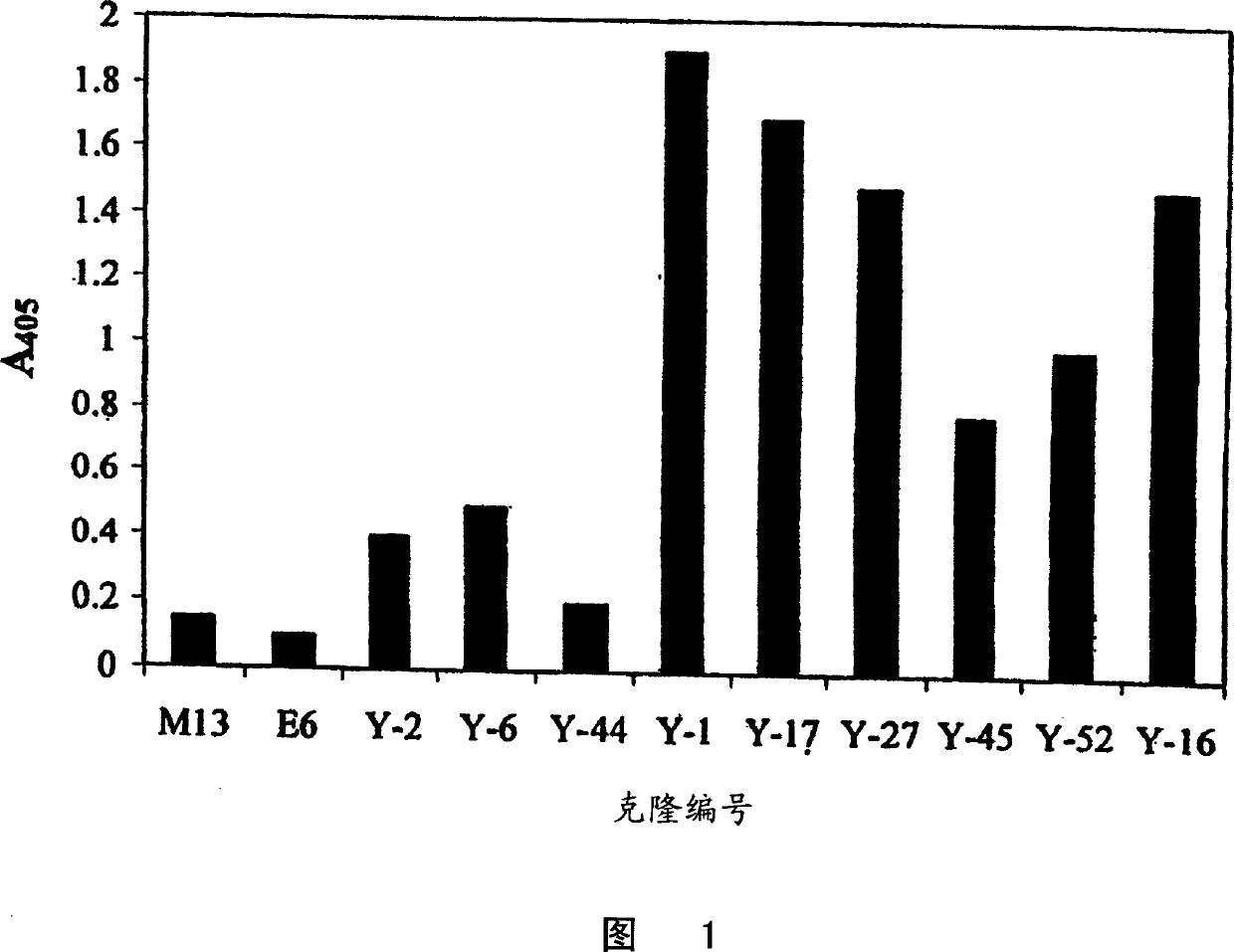
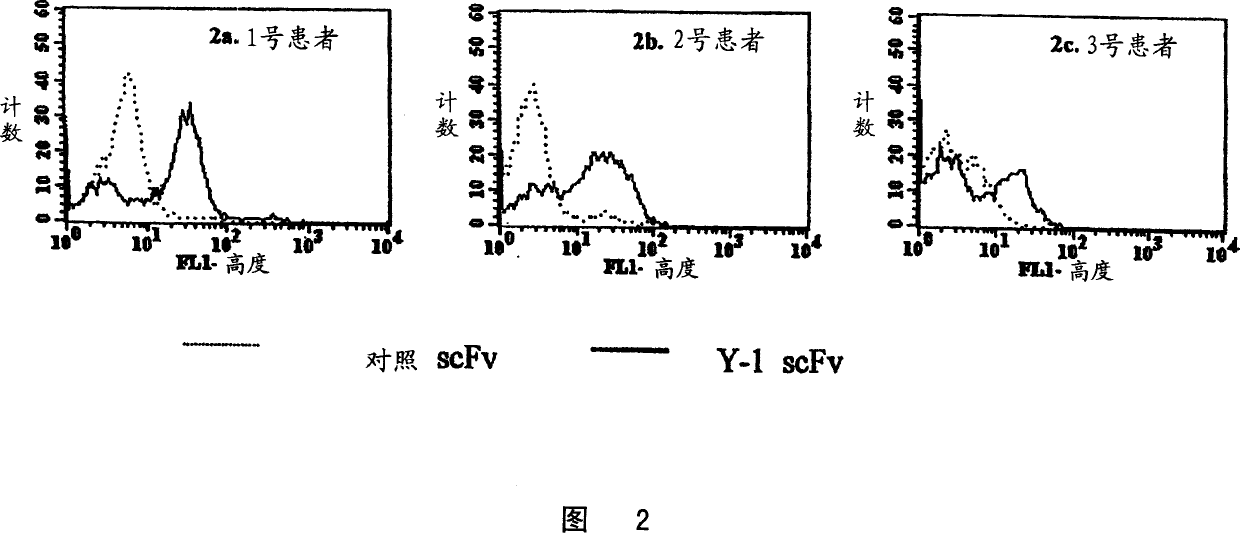
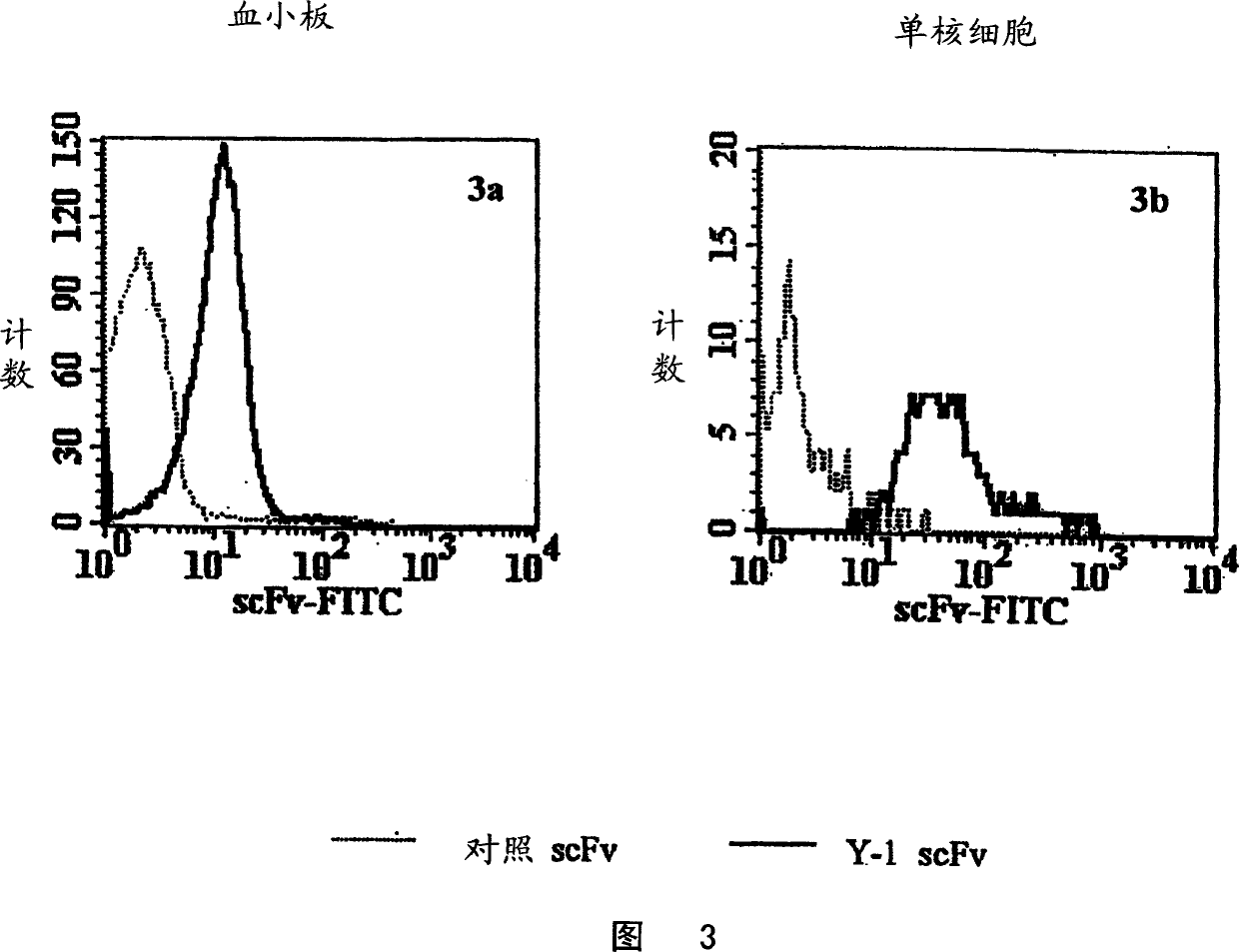
Specific human antibodies for selective cancer therapy
A selective and specific technology, applied in the field of peptides and polypeptides, can solve problems such as difficult separation, hindering repeated treatment, and reducing the therapeutic value of antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0336] 1. Preparation and protein purification of cells, bacterial strains, scFv phage display libraries, cell membranes for biopanning methods.
[0337] 1.1 Preparation of leukemia cells. Blood samples were obtained from leukemia patients. Monocytes (primary cells) were separated from other blood cells on Ficoll mats (Iso-prep, Robbins Scientific Corp., Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Centrifuge at 110 x g for 25 minutes. Cells at the interface were collected and washed twice with PBS. Cells were then suspended in RPMI+10% fetal calf serum (FCS) and counted. For long-term storage, 10% FCS and 10% DMSO were added to the lymphocytes and then frozen at -70°C.
[0338] 1.2 Preparation of fixed platelets. Platelet concentrates obtained from blood banks were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C. An equal volume of 2.0% paraformaldehyde was added and platelets were fixed at 40°C for 18 hours. Platelets were washed twice with cold saline (centrifuged at 2500 xg for 10 minutes). Resuspended in s...
Embodiment 2
[0344] 2. Manipulation of Phagemid Particles: Biopanning Method
[0345] 2.1 Phagemid screening and amplification: through a four-step biopanning method, the library is screened for phagemids expressing epitopes of particular interest:
[0346] a) binding phagemid particles to a target site, more specifically, binding said phagemid particles to washed target cells or cell membranes
[0347] b) Removal of unbound phagemid particles, more specifically, removal of unbound phagemid particles by extensive washing
[0348] c) Elution of bound phagemid particles
[0349] d) Propagation and amplification of eluted phagemid particles, more specifically, propagation and amplification in E. coli
[0350] 2.2 Cloning identification: The biopanning method of the four steps was basically repeated 3-5 times. Selected phagemid clones were propagated individually and further characterized by:
[0351] a) DNA sequencing
[0352] b) Ex vivo comparison of phage binding to several cell types ...
Embodiment 3
[0356] 3. Biopanning method
[0357] 3.1 Basic biopanning method: The biopanning method is an integral part of the above-mentioned phage display technology. Three biopanning methods were developed and employed in this study:
[0358] a) Method AM (AML membrane panning / bacterial elution followed by intact AML cell panning / trypsin elution)
[0359] b) Method YPR (Fixed Human Platelet Panning / Acid Elution)
[0360] c) Method YPNR (Fixed Human Platelet Panning / Acid Elution)
[0361] The above method is disclosed in detail below
[0362] 3.1.1 Method AM
[0363] 3.1.1.1 Pre-wash: Quickly thaw at 37°C containing 2×10 7 A 1 ml aliquot of frozen AML cells was diluted immediately into 10 ml of cold 2% PBS-milk (MPBS). Cells were centrifuged at 120 xg for 5 minutes at room temperature (RT), resuspended in MPBS, and counted with a hemocytometer. Prepare cell membranes as described in section 1.5.
[0364] 3.1.1.2 Selection was made by adding 2ml containing 10 12 Phagemid MPBS wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com