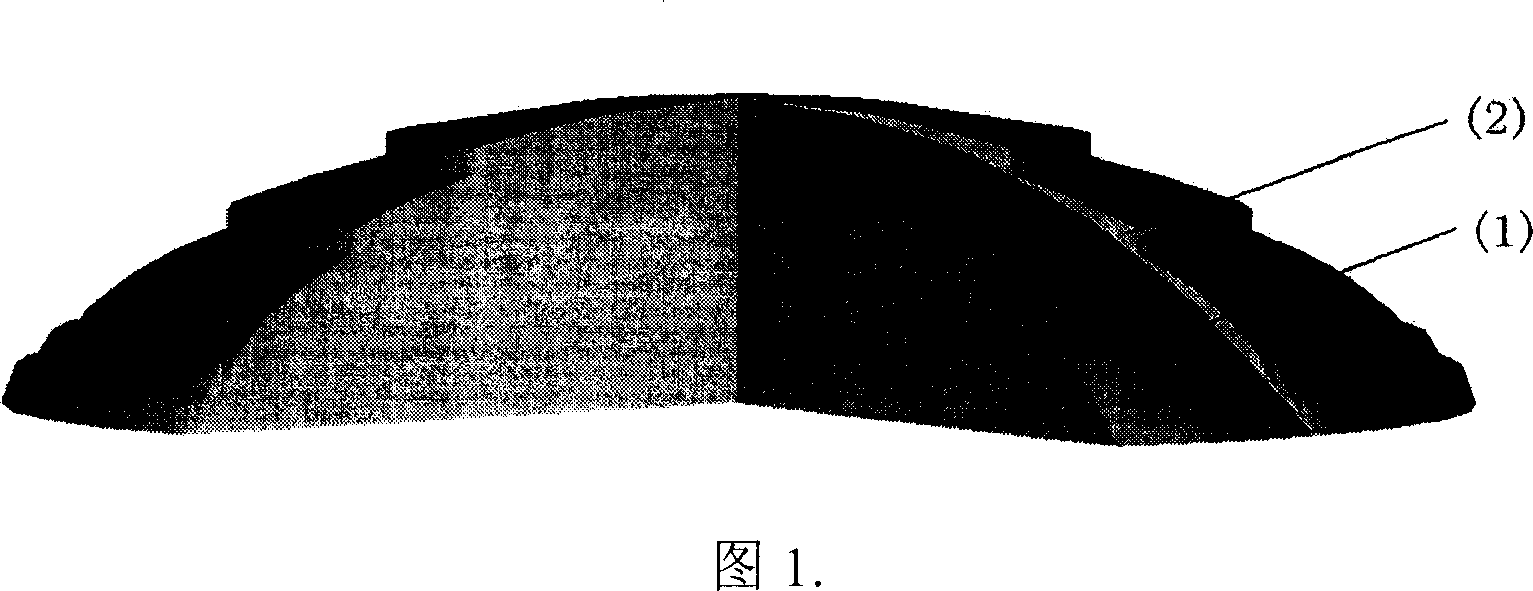
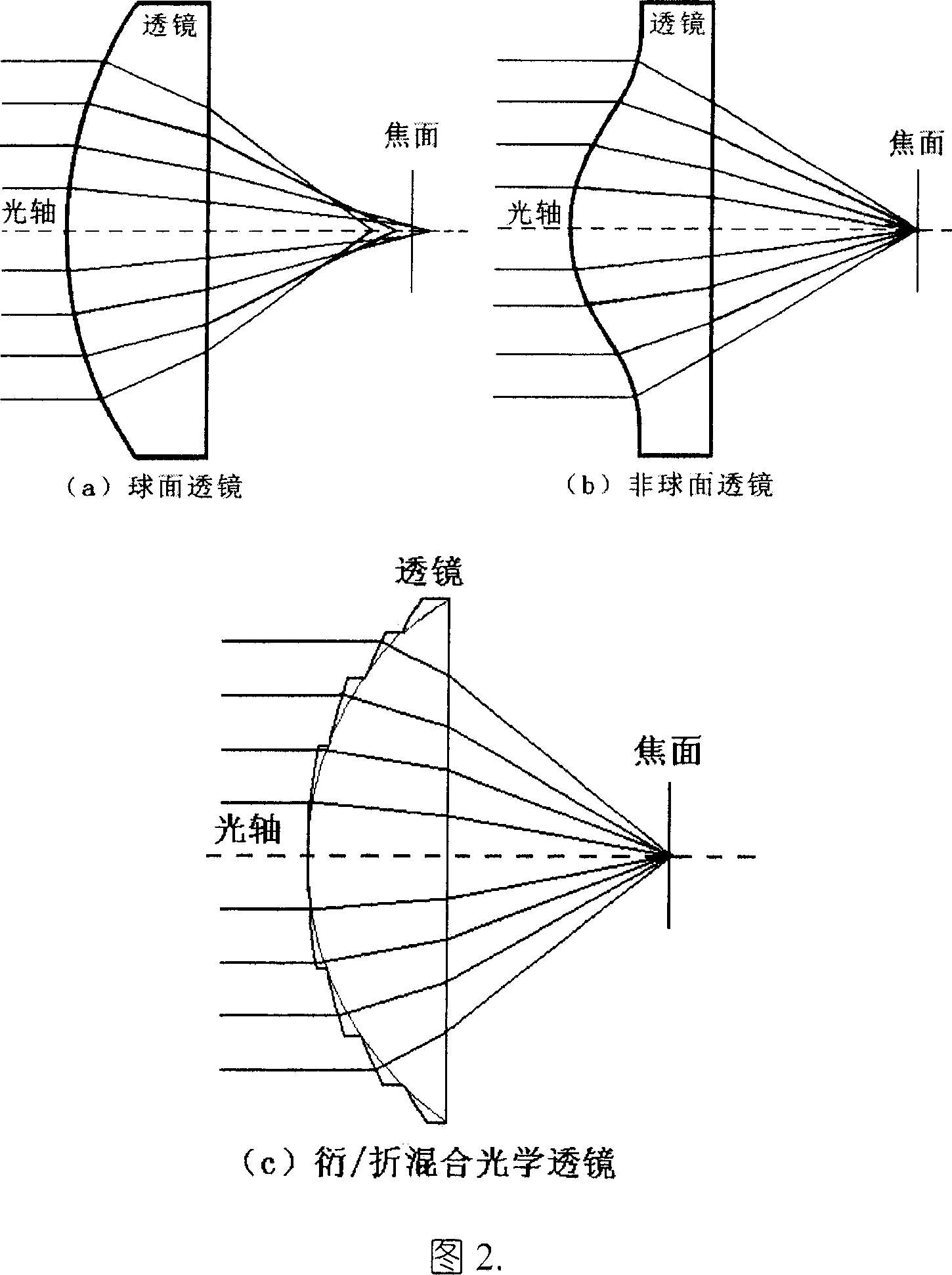
Diffractive and refractive mixed optical element for providing aspherical degree and design method thereof
A technology of diffractive optical elements and optical elements, which is applied in the direction of optical elements, optics, lenses, etc., can solve the problems of multiple structural periods, narrowing range, and small minimum period intervals, etc., and achieves expanded application range, convenient and reliable degrees of freedom, and high Effect of Surface Accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Fig. 6 is an example of replacing the laser beam collimating aspheric lens with a diffractive / refractive hybrid optical element composed of a spherical substrate combined with a binary microstructure surface. The structural parameters of this aspheric surface are: curvature c=0.5483, quadric surface coefficient k=0, high-order aspheric surface coefficient α 2 =-0.0114, α 3 =-0.0036, after calculation, when the aspheric surface is replaced by a diffractive / refractive hybrid optical element composed of a spherical base binary microstructure surface, the structural parameters of the optimal spherical base and the binary microstructure diffractive optical element are: the optimal spherical curvature c 0 =0.5051, the surface period of the binary microstructure is 27, and the intervals between three consecutive minimum periods are: 24 μm, 22 μm and 21 μm. Considering that there may be non-periodic rings on the edge or in the middle, the design program lists three consecutiv...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Fig. 7 shows an example of using a diffractive / refractive hybrid optical element composed of a spherical substrate combined with a binary microstructure surface to replace a large aspheric surface in an optical system with an aperture of Φ=90mm. The asphericity of this aspheric surface is relatively large, and it is a high-order aspheric surface, with a curvature c=0.007612, a quadratic surface coefficient k=-5.463953, and a high-order aspheric surface coefficient α 2 = 1.3416435e -7 , α 3 =-4.2867228e -11 . The calculated structural parameters of the optimal spherical substrate and the binary microstructured diffractive optical element are: equivalent spherical curvature c 0 =0.006835, the surface period of the binary microstructure is 483, and the intervals of three consecutive minimum periods are: 22μm, 21μm and 20μm, which are also within the micromachinable range, so as long as the appropriate optimal spherical substrate is selected, most All aspheric surfaces ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com