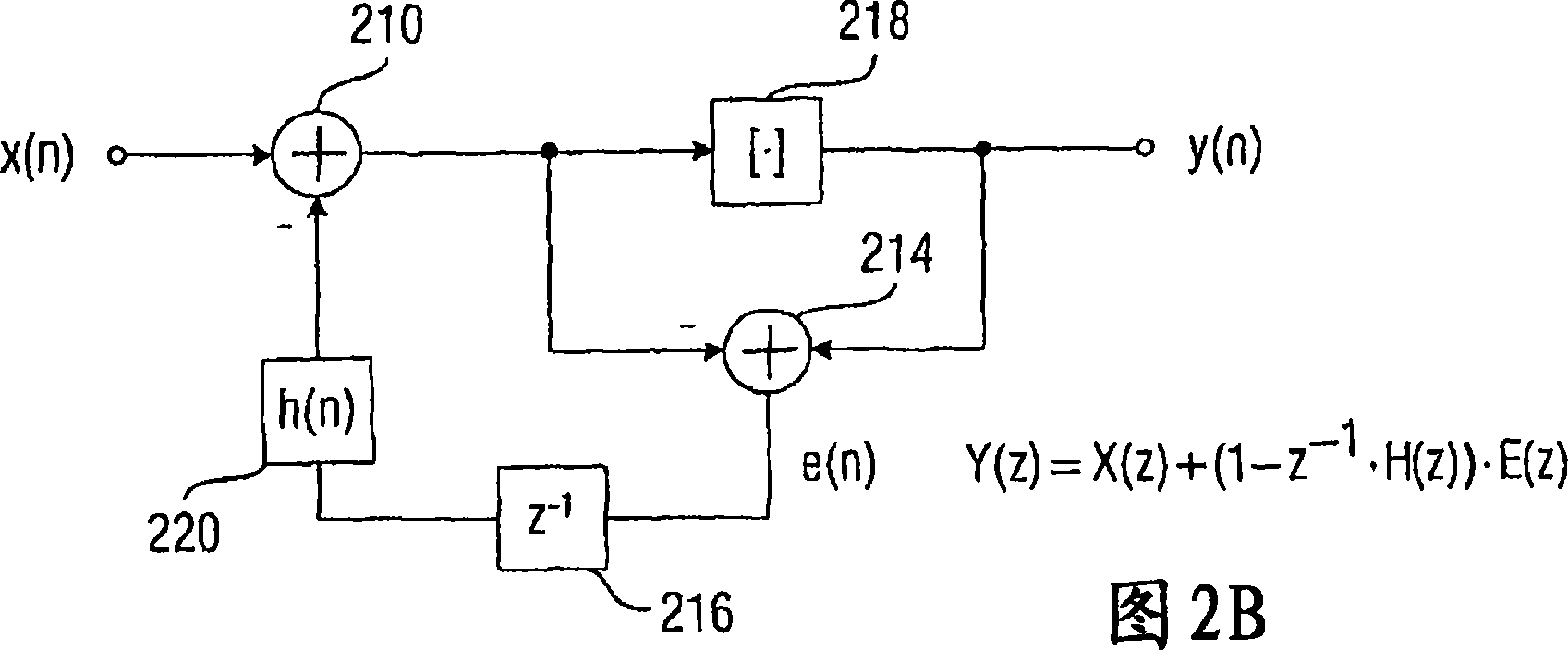
[0103] The manipulation means 202 is generally configured to manipulate a sequence of discre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com