Tensioner
A technology for tensioning devices and shaft components, applied to transmission devices, belts/chains/gears, mechanical equipment, etc., to achieve the effects of suppressing amplitude, reducing output loss, and increasing frictional torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
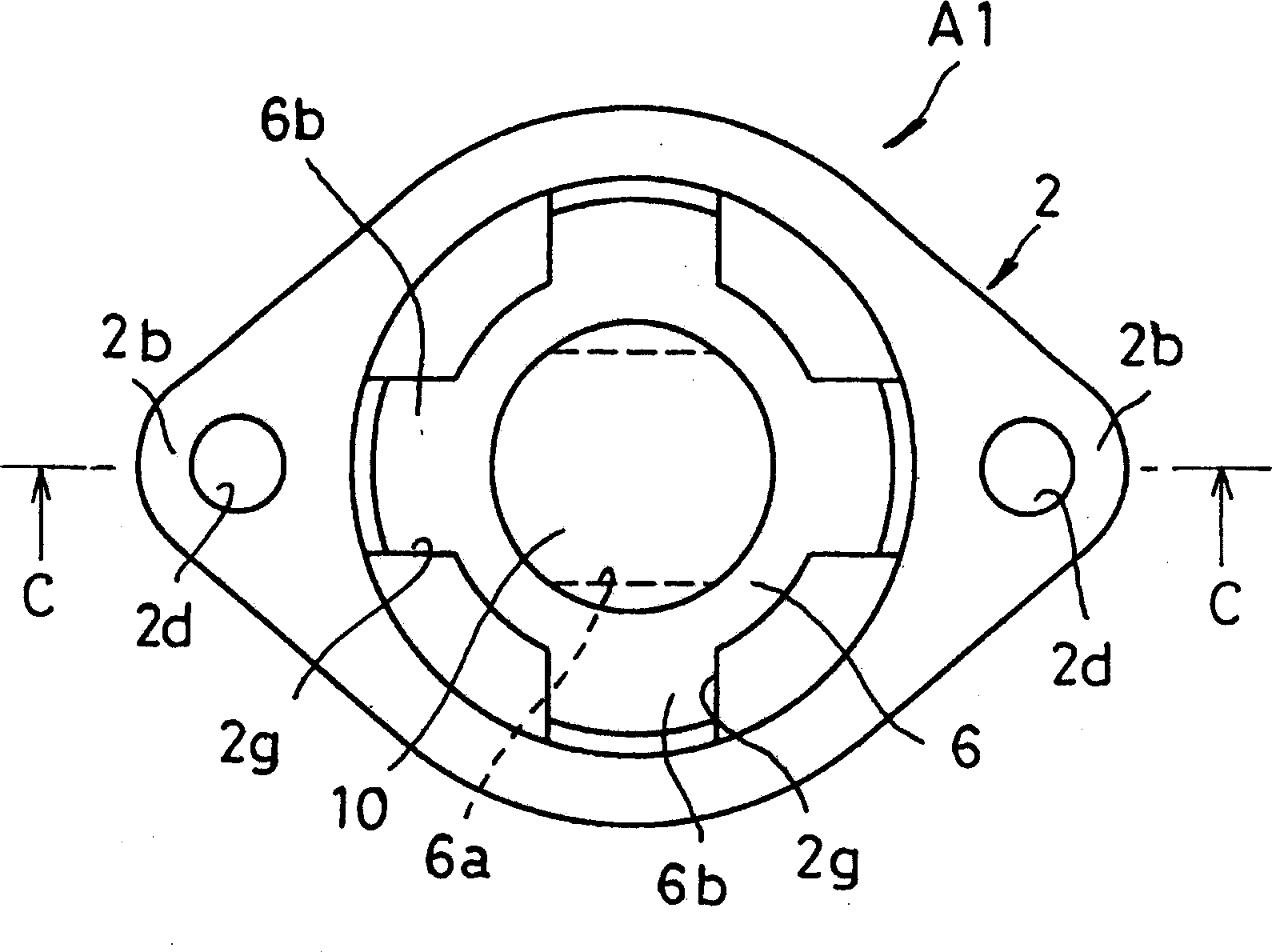
[0057] Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 A tensioner A1 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown, which includes a housing 2 , a first shaft member 3 , a second shaft member 4 , a torsion spring 5 , a bearing 6 , and a spacer 7 .
[0058] The housing 2 is substantially T-shaped in cross section, and its flange portion 2b extends from the top end of the trunk portion 2a in a direction substantially perpendicular to the driving direction. Also, an accommodation hole 2c is formed extending in the axial direction (driving direction) from the trunk portion 2a to the flange portion 2b. The top end portion of the housing hole 2c is open, and an assembly of the first and second shaft members 3, 4, the torsion spring 5, and the partition plate 7 is placed in the housing hole 2c.
[0059] The flange part 2b of the housing 2 is used to connect with the engine body of the equipment used, and a mounting hole 2d is formed in the flange part 2b, through which a bolt (not shown) is scr...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Figure 4 A tensioner A2 according to the second embodiment of the present invention is shown, and a buffer plate 22 is inserted between the coil spring 20 constituted by a compression spring and the flange portion 3c of the first shaft member 3 . The buffer plate 22 is made of a thin metal plate such as a washer, and is sandwiched between the other end portion 20 b of the coil spring 20 and the flange portion 3 c of the first shaft member 3 .
[0079] By providing such a buffer plate 22 , it is possible to prevent the other end portion 20 b of the coil spring 20 from biting into the first shaft member 3 . This enables smooth operation of the coil spring 20, suppresses abrasion of the coil spring 20 and the first shaft member 3, and improves durability of the tensioner.
[0080] Figure 5 and Figure 6 A variant of this embodiment is shown. exist Figure 5 In this way, between the flange portion 3c of the first shaft member 3 and the other end portion 20b of the co...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Figure 7 A tensioner A3 according to Example 3 of the present invention is shown. In the tensioner A3 of this embodiment, both end portions 20a, 20b of the coil spring 20 constituted by a compression spring are supported by the first shaft member 3 and the second shaft member 4 .
[0085] That is, between the flange portion 3c and the threaded portion 3b of the first shaft member 3, a raised portion 3g having an outer diameter corresponding to the inner diameter of the coil spring 20 is formed. On one side of the shaft member 3 is formed a shoulder protrusion 4g having an outer diameter corresponding to the inner diameter of the coil spring 20 . These convex portions 3 g , 4 g are support seats that support the ends of the coil spring 20 . Furthermore, by inserting these protrusions 3g, 4g into both end portions 20a, 20b of the coil spring 20, a more stable support state can be maintained. Furthermore, a metal washer 22 serving as a buffer plate is sandwiched betwee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com