Hamming iteration and interpretation method based on sum and product algorithm
An iterative decoding, Hamming code technology, applied in the direction of error correction/detection using linear codes, error correction/detection using block codes, data representation error detection/correction, etc., which can solve decoding complexity and performance tradeoffs, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
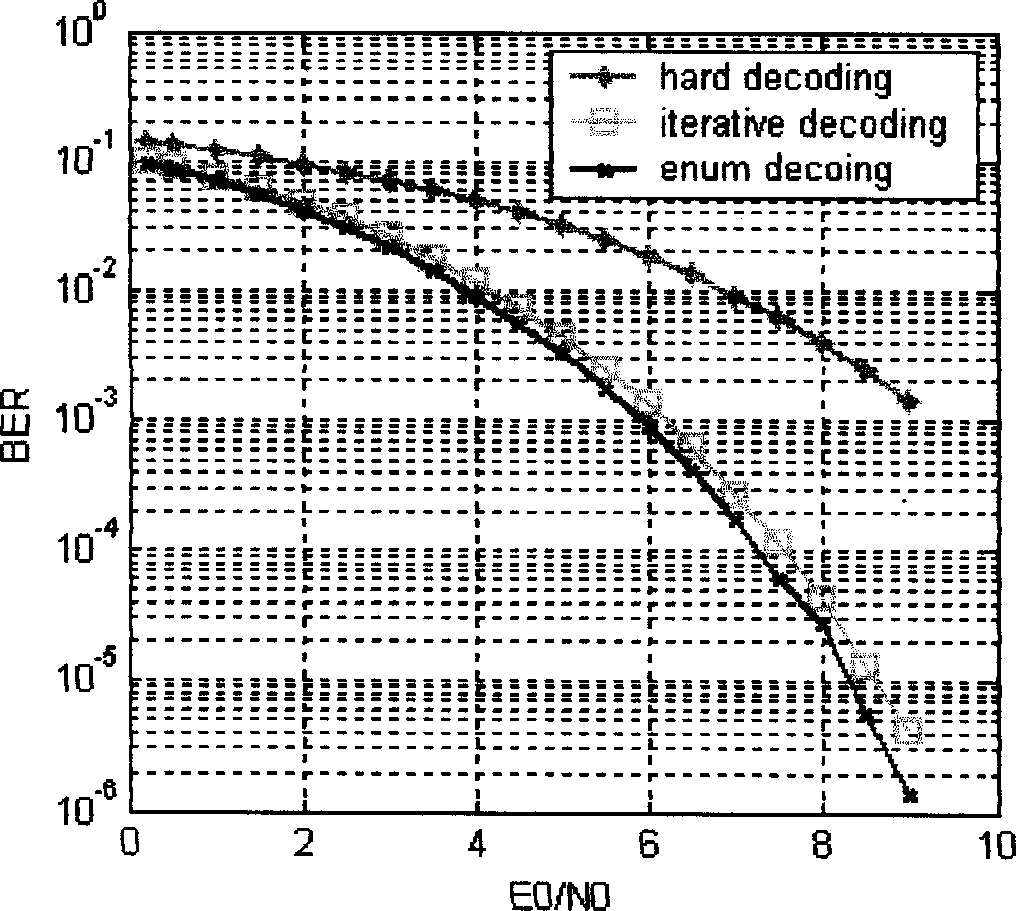
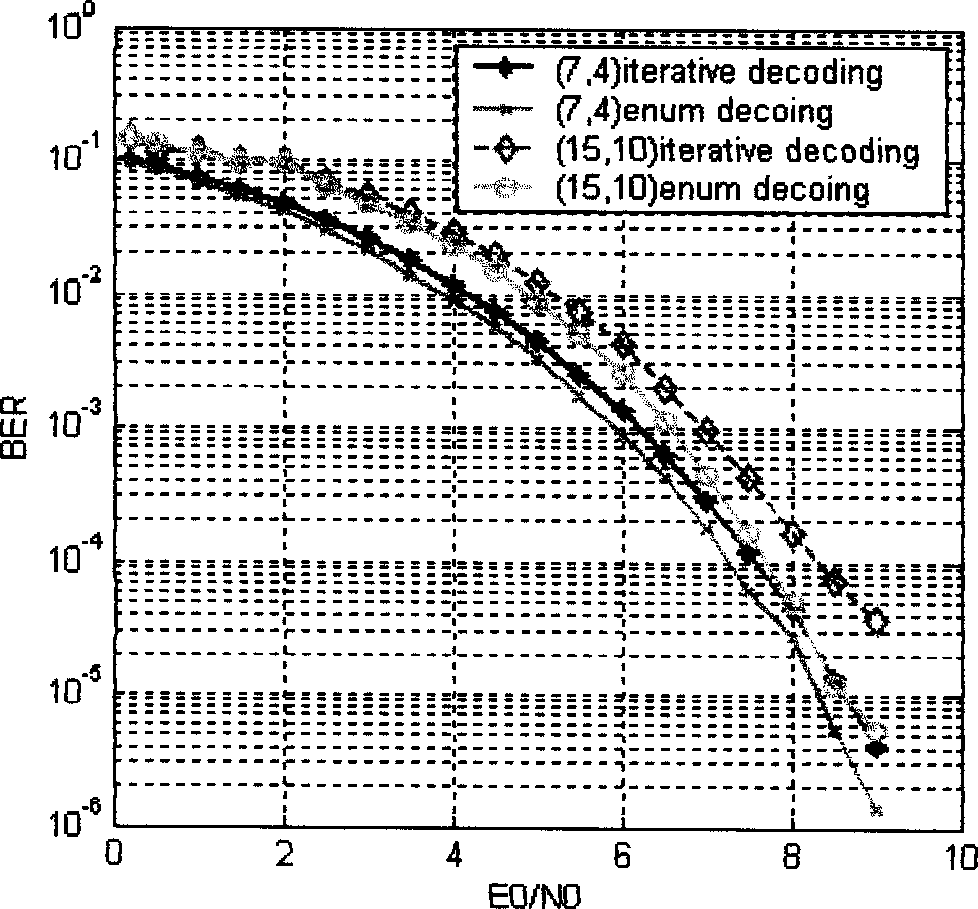
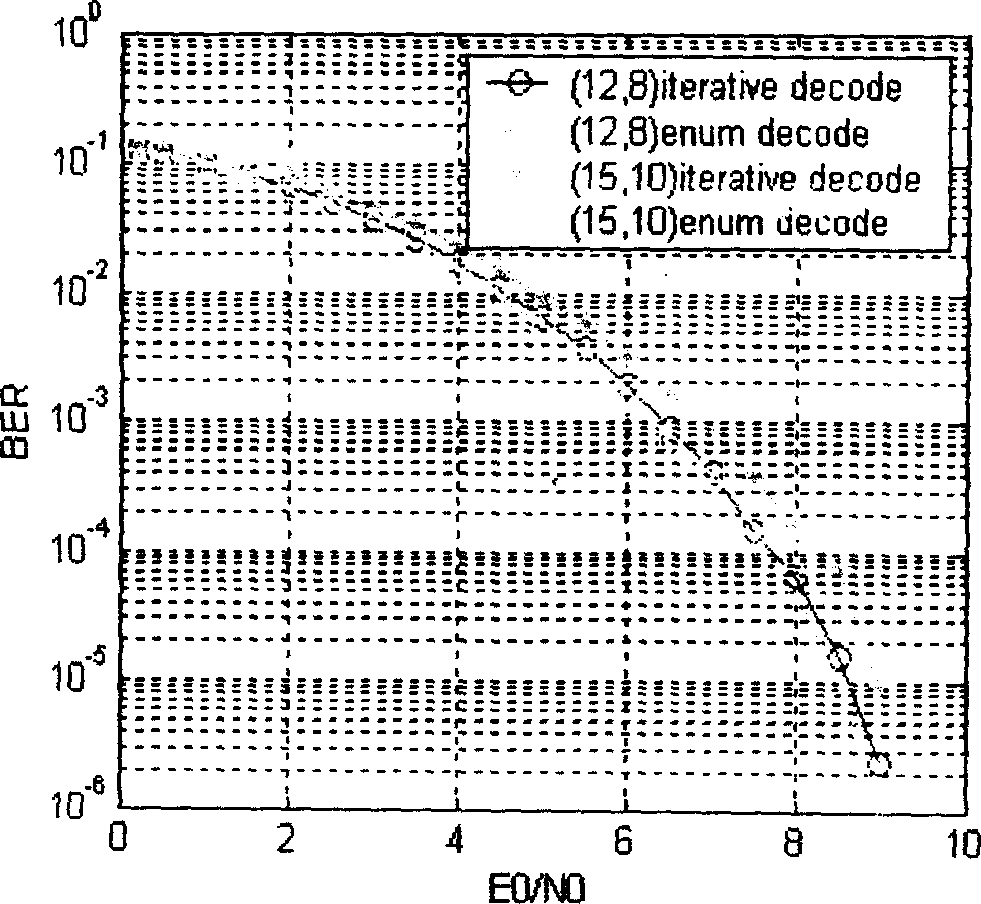
[0045] A concrete example of realizing the sum-product algorithm under the AWGN channel with the (7,4) Hamming code modulated by BPSK is given below.
[0046] 1. Encoding of (7,4) Hamming code.
[0047] Convert the parity check matrix H of the (7,4) Hamming code into a generator matrix G. Put the information source through the generating matrix G
[0048] put m i encode into c i .
[0049] 2. BPSK modulation
[0050] put c i (0 or) modulated to ±1 by BPSK, ie x i .
[0051] 3. Channel
[0052] Modulated baseband signal x i Through the AWGN channel, add Gaussian noise.
[0053] 4. Receive
[0054] received y i Thereafter, iterative decoding using the sum-product algorithm of the Hamming code is performed.
[0055] 5. Decoding steps
[0056] Given the bilateral graph of (7,4) Hamming code as Figure 5 , where f refers to the checkpoint and x refers to the variable point. Received codeword y i =x i +n i , where n i ~N(0,σ 2 ), satisfying a Gaussian distributi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com