Improved polymer blends for dewatering
A technology of polymers and blends, applied in the field of polymer flocculants for the introduction of suspended solids and the manufacture of the composition, can solve the problems of high dosage, the inability of linear polymer flocculants to achieve flocculation characteristics, and increasing environmental burdens.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Preparation of Structured AMD-AETAC Copolymer Emulsions
[0090] This example describes the preparation of acrylamide (AMD) (60 mole %) and dimethylaminoethyl acrylate, methyl chloride, using N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide crosslinker and isopropanol chain transfer agent Inverse emulsion of structured cationic copolymer of quaternary salt (AETAC) (40 mole %).
[0091] Prepare the water phase by mixing the following ingredients together:
[0092] Acrylamide (50% aqueous solution) 210.00 grams
[0093] Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate, methyl chloride quaternary salt (80% solution) 238.74
[0094] Deionized water 120.00
[0095] Citric acid (anhydrous) 17.76
[0096] Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, pentasodium salt (40%) 0.74
[0097] Isopropanol 2.16*
[0098] N,N'-Methylenebisacrylamide 0.0030**
[0100] *Equivalent to 0.73% by weight on a monomer basis
[0101] **Equivalent to 10ppm on a monomer basis
[0102] Adjust the pH to 3.5 us...
Embodiment 2-6
[0108] Additional copolymers of AMD and AETAC were prepared following the general procedure described in Example 1, using different relative amounts of comonomer and different amounts of MBA crosslinker, or without any crosslinker. The composition and properties of the resulting linear (Examples 5 and 6) or structured (Examples 2-4) cationic copolymers are listed in Table I below.
[0109] Example
serial number
in copolymer
AETAC's
mol%
chain transfer agent
(wt%)
crosslinking agent
SV
(cps)
SED%
0.001M
NaCl
SED%
1.0M
NaCl
1
40
IPA 0.73%
MBA 10ppm
3.0
2
18
2
35
LA 0.3%
MBA 20ppm
1.9
0
40
3
55
IPA 0.52%
MBA 8ppm
3.0
0
24
4
55
LA 0.2%
MBA 30ppm
1.7
7
63
5
40
IPA 0.64%
non...
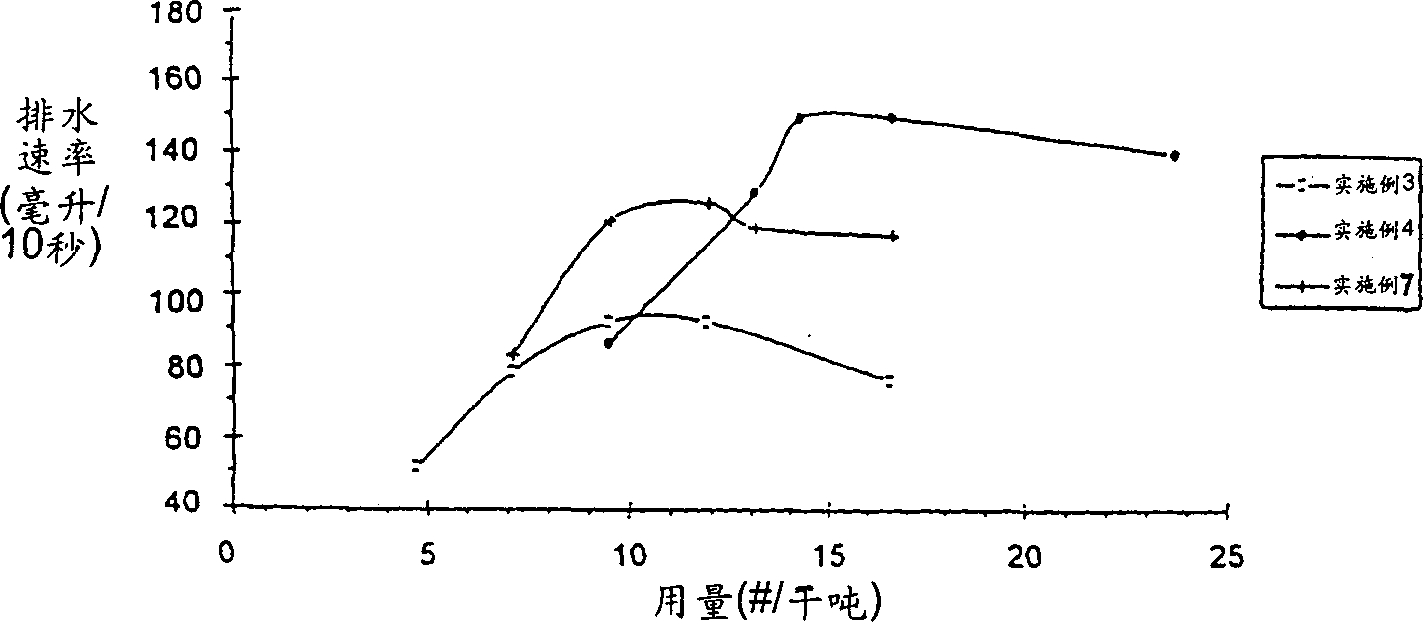
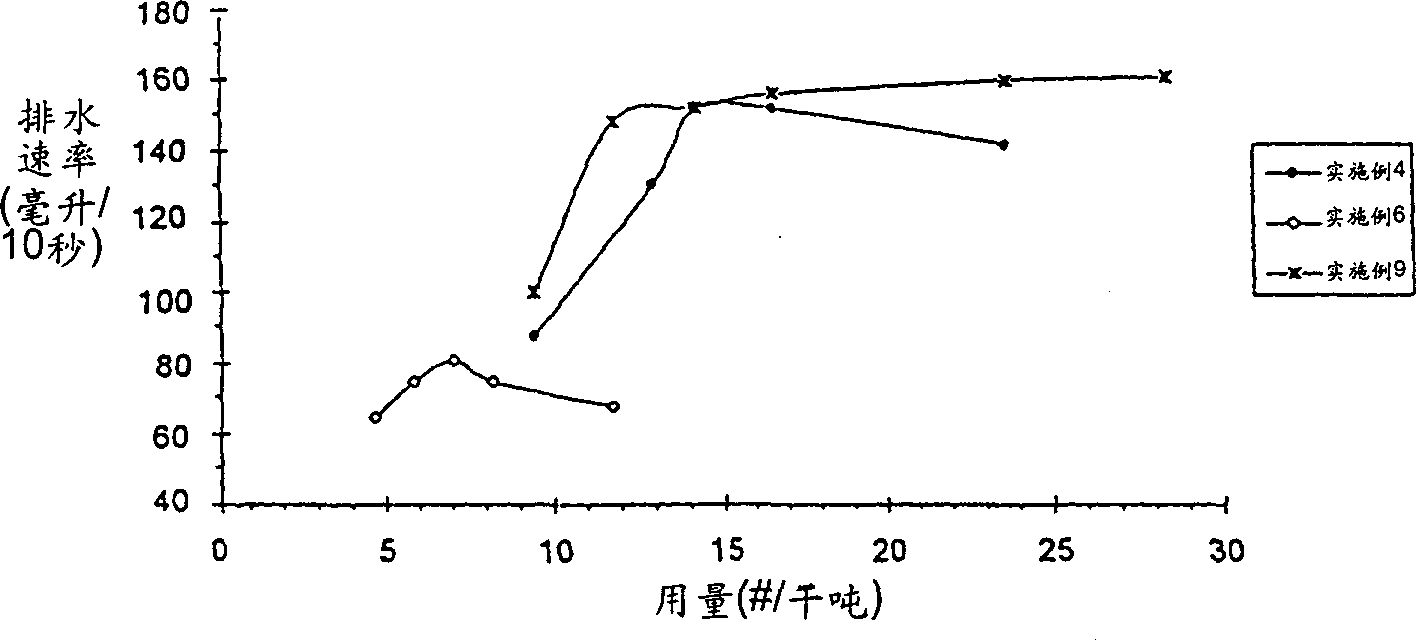
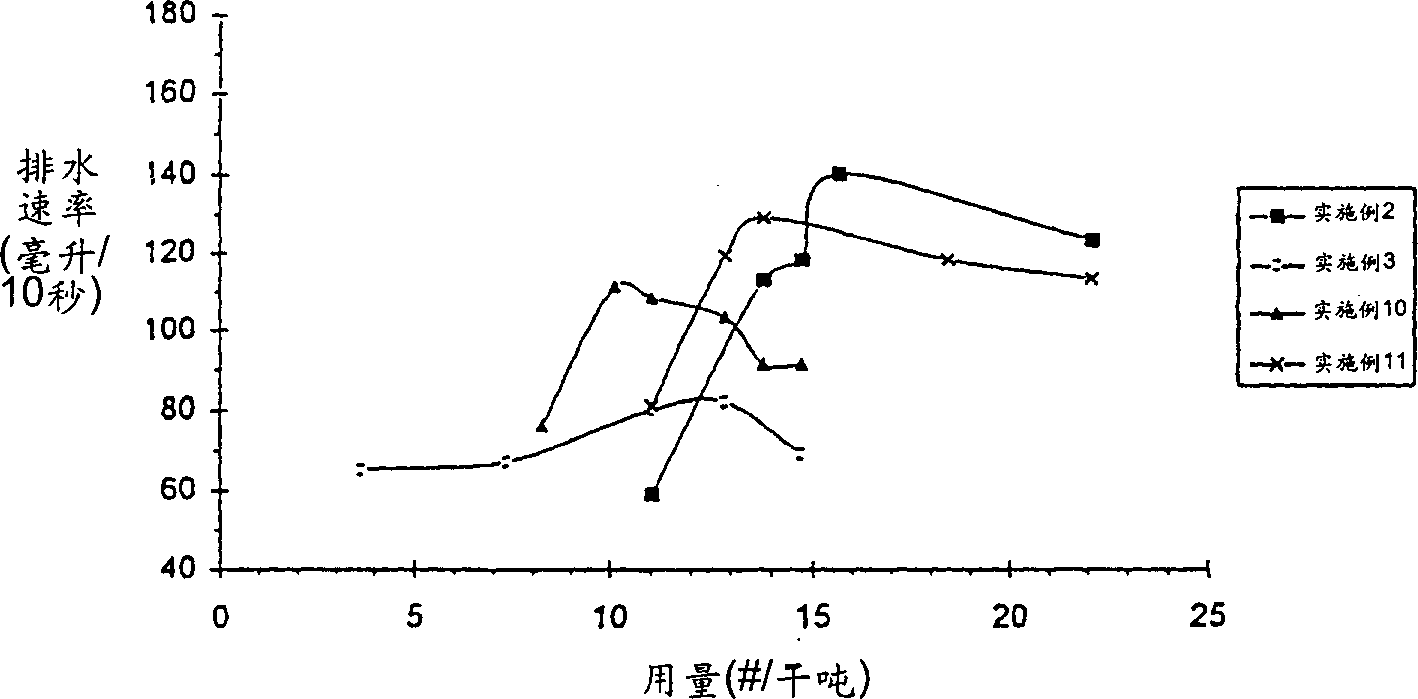
Embodiment 7-12
[0120] Preparation of linear or blends of less structured polymers and higher structured polymers
[0121] Using the polymer emulsions of Examples 1-6, six polymer blends were prepared by mechanically mixing the emulsions.
[0122] Mixing is accomplished by weighing the appropriate amount of polymer emulsion to be blended in a glass bottle, making sure that the bottle is about 1 / 4-1 / 3 empty for proper mixing. The capped bottle was then tumbled for approximately 1 hour to ensure thorough mixing was verified visually.
[0123] The compositions and SED values of the resulting blends are listed in Table II below.
[0124] Example
serial number
Blend type
Component 1 / Component 2
polymer
component 1
polymer
component 2
SED
0.001M NaCl
SED
1.0M NaCl
7
Structured /
Structured
Example 4
50wt%
Example 3
50wt%
4
44
8
Structured /
Structured
Examp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com