Methods for humanizing rabbit monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody and humanized technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, organic chemistry, etc., can solve difficult model analysis and cannot easily use rabbit monoclonal antibody human source issues such as
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
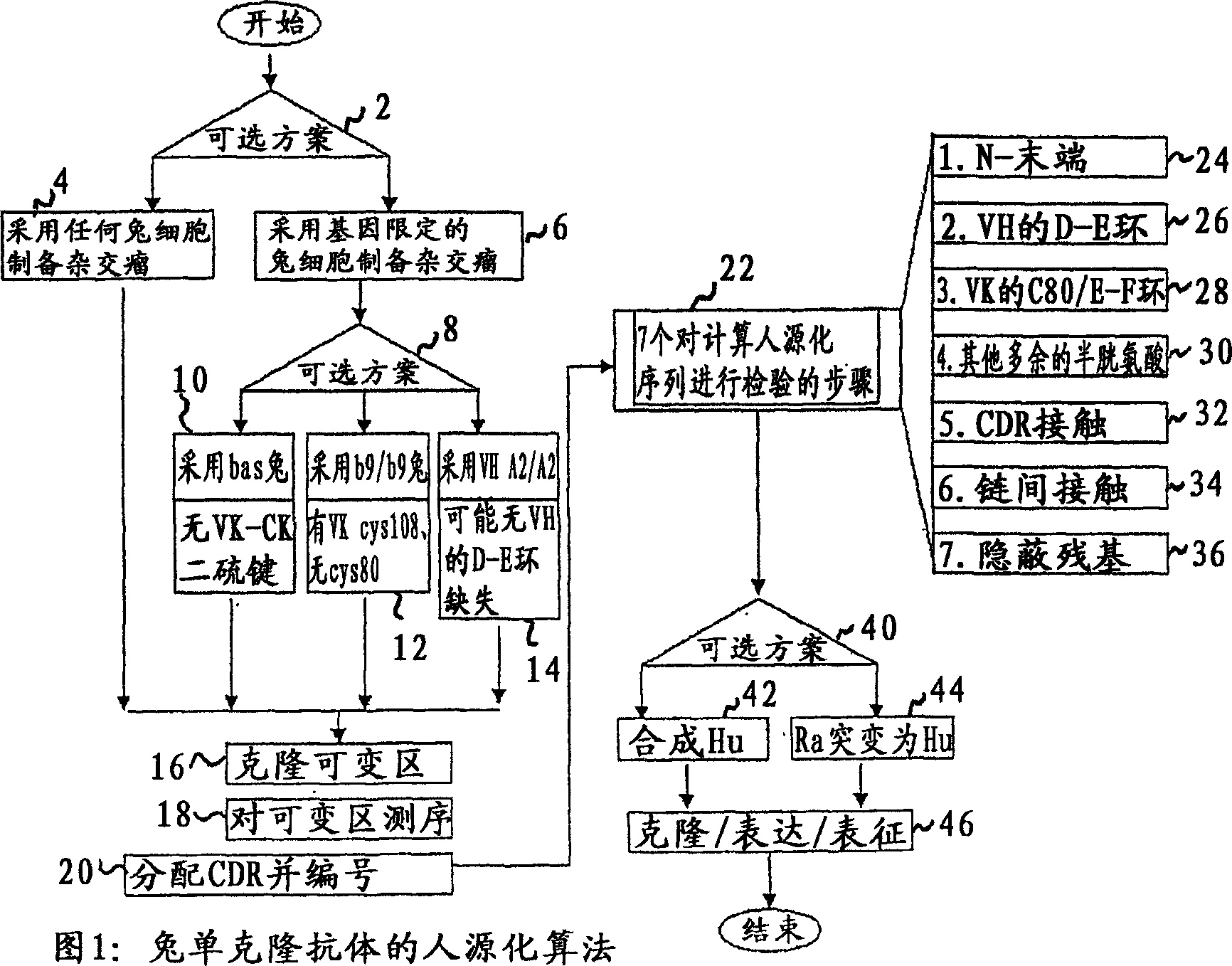
[0144] Rabbit monoclonal antibody
[0145] figure 2 A procedure is described for the sequence alignment of the variable heavy and kappa chains cloned from various rabbit monoclonal antibodies developed by Epitomics. It shows that the structural features of the rabbit chain are distinct from those of human and murine antibodies. Most of the VK chains and half of the VH chains lack one residue at the N-terminus (compared to other rabbit antibody sequences relative to human antibody sequences). Most heavy chains also lack one or two residues in the D-E loop region. All isolated kappa chains have a cysteine residue at position 80. The CDR3 sequences of many kappa chains are longer than the corresponding sequences of previously known human or murine antibodies. A few kappa chains have an extra pair of cysteine residues within their third complementarity determining region. An extra pair of cysteines is also present in some VH regions. Finally, the fact...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Humanization of Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody B1
[0148] The variable region κ chain and heavy chain of rabbit anti-integrin β-6 monoclonal antibody B1 were cloned according to the following polymerase chain reaction (PCR) procedure. Several independent PCR products were sequenced, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with one set of primers was generally sufficient.
[0149] Preparation of a suspension of hybridoma cells
[0150] - 1 ml of grown B1 cells, centrifuged at 1100 rpm for 5 min
[0151] - Rinse with 1×PBS
[0152] - Check the number of cells and adjust to 400,000 cells per ml
[0153] Preparation of RNA
[0154] -Add 1ul cells to 9ul buffer A and place on ice
[0155] -Add 5ul of cold buffer B
[0156] -Heat to 65°C for 1 minute
[0157] -Gradual cooling on the thermal cycler
[0158] 55°C 45°C 35°C 23°C Freezing point
[0159] 30 seconds 30 seconds 30 seconds 2 minutes
[0160] - Add cooling buffer C 5ul per tube
[0161] -Incubate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com