Flash device, camera therewith, semiconductor laser and manufacture thereof
A flash device, semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor lasers, cameras, lasers, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient light output power, etc., and achieve the effect of improving flash photography performance, low power consumption, and high output power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
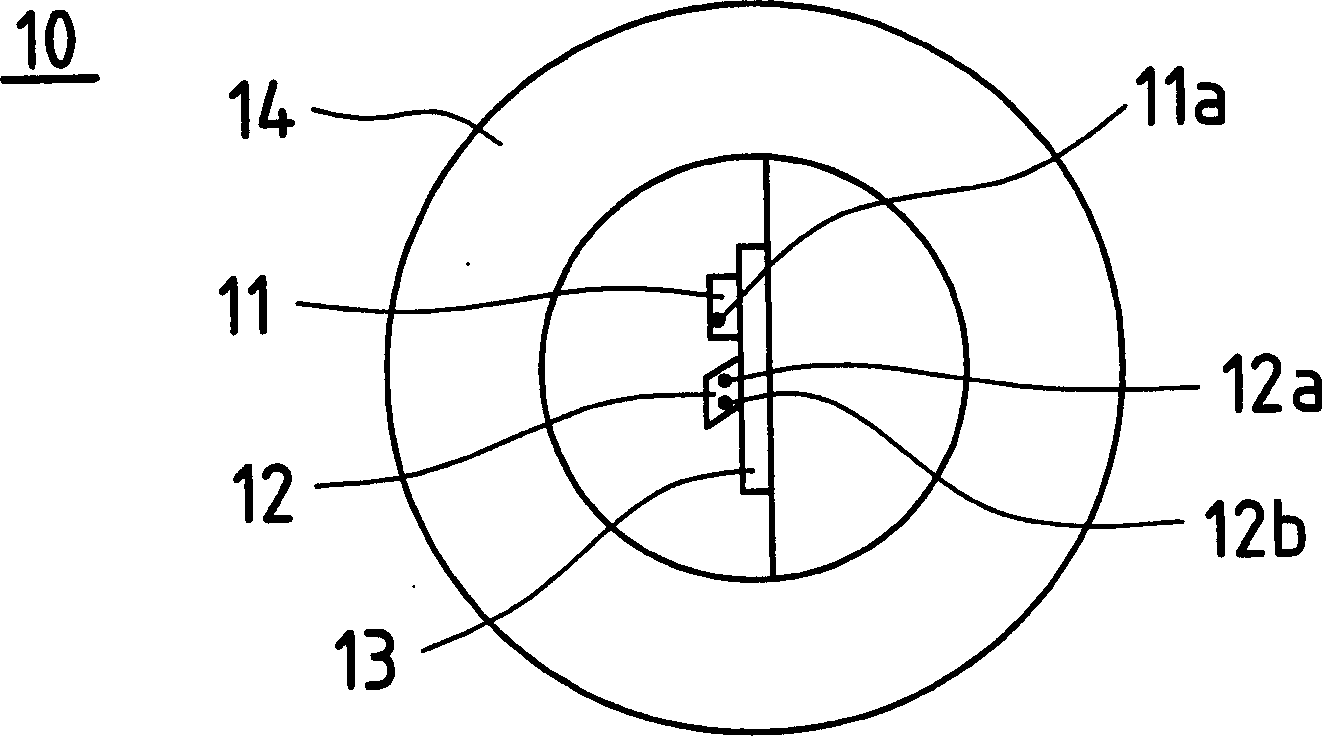
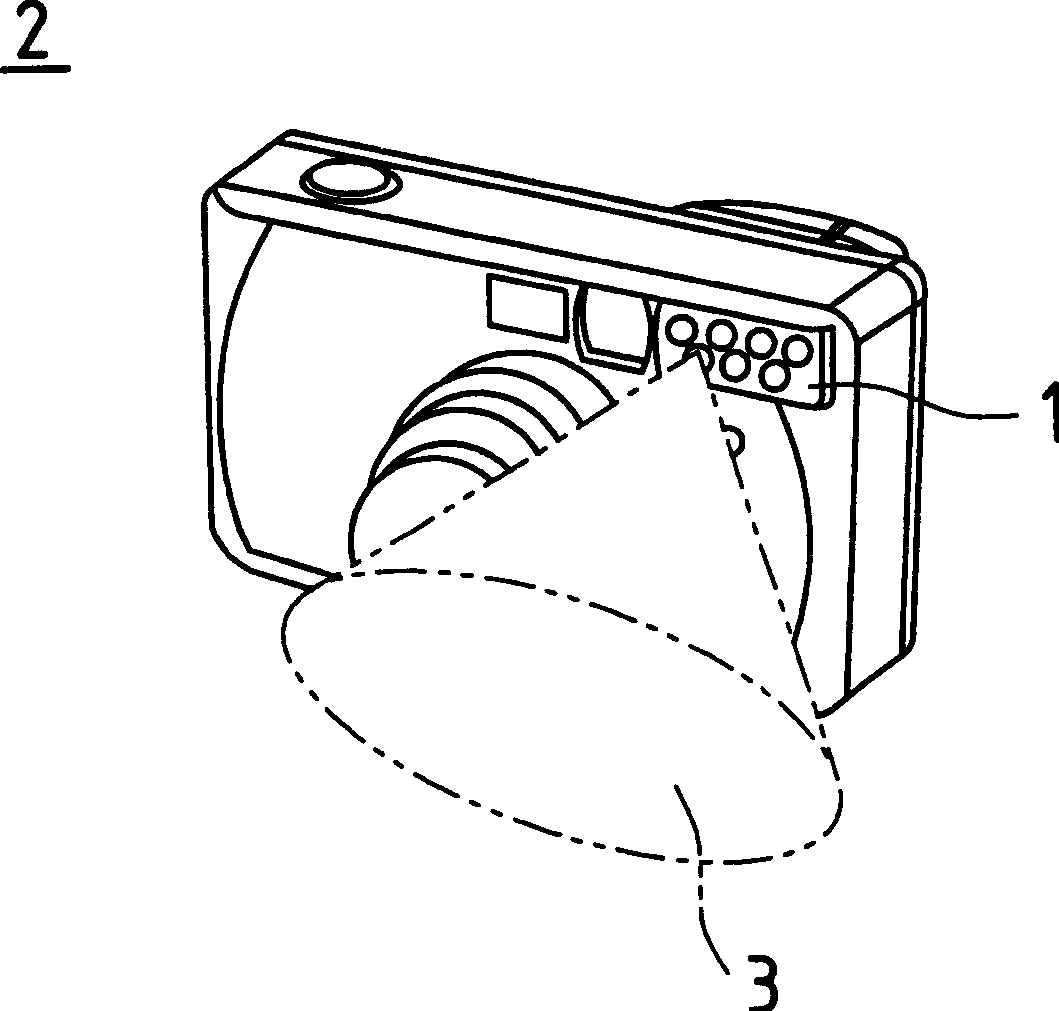
[0074] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the internal structure of the semiconductor laser 10 used in the flash device related to the first embodiment of the present invention, and shows the structure for the photographic area for the standard size frame of film.
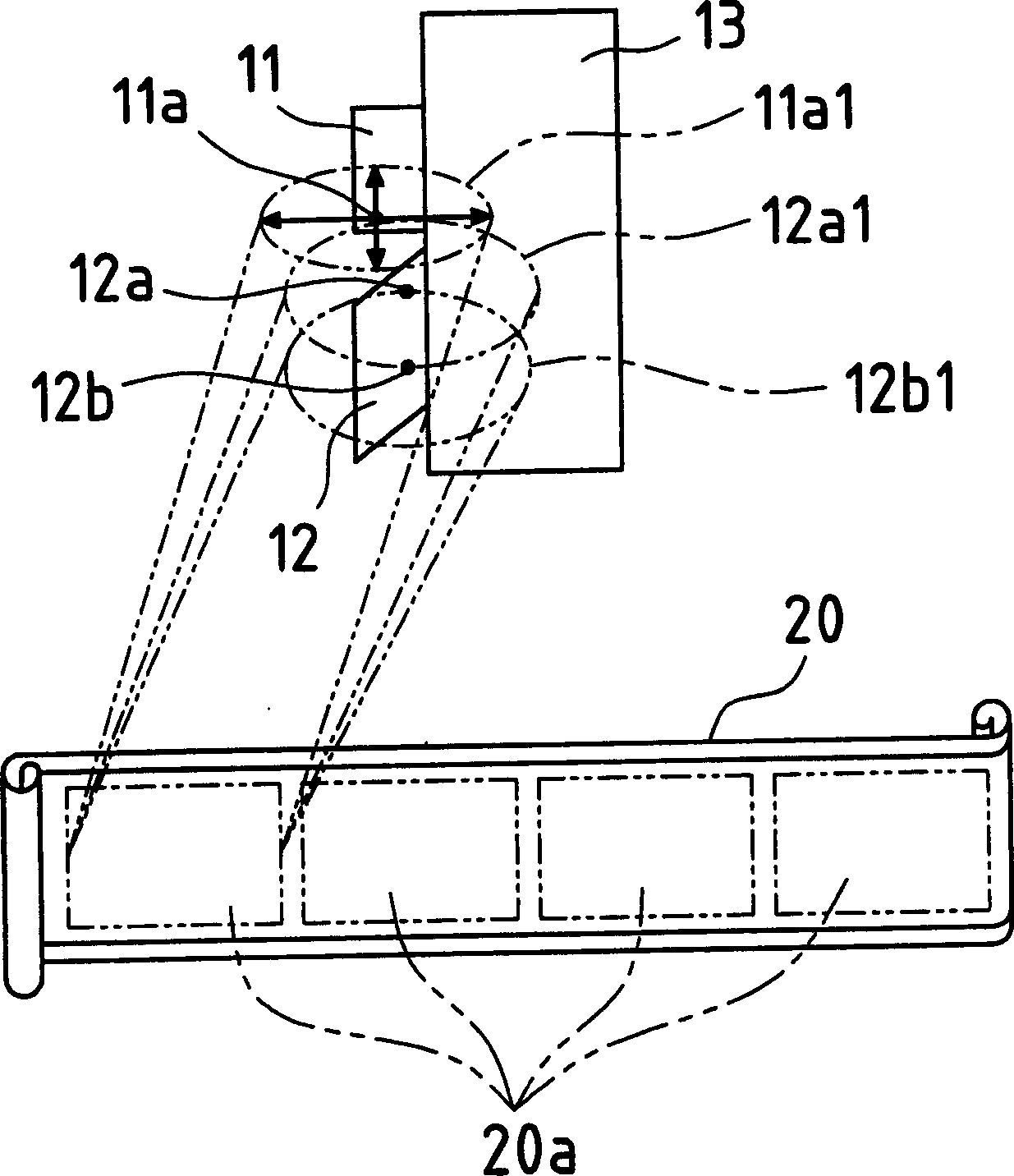
[0075] like figure 1 As shown, a plate-like submount 13 (radiation fin) is vertically provided in the circular stem portion 14 of the semiconductor laser 10 . The blue laser substrate 11 is placed on one side surface of the upper part of the auxiliary support 13, and blue laser light (wavelength 450 nm, GaN) is emitted from the blue laser light-emitting point 11 within the cross section of the blue laser substrate 11 . The red / infrared dual-wavelength monolithic laser 12 is placed slightly under the blue laser substrate 11 on the side surface of the submount 13 where the blue laser substrate 11 is placed. Infrared laser (790nm, GaAs) is emitted from the infrared light-emitting point 12a in the cross section of t...
no. 2 example
[0097] In the first embodiment, a plurality of laser beams of different wavelengths from semiconductor lasers are synthesized to obtain white light which is diffused with a reflective sheet to obtain a flash of light. In the second embodiment, white light is obtained from laser light of a single wavelength by applying three types of phosphors emitting red, green, and blue to a reflective sheet. Since the second embodiment and the first embodiment are the same except for the points described below, only the differences between the first and second embodiments will be described.
[0098] 10(a) and 10(b) are examples of emitter boards for scattering laser light used in a flash device related to a second embodiment of the present invention. Fig. 10(a) shows the entire reflection sheet 40, and Fig. 10(b) shows an enlarged part 40a. 11( a ) and 11 ( b ) are schematic diagrams showing an example of a reflective sheet for laser light scattering used in a flash device related to a sec...
no. 3 example
[0105] In the third embodiment, white light is obtained using a sapphire hexagonal laser and combining a blue laser beam with fluorescent beams from two types of phosphors that emit red and green light as a result of being activated by the blue laser. Since the third embodiment and the second embodiment are the same except for the points described below, only the differences between the third and second embodiments will be described.
[0106] Figure 13 is a schematic diagram of a sapphire hexagonal laser 50 used in a flash device related to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0107] like Figure 13 As shown in , the sapphire hexagonal laser 50 has a hexagonal shape and is a crystal including a hexagonal structure obtained by forming GaN on a sapphire substrate. Blue laser beams 51a, 52a, and 53a are emitted from three adjacent surfaces of the sapphire hexagonal laser 50, and blue laser beams 51b, 52b, and 53b are emitted from the surface opposite to the three surfa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com