Artificial blood vessel scaffold and artificial organs
A kind of artificial blood vessel, artificial organ technology, applied in artificial blood vessel stent and its manufacture, the field of artificial organ
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
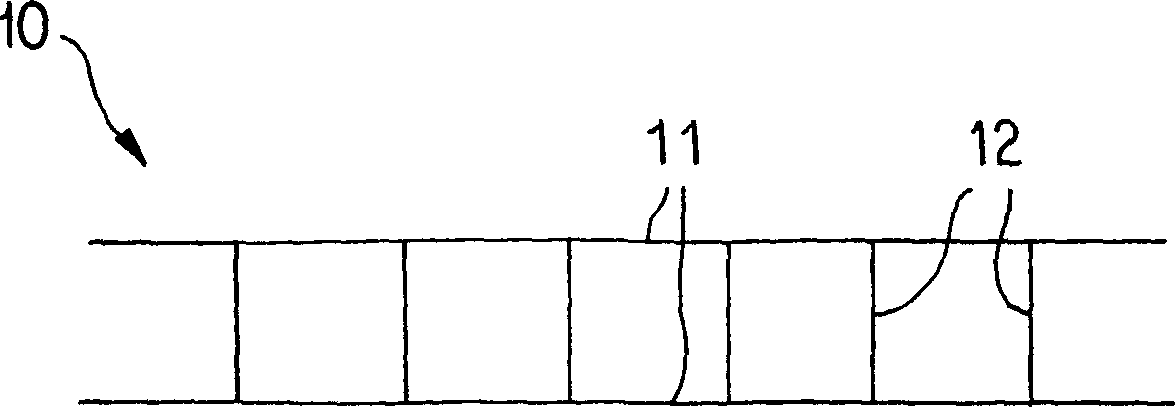
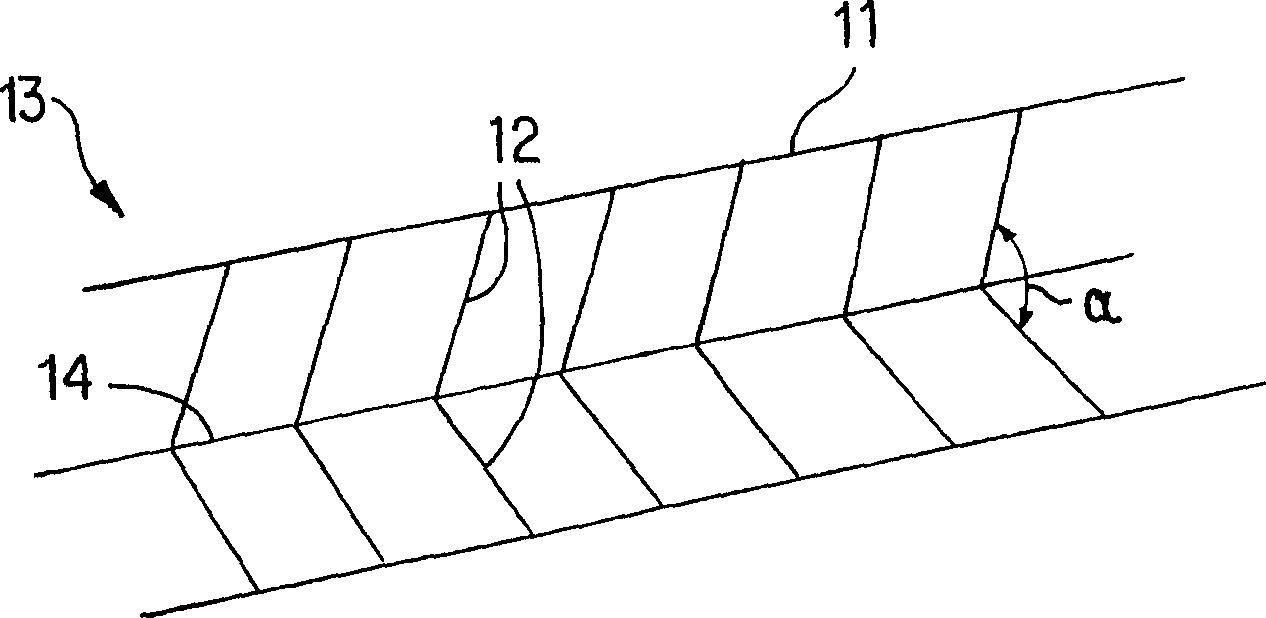
[0078] Such as Figure 1AAs shown, the panel 10 is formed by joining two or more, preferably two or three, parallel strands 11 with minimally elastic (such as #10 nylon fibers), shorter vertical strands 12, wherein the parallel strands 11 is non-absorptive material, and preferably does not have immunity, and vertical beam 12 has the same diameter as parallel beam 11. The vertical beams 12 are spaced approximately 0.5-1.0 μm apart and are approximately 90° to the parallel beams 11 . All fiber bundles are fixedly connected by methods appropriate to their materials, including but not limited to heating and bonding. For example, high temperatures can induce binding and make certain fibers such as SILASTIC TM Toughen; or use a small amount of sealant such as silicone, polyurethane or polyethylene, which can permanently join the fibers, which is the method used in the present invention.
[0079] exist Figure 1A In the embodiment shown, the panel exhibits a relatively flat shape, ...
Embodiment 2
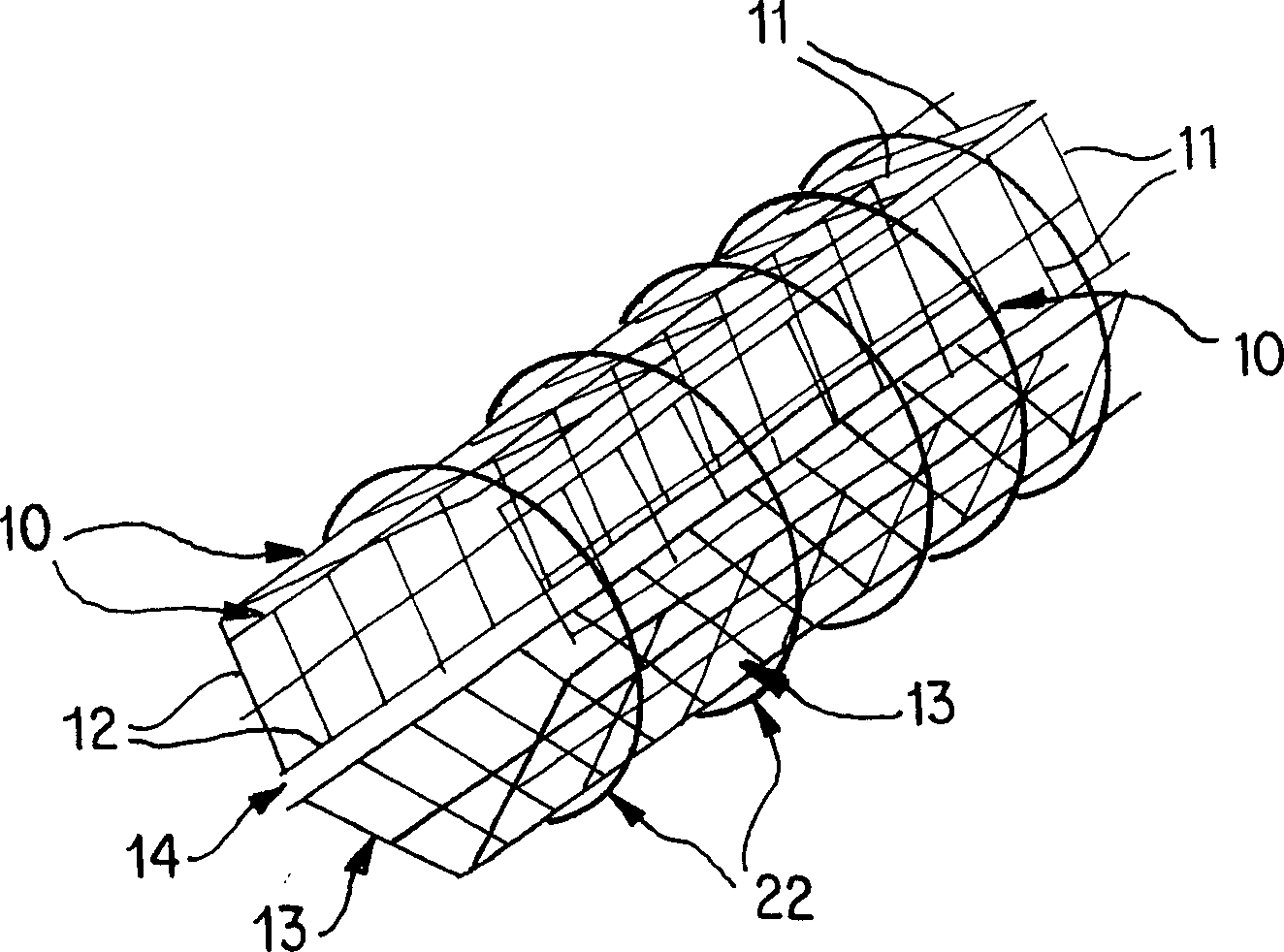
[0087] Before implanting the aforementioned prosthetic blood vessels, vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells must be cultured on a fixed structure. This process begins when the artificial vascular stent is constructed, which may be the stent 20 in Embodiment 1. A layer of smooth muscle cells is cultured along the outer surface of the scaffold 20 , and a layer of endothelial cells is cultured on the inner surface of the scaffold 20 . The cell layer can be added by placing the scaffold 20 as image 3 The vascular cell growth chamber 30 shown is completed, whereby an outer chamber 31 and an inner chamber 32 are formed in 30 . The outer chamber 31 is filled with a culture solution containing vascular smooth muscle cells, and the scaffold 20 is incubated there for about 2 days to allow the cells to attach to its outer surface.
[0088] After the outer layer cells are attached, the culture solution containing the endothelial cells flows into the inner chamber 32 . Thi...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Figure 6A is a schematic diagram of an artificial internal liver unit 60 . A common input port 61 on the artificial internal liver unit 60 is sutured to the abdominal artery (not shown). The inner diameter of 61 is about 2cm, and the length is about 1-2cm. Extending from 61 opposite the artery are 2-20 individual input ports 62, each of which is approximately 80-100 [mu]m in diameter. Each individual input port 62 leads to a first end of an inner conduit 63, 4-8 of which have an inner diameter of about 30-50 μm each and a length of 8-12 cm. Inner conduits 63 originating from separate input ports 62 mostly connect their second ends to separate output ports 64, which are approximately 80-100 μm in diameter. 64 is connected with a common output port 65, the inner diameter of 65 is about 2cm, and the length is 2-4cm. 65 sutured with abdominal veins (not shown). Such as Figure 2A As shown, 62 and 64 are interlaced with each other in a branched form.
[0100]The comm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com