[0003] 1. Fusion welding method: Fusion welding is one of the most common welding methods for joining metal materials, but when it is applied to the welding of aluminum matrix composite materials, it faces some urgent problems to be solved as follows: (1) Physical Compatibility Issues: Partially Solid SiC or Al in Liquid Melt Pool 2 o 3 It seriously affects the heat transfer and mass transfer process in the molten pool, so that the molten pool exhibits high viscosity, poor flow, and high sensitivity to defects such as pores, incomplete fusion, and incomplete penetration; the molten aluminum matrix composite material and the applied Filling materials are difficult to mix, the dilution rate is low, and forming is difficult; at the same time, the segregation of the reinforcing phase when the liquid metal solidifies destroys its original distribution characteristics and deteriorates the performance of the joint; in addition, when the linear expansion coefficient of the reinforcing phase and the matrix differs greatly , a large internal stress will remain in the joint during the heating and cooling process of welding
(2) Chemical compatibility problem: Some reinforcing phases (such as SiC) and the matrix Al are thermodynamically unstable in a large temperature range, and harmful interfacial reactions at high temperatures in welding are inevitable
In recent years, there have been few studies on this method, and the main problem is that the strength of the joint is limited by the solder, and the strength is low
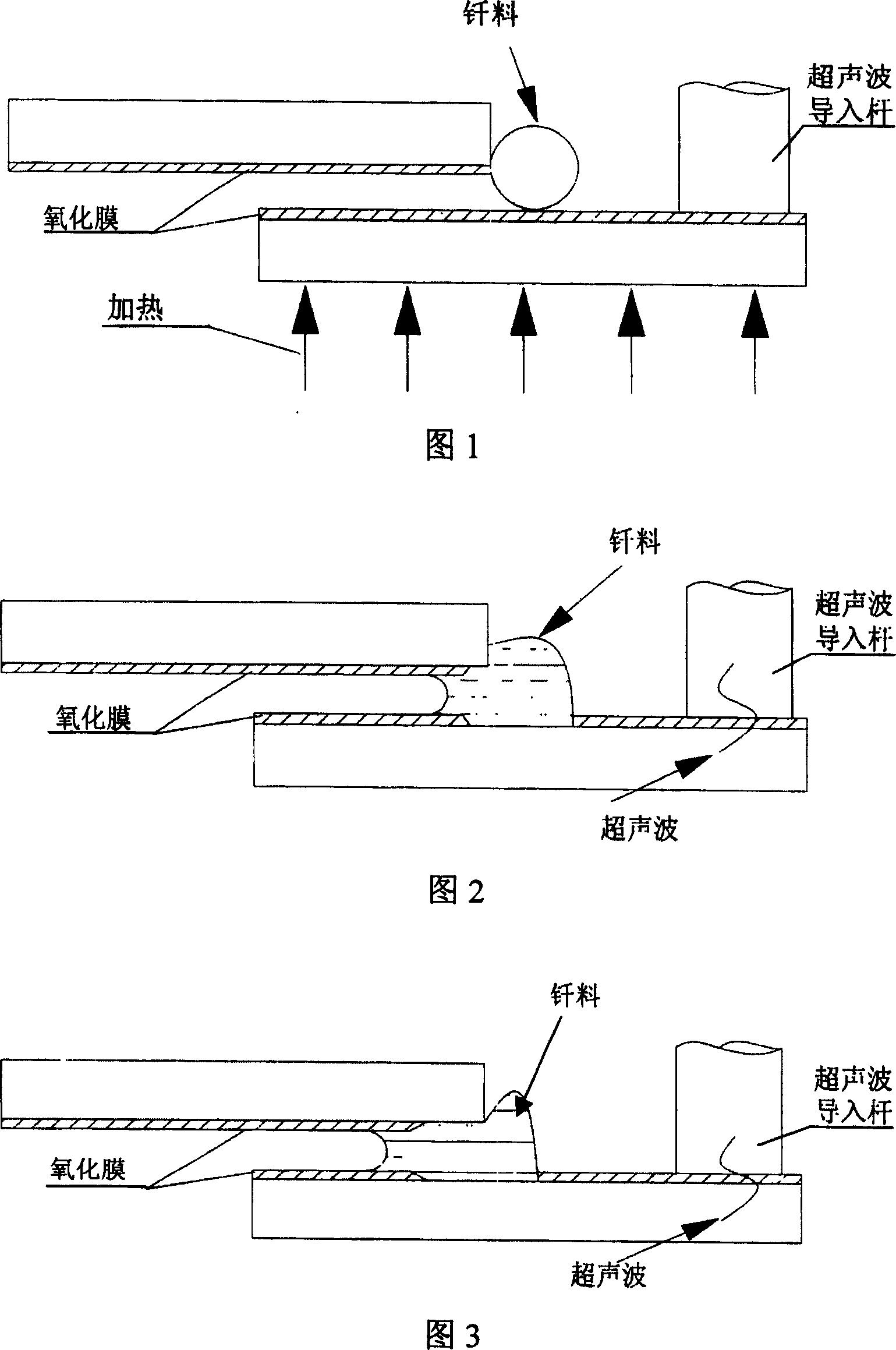
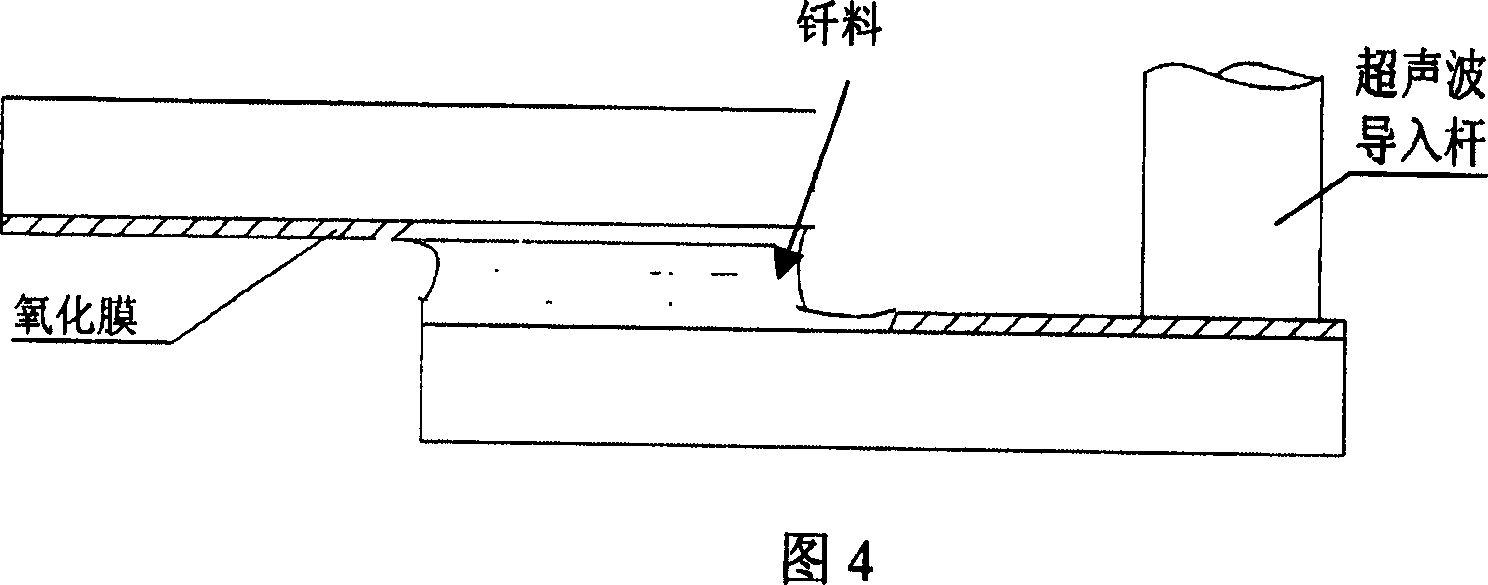
For the welding of aluminum matrix composite materials, the brazing method has the following problems: (1) The oxide film on the surface of aluminum matrix composite materials seriously affects the welding quality
If flux is used to remove the oxide film, there must be a subsequent cleaning process to avoid corrosion problems caused by residual flux, and the welding process is cumbersome
(2) Improper control of the welding process will lead to excessive melting of the matrix, and the weld area is prone to appear reinforced phase segregation areas and non-enhanced phase areas, and the joint performance is uneven, and inconsistent with the original special structure and special properties of the base metal
This is not suitable for occasions with special performance requirements for joints, such as joints that need to maintain good anti-damping characteristics and dimensional stability, etc.
(3) The melting points of the aluminum alloy matrix and the reinforcement phase are very different. At the brazing temperature, the matrix part melts, but the reinforcement does not melt, resulting in stickiness of the brazing filler metal, poor fluidity, and wetting of the brazing filler metal on the base metal. Spreading is seriously hindered by the presence of solid reinforcement phase, adding some alloying elements and increasing the brazing temperature can be improved to some extent, but the temperature is too high and it is easy to cause overburning and erosion of the base metal, which brings a negative impact on the brazing process. come very difficult
[0006] 4. Friction welding method: During the friction welding process, large plastic deformation occurs at the joint, which will lead to severe fracture of the fiber, so it is not suitable to weld continuous reinforced aluminum matrix composites by this method
However, when using diffusion welding aluminum matrix composites, the same difficulties are encountered as when diffusion welding aluminum
There are the following main problems in diffusion welding of aluminum matrix composites: (1) There is a dense oxide film on the surface of aluminum matrix composites, which seriously hinders the diffusion bonding between the two connected surfaces
(2) In the absence of an intermediate layer, there is a phenomenon of direct contact between the reinforcement phase and the reinforcement phase on the contact surface of the aluminum matrix composite material, and it is difficult to achieve the diffusion connection between the reinforcement phases under the conditions of diffusion welding
While instantaneous liquid phase welding has more advantages, it also has some disadvantages: (1) The segregation of the reinforcing phase becomes the main problem of TLP welding of this material
Many scholars at home and abroad solve this problem by choosing a thinner intermediate foil layer, but this method requires high surface roughness to be welded and needs to be carried out in a vacuum environment. more difficult
(2) The instantaneous liquid phase welding temperature generally exceeds 550°C. At this temperature, the base metal will soften to varying degrees, which is a challenge for the composite material matrix
However, at present, a large number of welding work of aluminum matrix composite materials is still carried out in the laboratory, and further efforts are still needed for the TLP welding process with more application significance.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More