Planar luminescent illumination device including auxiliary electrode
A technology for auxiliary electrodes and light-emitting devices, which is applied in the field of light-emitting devices including auxiliary electrodes, and can solve problems such as insufficient suppression of uneven brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
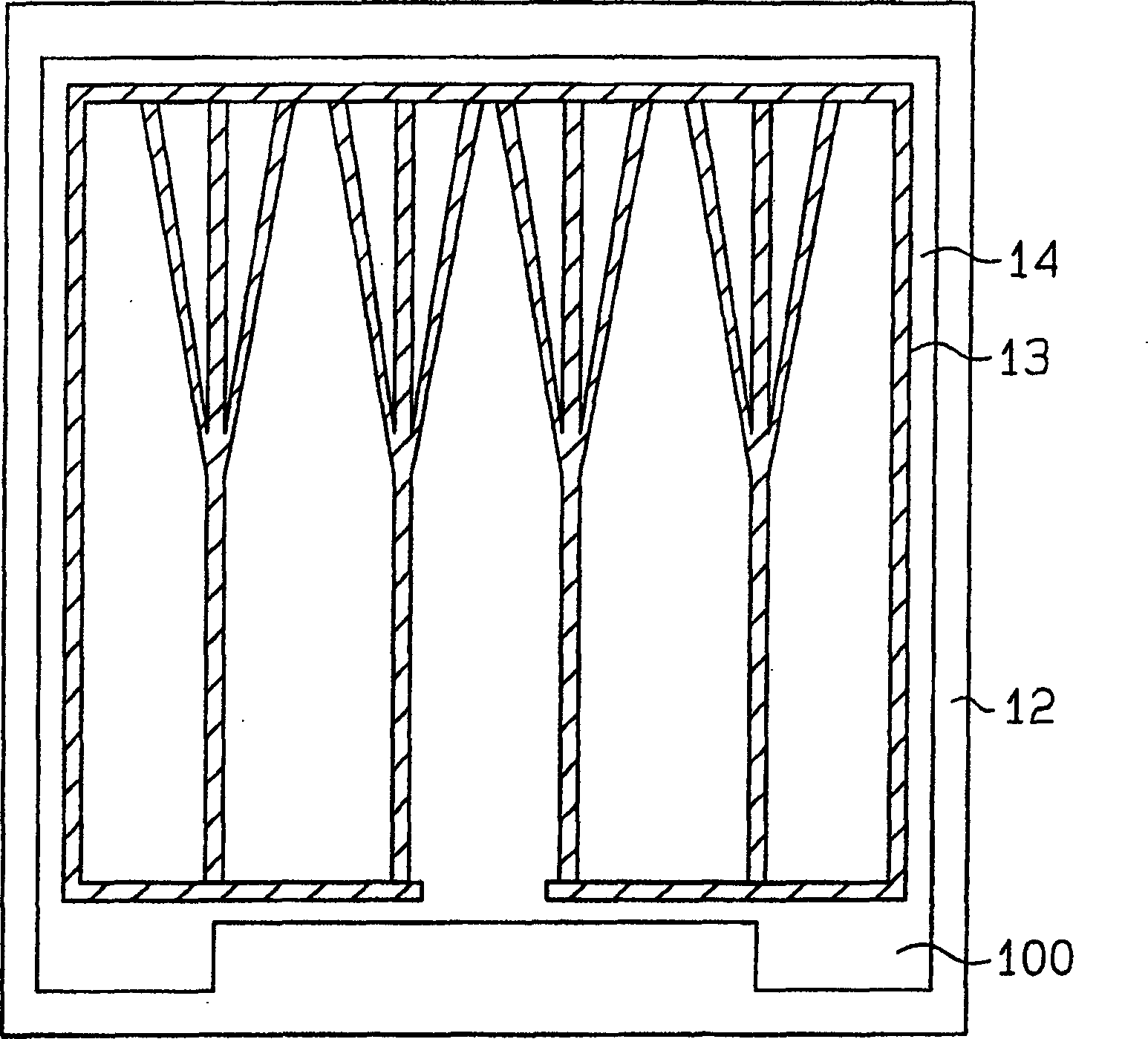
[0025] will refer to Figure 1~3 An organic electroluminescent device 3 according to a first embodiment of the present invention is described. The organic electroluminescent device 3 is used as a backlight for the passive matrix transmissive liquid crystal display 1 .
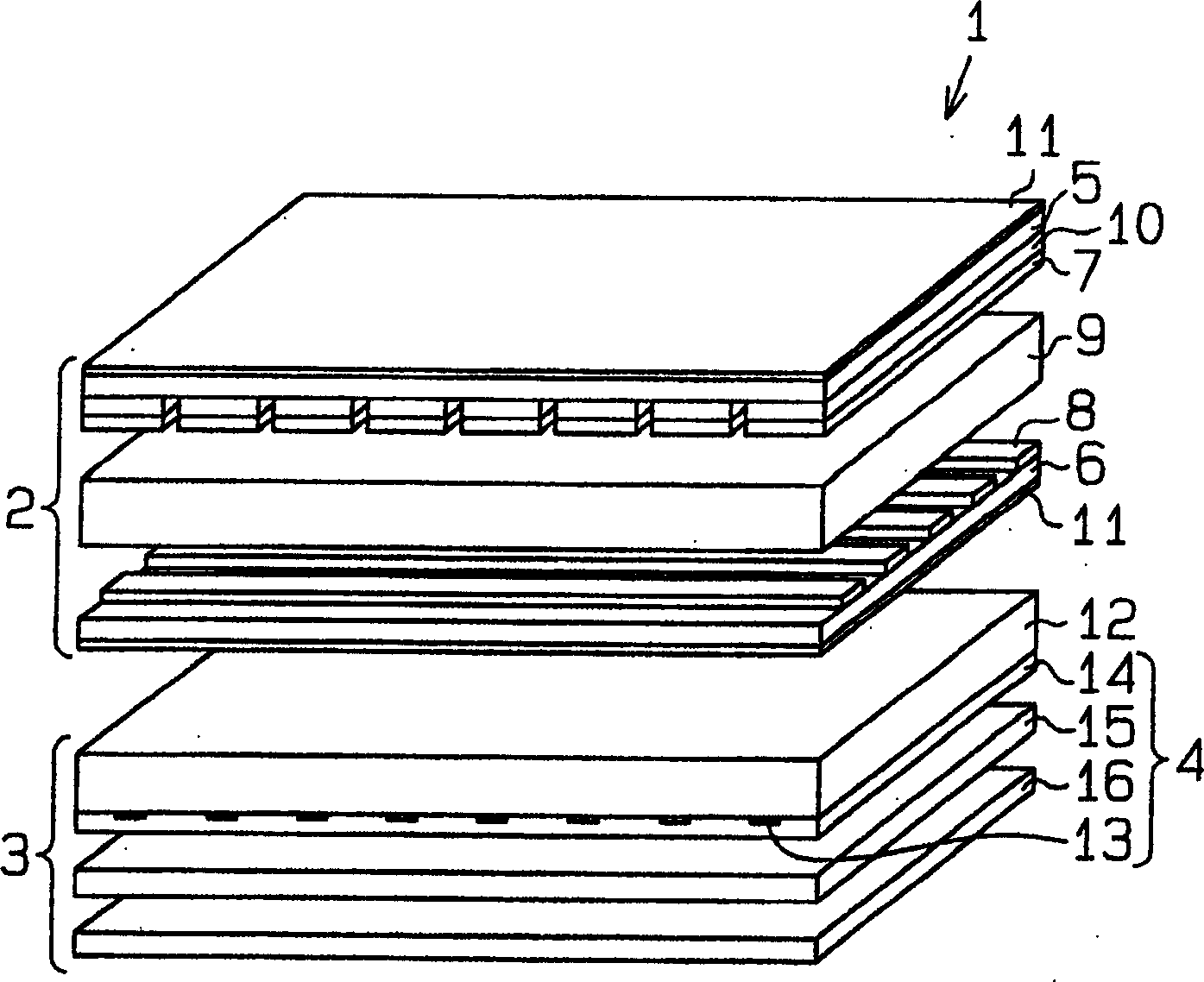
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, a transmissive liquid crystal display 1 includes a passive matrix liquid crystal panel 2 and an organic electroluminescent device 3 used as a surface emitting device.
[0027] A liquid crystal panel 2 , which is a known panel, includes a first transparent substrate 5 , a second transparent substrate 6 , and a liquid crystal layer 9 arranged between the first transparent substrate 5 and the second transparent substrate 6 .
[0028] Two polarizers 11 are arranged on the outer surface of the first transparent substrate 5 and the outer surface of the second transparent substrate 6, respectively.
[0029] A plurality of parallel stripes of color filters 10 are formed on the surfa...
no. 2 example
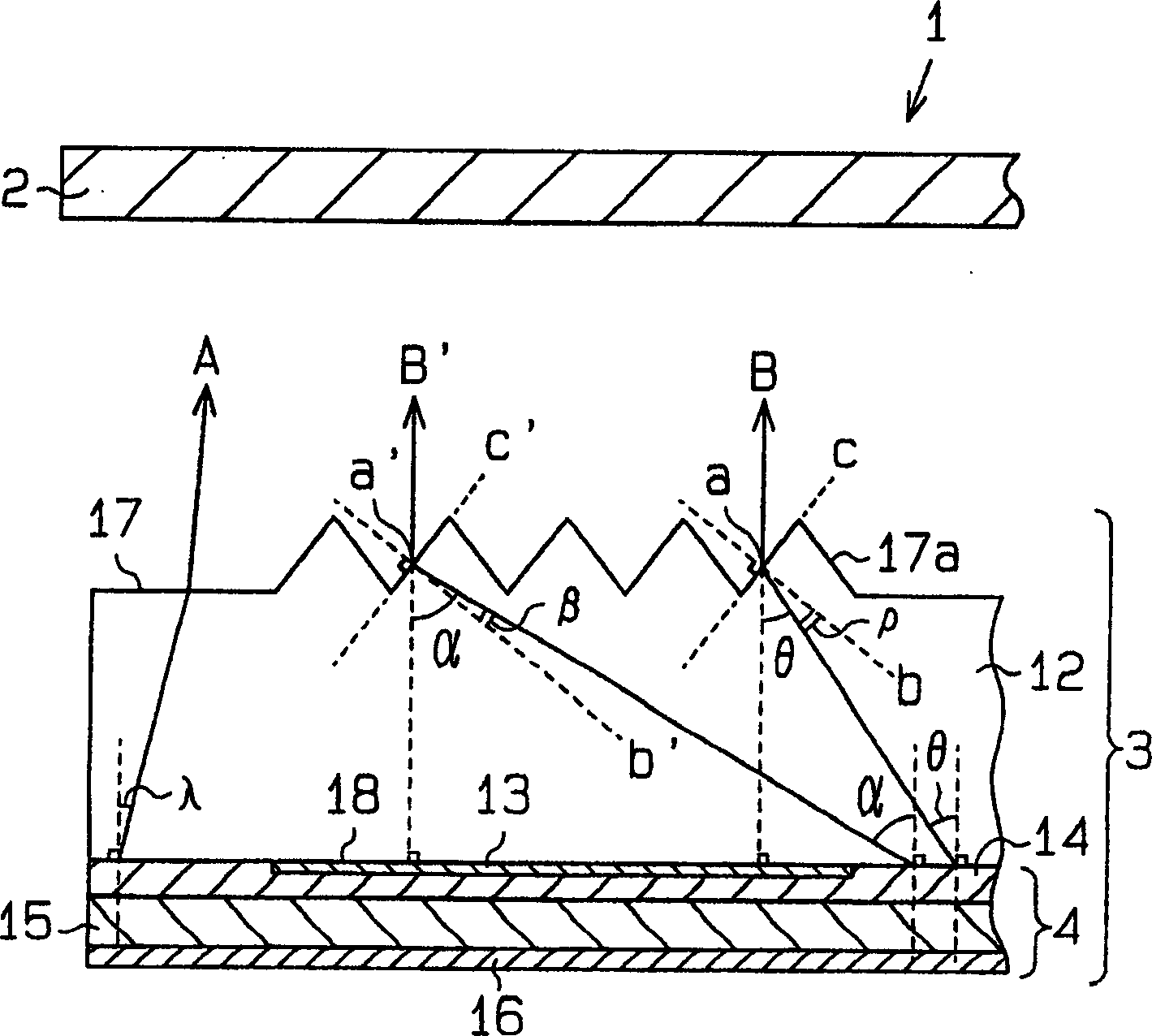
[0055] In a second embodiment of the invention, the organic electroluminescent device 33 of a passive matrix transmissive liquid crystal display 30 comprises a transparent substrate 31 with a planar light exit surface 34, such as Figure 4 shown. On the light exit surface 34 of the transparent substrate 31 is arranged a prism sheet, which is an optical sheet. In other respects, the structure of the liquid crystal display 30 is the same as that of the liquid crystal display 1 in the first embodiment.
[0056] At the portion of the prism sheet 32 corresponding to the auxiliary electrode 13, parallel microprisms or protrusions 32a having a triangular cross section are formed.
[0057] The organic electroluminescent device 33 of the second embodiment has the same advantages as the organic electroluminescent device 3 of the first embodiment.
no. 3 example
[0059] In a third embodiment of the present invention, an organic electroluminescent element 45 of an organic electroluminescent device 44 for a passive matrix transmissive liquid crystal display 40 includes an auxiliary electrode 43 . Such as Figure 5 As shown, on the surface of the auxiliary electrode 43 facing the transparent substrate 12, parallel microprisms or protrusions 43a having a triangular cross-section are formed. In other words, the auxiliary electrode 43 has an uneven surface. As for other parts, the structure of the liquid crystal display 40 is the same as that of the liquid crystal display 1 in the first embodiment.
[0060] The organic electroluminescent device 44 of the third embodiment has the following advantages in addition to the above advantages (1) and (2).
[0061] A protruding portion 43 a is formed on the surface of the auxiliary electrode 43 facing the transparent substrate 12 . Thus, the angle of light propagating in the transparent substrate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com