Plant epidermal hair specific expression promoter
A plant epidermis and promoter technology, applied in the field of plant bioengineering and plant improvement genetic engineering, can solve the problem of lack of plant epidermal hair cis-regulatory elements and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
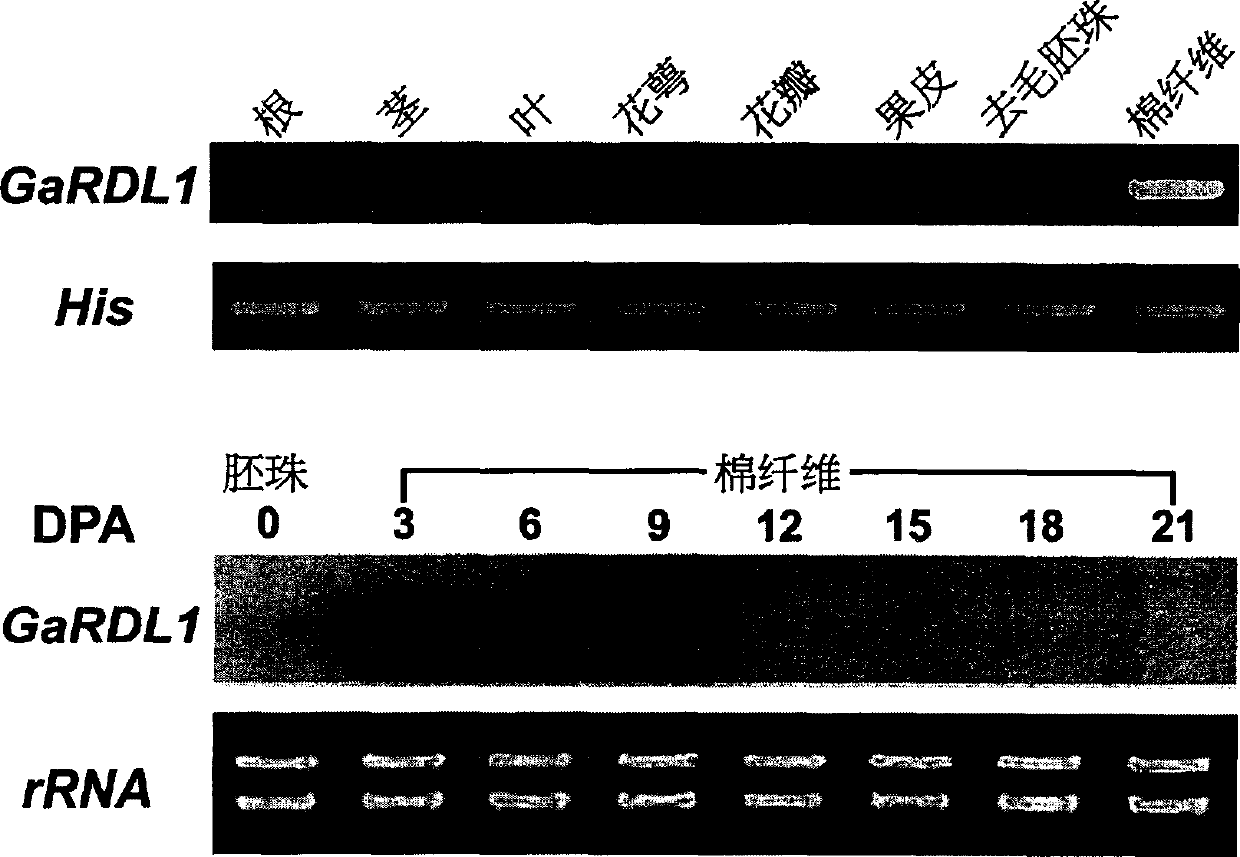
[0056] Example 1 Isolation of GaRDL1 promoter
[0057] Cotton DNA was extracted by cold phenol method. 2 g of material (cotton fiber of Asian cotton (Gossypium arboreum)), ground into powder in liquid nitrogen, transferred to a 50 ml centrifuge tube, added 8 ml of extraction buffer (1M Tris HCl, 50 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, pH 9.0 ) and an equal volume of water-saturated phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) were shaken and mixed, placed on ice for 1 hour, and mixed every 10 minutes. Centrifuge at 13000g for 20 minutes at 4°C. Repeat phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol extraction 2 to 4 times, and finally extract once with chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1). Take the supernatant, add 1 / 2 volume of high salt solution (0.8M sodium citrate, 1.2M NaCl) and 1 / 2 volume of isopropanol, mix well, and place at -70°C for 1 hour. Centrifuge at 13000g for 20 minutes at 4°C. The following operations are performed according to the extraction of DNA and RNA. Remove the supernatant, wash ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Vector Construction and Agrobacterium Transformation
[0062] According to the distribution of the multi-cloning region of the vector, the GaRDL1 promoter and the restriction site of the target gene, determine the restriction site for the fusion fragment to be inserted into the vector, and then introduce the restriction site into the GaRDL1 promoter and the target gene by PCR . After digestion and ligation, heat shock method was used to transform Escherichia coli, positive clones were identified by PCR, and sequenced for verification.
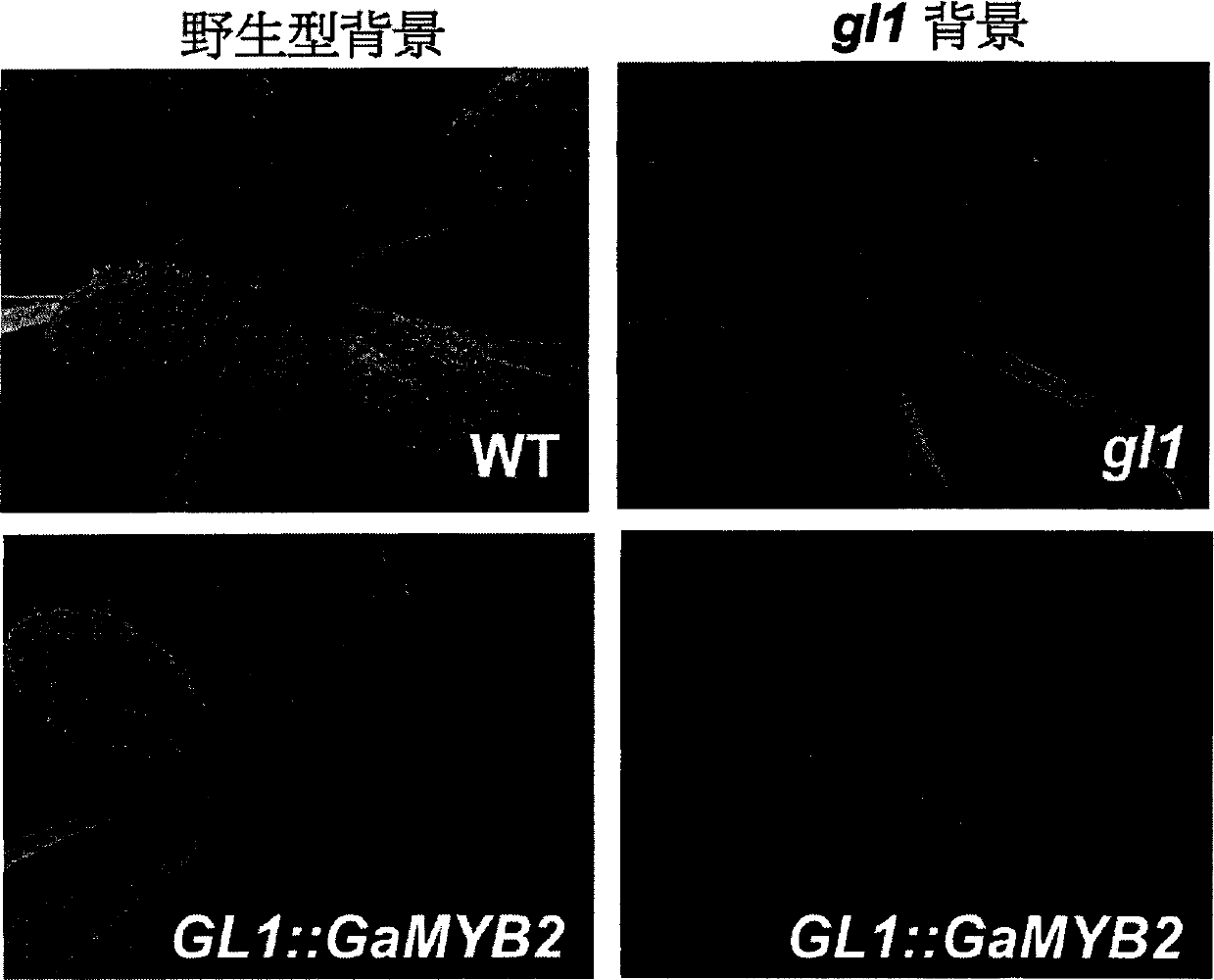
[0063] According to the full-length coding sequence of the exogenous gene GUS gene, primers (corresponding to the first 20 bp and the last 20 bp) were designed to amplify the complete coding reading frame, and the GUS sequence was obtained after PCR amplification, and then directly connected to the GaRDL1 promoter (located at downstream of the promoter). Then the DNA sequence (GaRDL1::GUS sequence) was cloned into the interme...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Plant Transformation and Screening of Transgenic Progeny
[0066] In this example, the transgenes of cotton and Arabidopsis are taken as examples, which can be used as a reference for the transformation of other plants.
[0067] a. Transgenic cotton
[0068]Cotton was transformed using an Agrobacterium-mediated method.
[0069] The upper part (0.5 cm) of the hypocotyl of the 5-day-old aseptic seedling was pre-cultured for 36 hours. Medium: SH+2,4-D 0.1mg / L+KT 0.1mg / L.
[0070] The hypocotyl sections were soaked in the Agrobacterium bacterial solution (SH+2,4-D 0.1 mg / L+KT 0.1 mg / L+acetosyringone 100 μmol / L) for 20 minutes.
[0071] Co-cultivate for 3 days. Medium: SH+2,4-D 0.1mg / L+KT 0.1mg / L+acetosyringone 100μmol / L.
[0072] The callus was initially induced for 25-30 days. Medium: SH+2,4-D 0.1mg / L+KT 0.1mg / L+Km50mg / L+cephalosporin (cef) 300mg / L or MSB+2,4-D 0.1mg / L+IAA 0.1mg / L L+ZT0.1mg / L+Km 50mg / L+cef 300mg / L.
[0073] Embryogenic callus was induced ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com