Degradation bacteria for highly effective degrading organophosphorus pesticide and its use
A technology for organophosphorus pesticides and degrading bacteria, applied in the field of degrading bacteria, can solve problems such as high cost and slow action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1: Degradation of methyl parathion using bacterial strain B2
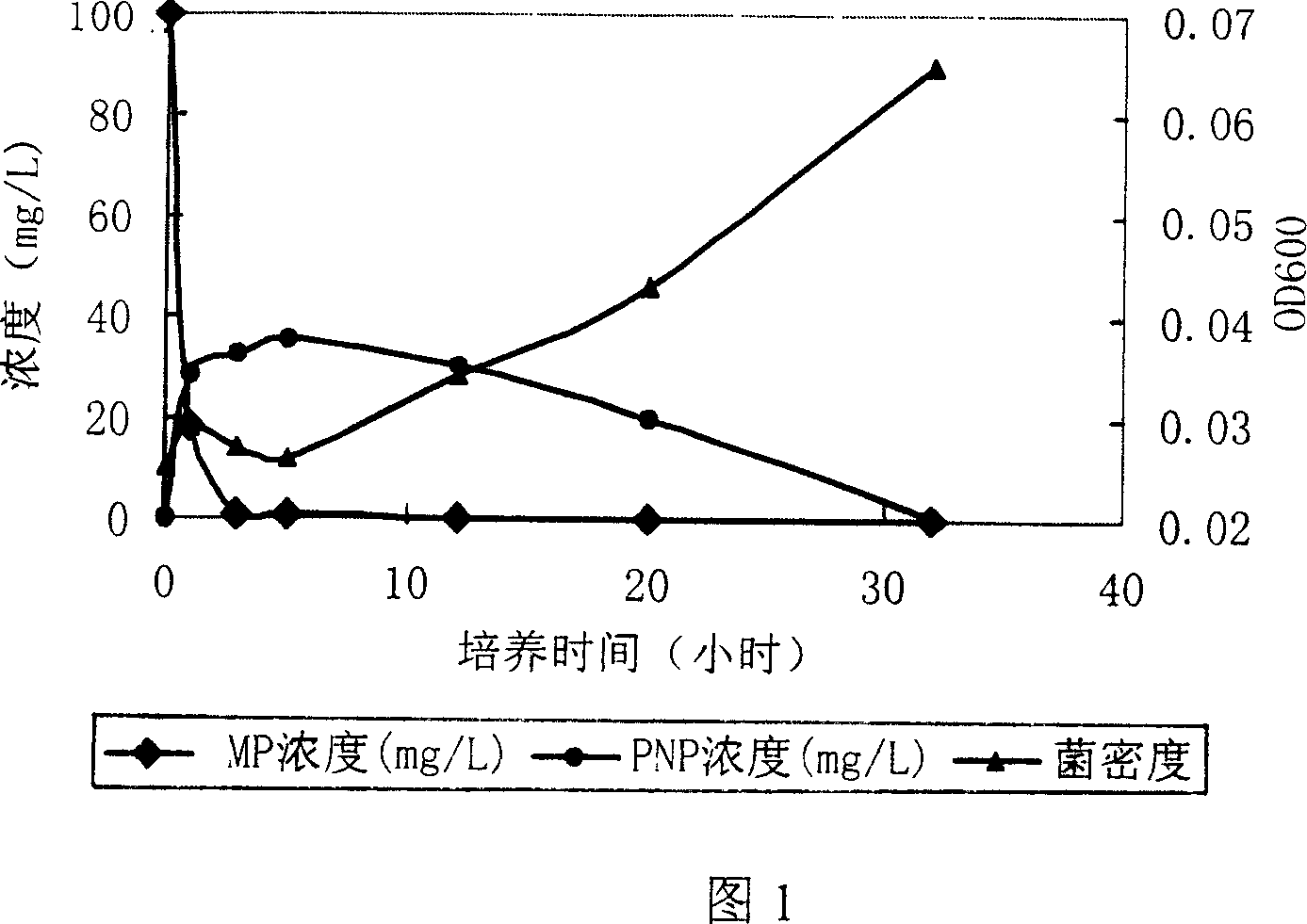
[0061] The degradation rate of MP by strain B2 was determined by gas chromatography, and the production and degradation of the intermediate p-nitrophenol was measured by a spectrophotometer, as well as the growth of the strain using MP as a carbon source (see Figure 1).
[0062] During the cultivation process, the strain B2 could rapidly degrade MP. After 3 hours of cultivation, the concentration of MP dropped from the initial 100mg / L to 0.805mg / L, while the bacterial concentration hardly increased during this period. With the reduction of methyl parathion, the concentration of its degradation intermediate p-nitrophenol increased. After a period of time, the concentration of p-nitrophenol began to decrease, and it was completely degraded after 32 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: Bacterial strain B2 takes p-nitrophenol (PNP) as carbon source growth and its degradation to PNP:
[0064] Strain B2 was induced and cultivated with 50mg / L PNP first, and then inserted into the inorganic salt with 50mg / L PNP as carbon source to detect its growth and PNP degradation. As can be seen from Figure 2, strain B2 can grow with PNP as a carbon source and degrade PNP at the same time. When the concentration of PNP is 50mg / L, the lag period of bacterial strain growth is less than 4 hours, and bacterial strain B2 reaches growth after 24 hours of cultivation. Peak, with the increase of bacterial density, the amount of PNP is decreasing, and within 48 hours, bacterial strain B2 completely degrades 50mg / L of PNP. In the first 8 hours of culture, the concentration of PNP decreased slowly, and then the degradation rate accelerated, which may be due to the induction of enzymes that degrade PNP after a period of culture, thereby accelerating the degradation ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Bacterial strain B2 grows with p-nitrocatechol (4-NC) as carbon source and its degradation effect on 4-NC
[0066] Insert 1ml of B2 seed solution into the inorganic salt medium containing different concentrations of 4-NC, the concentrations are 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 mg / L, respectively, and measure the disappearance of brown 4-NC. After culturing for 3 days, it was found that 10, 20, and 30 mg / L 4-NC culture fluids became colorless, while in 40, 50 mg / L 4-NC culture fluids, the concentration of 4-NC did not change. Therefore, we choose the highest concentration that does not inhibit the metabolism of 4-NC by the strain, that is, 30mg / L as the test concentration, and measure the growth of the strain B2 in the medium with 30mg / L 4-NC as the carbon source and the degradation of the 4-NC by the strain. case, the results are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen from the figure that the growth of bacterial strain B2 goes through a period of lag phase (12h), and during th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com