Supercritical extraction and drying method in preparation of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibre
A polyethylene fiber, ultra-high molecular weight technology, applied in the direction of single-component polyolefin rayon, wet spinning, etc., can solve the problems of increasing cost and time, and achieve the effect of reducing equipment investment and simplifying the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
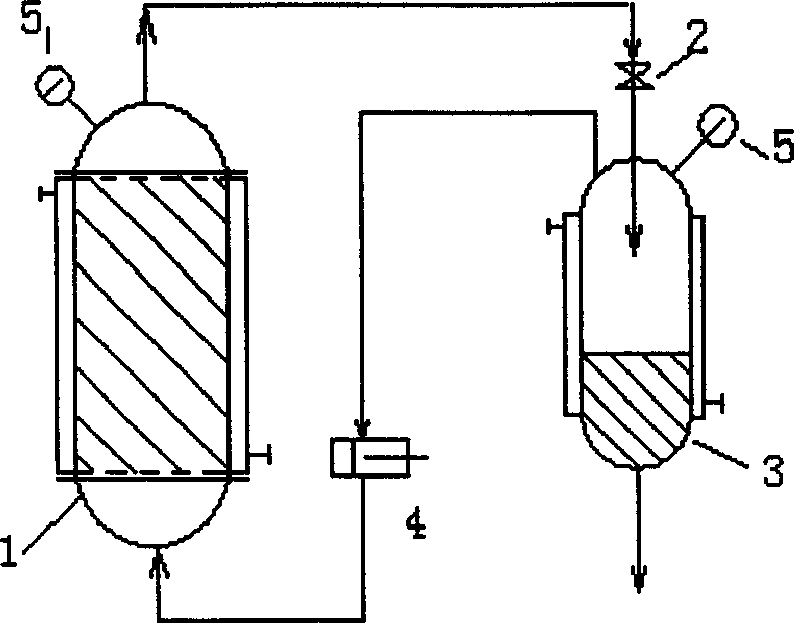
[0034]Extraction and separation by isothermal method. The temperature of the extraction tank is 120°C and the pressure is 6MPa. 30 kg of condensed fibers fall into the extraction kettle and arrange them neatly and seal them. Use a high-pressure pump to press 40 liters of extractant propane from the bottom into the extraction kettle, and use isothermal extraction and separation. The extractant is propane. After the extraction of propane is completed, it flows out from the top, and enters the separation tank after being decompressed by the pressure reducing valve. The gaseous propane is pumped out from the top, and then pressed into the extraction kettle through a high-pressure pump for recycling. Liquid solvent is pumped from the bottom and recycled. The extraction time is 0.2D minutes (D is the fineness of single filament, the unit is dtex).
[0035] After the extraction is finished, feed hot nitrogen into the extraction kettle for drying, the nitrogen flow rate is 50 lite...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Extraction and separation by isobaric method. The extractant is propane. The temperature of the extraction tank is 100°C and the pressure is 5MPa. Condensation-molded fibers fall into the extraction kettle to arrange them neatly and seal them. The fiber quality that puts in is 30 kilograms. Use a high-pressure pump to press 40 liters of propane, the extraction agent, into the extraction kettle from the bottom. After the propane extraction is completed, it flows out from the top and enters the separation kettle after heat exchange. The pressure remains constant and the temperature drops to 20°C. Bottom pumps away and recycles. The gas is pumped out from the top, and then pressed into the extraction kettle through a high-pressure pump for recycling. The extraction time is 0.2D minutes (D is the fineness of single filament, the unit is dtex).
[0040] After the extraction is finished, feed hot nitrogen into the extraction kettle for drying, the nitrogen flow rate is 5...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Extraction and separation by adsorption. The extractant is propylene. The temperature of the extraction tank is 100°C and the pressure is 10MPa. 35 kg of condensed fibers fall into the extraction kettle and are neatly arranged and sealed. Use a high-pressure pump to press 30 liters of extractant propylene into the extraction kettle from the bottom. After the propylene extraction is completed, it flows out from the top with the pressure and temperature kept constant, and enters the separation kettle. Molecular sieve adsorbent is filled in the separation kettle. Propylene is separated from the first solvent by adsorption separation. The extraction time is 0.1D minutes (D is the fineness of single filament, the unit is dtex).
[0045] After the extraction is finished, use a vacuum pump to extract the gas in the extraction kettle, and stop when the gauge pressure drops to 100kPa.
[0046] After supercritical extraction, the content of solvent in the fiber is less than ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com