Sawdust alkaline pulp having low average degree of polymerization values and method of producing the same
一种平均聚合度、碱法浆粕的技术,应用在用无机碱制浆、熔融纺法、纸浆漂白等方向,能够解决机会难得等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
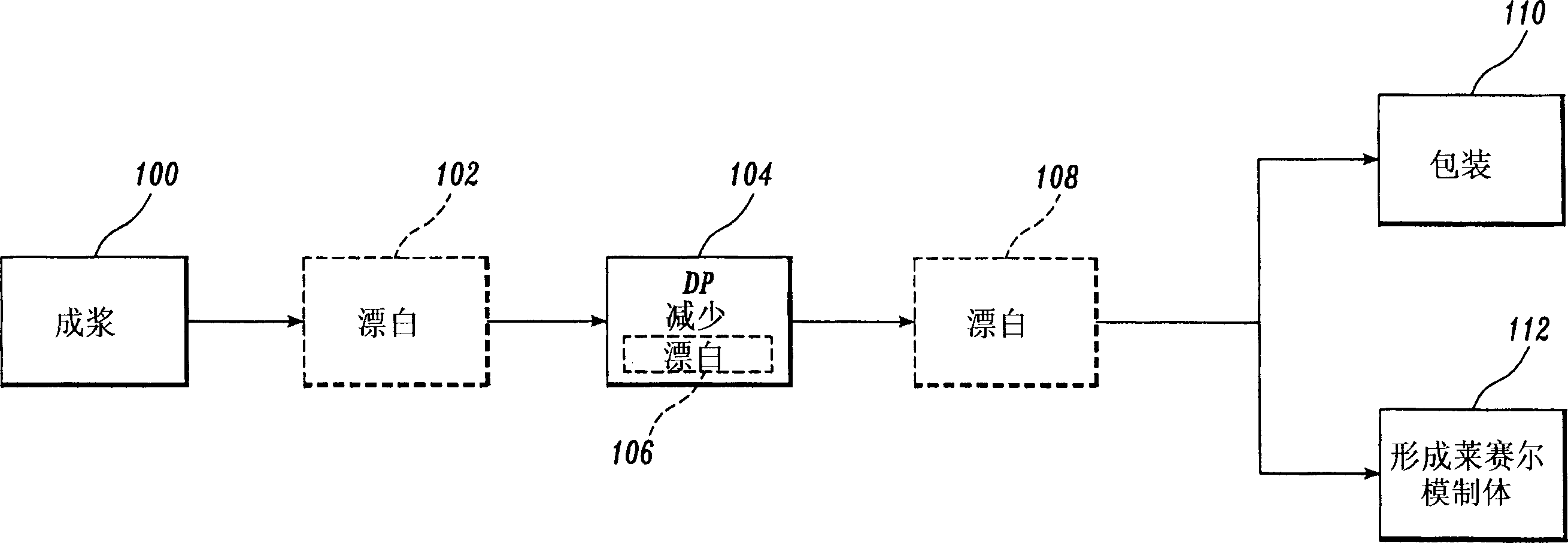
[0104] Brown finished wood pulp was produced in an industrial scale M&D digester, which was cooked at about 182°C and had an average residence time in the digester of about 60 minutes. White liquor is used as the cooking liquid for the digester. The white liquor has the equivalent of Na 2 115.2 g total titratable base (TTA) per liter of O, equivalent to Na 2 99.2 grams of active alkali (AA) per liter of O, equivalent to Na 2 O has 81.6 grams of effective base (EA) per liter. The degree of sulfidation of the white liquor is 28% TTA. The white liquor specific gravity is 1.15.
[0105] The unbleached alkaline kraft pulp (main wood species is redwood, spruce and black pine) of the northern conifer sawdust prepared under the above-mentioned conditions has a kappa value of 21.0 ((TAPPI standard T236cm-85, viscosity 110cp( TAPPI T230) (D.P.1264), copper value 0.6, hemicellulose content 14.1% ± 1.5%, the pulp was treated with chlorine dioxide in the first D stage.
[0106] D1 ...
Embodiment 2
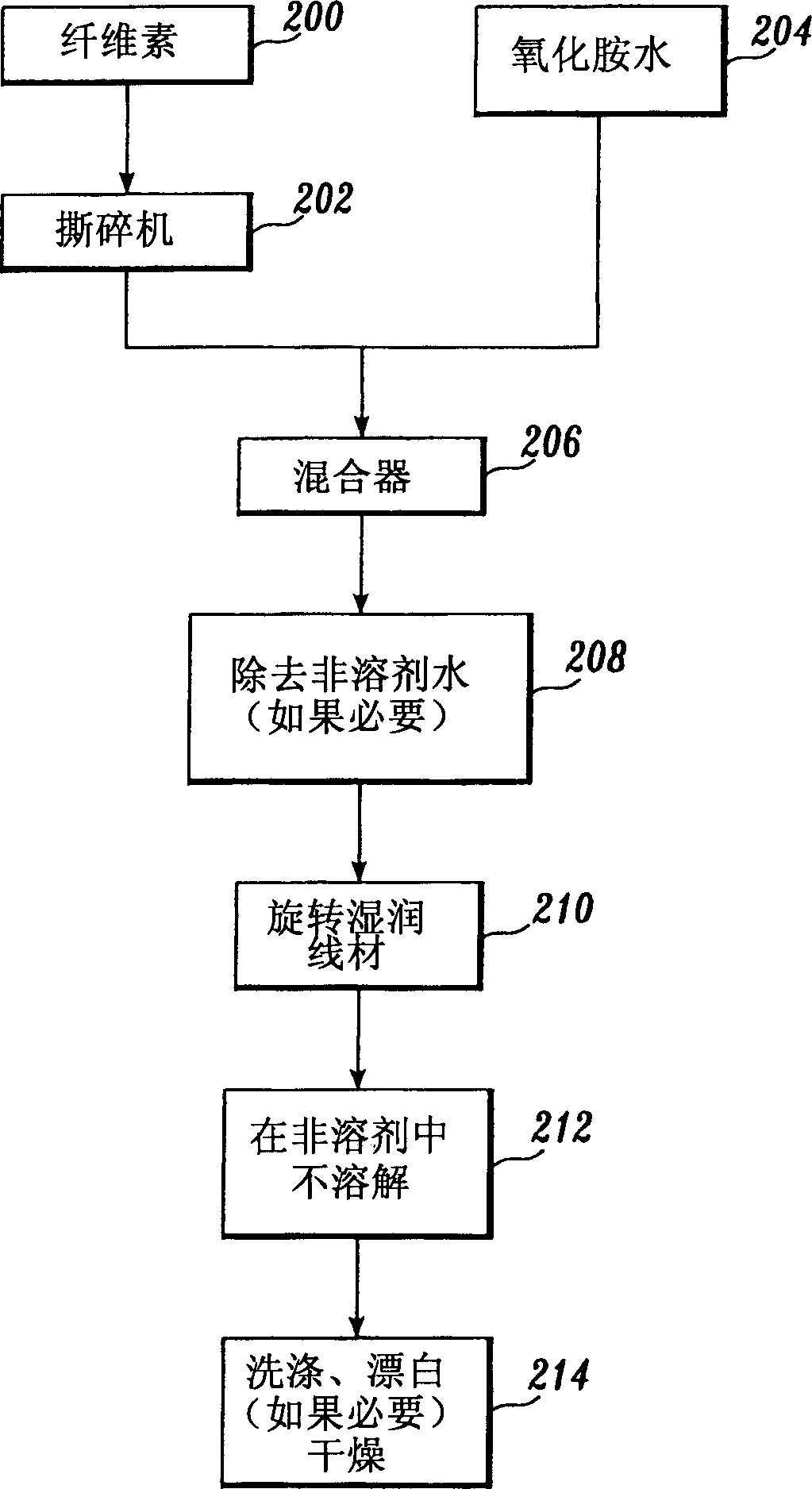
[0116] NMMO monohydrate dissolution test
[0117] In the first dissolution test, NMMO monohydrate pulp samples produced according to Application No. 09 / 574,538 and the present invention were mixed with N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate to obtain two independent mixture. Each individual mixture was then heated to 85°C using an electric furnace. The dissolution process of fibers in NMMO monohydrate was observed using an 88× optical magnification microscope. A camera was attached to the microscope and individual fibers were photographed when the mixture reached 85°C. Figure 3 is a micrograph of fibers produced in accordance with Application No. 09 / 574,538 in solvent. Figure 5 is a micrograph of fibers produced in accordance with the present invention in solvent. Photos are taken at 30 second intervals. Figure 4 is a micrograph of the fiber of the prior application '538 after about 2 minutes. Figure 6 is a micrograph of fibers produced in accordance with the present i...
Embodiment 3
[0119] dry jet wet spun fiber
[0120] Pulp made according to the present invention can be prepared as a dope sample by dissolving the treated pulp in NMMO. The dope was spun into lyocell fibers by a dry jet wet spinning process as described in US Pat. No. 5,417,909, incorporated herein by reference. Dry jet wet spinning process by TITK. The properties of fibers prepared by dry-jet wet spinning of spinning dope samples according to the present invention are summarized in Table 1. Table 2 shows control lyocell fibers prepared from pulp by the process of application No. 09 / 574,538, also using dry jet wet spinning. The difference between Table 1 and Table 2 is at least the raw materials used in the process.
[0121] A second dissolution test was performed on the pulp samples in Tables 1 and 2 used to make lyocell fibers. The pulp was separately dissolved in NMMO at 80°C to 100°C without any stirring to obtain a 0.6% cellulose solution. The time for complete dissolution was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com