Method, probe and kit for identifying human embryo bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and application of method, probe and kit
A bone marrow-derived, mesenchymal stem cell technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of DNA methylation differences in cells and MSCs that cannot truly reflect the functions in vivo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
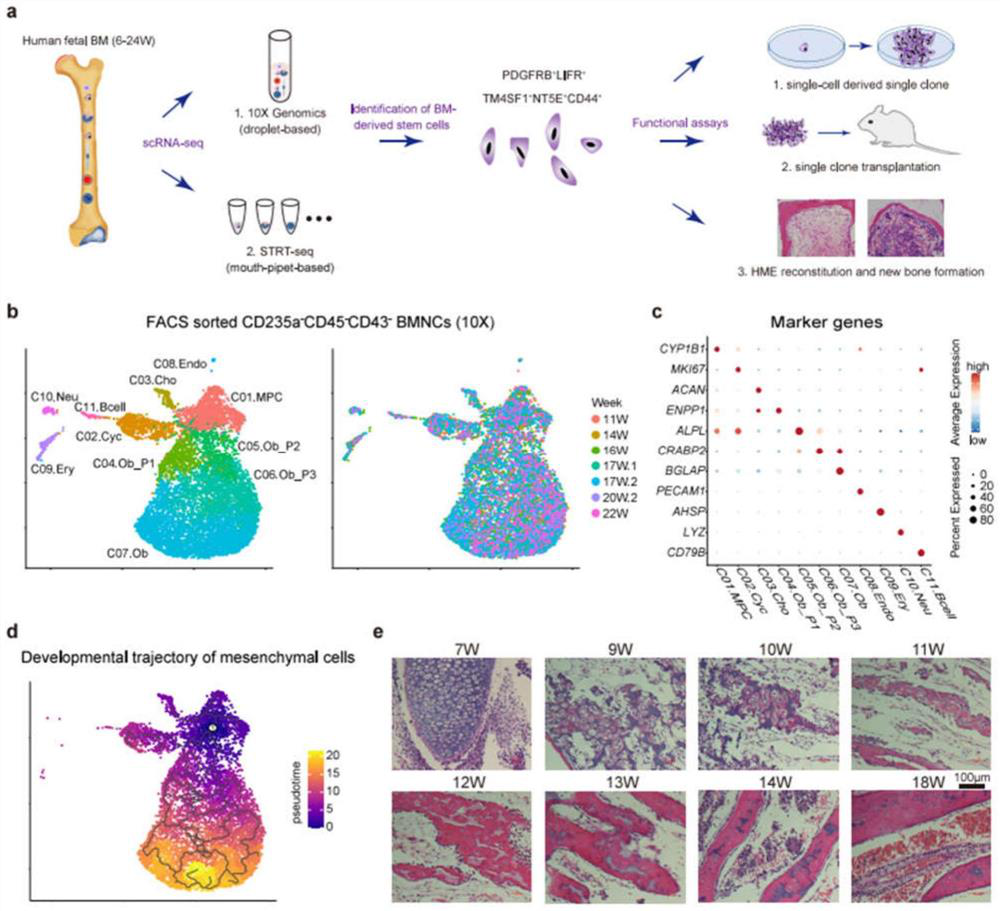
[0072] Example 1 - Human Embryonic Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Expression Profile
[0073] To explore the diversity of human embryonic BM stromal cells, the inventors performed single-cell transcriptome analysis of BMNCs using 10X genomics and scRNA-seq technology.
[0074] Since the BM is full of red blood cells, the inventors used ice-cold sterile water to lyse the red blood cells 18 . To test the feasibility of the experimental protocol, 2,634 quality-controlled single cells derived from two embryos (ie: 20 and 21 weeks old) were obtained. The nucleated cells derived from human embryonic bone marrow used in the present invention were obtained from the Third Hospital of Peking University.
[0075] The results show that the inventors identified 12 clusters with batch effect correction in Harmony and unsupervised clusters in Seurat ( Figure 7 A) 19,20 . These clusters are annotated according to classical marker genes: two erythrocyte subsets (specifically expressing GYPA ...
Embodiment 2
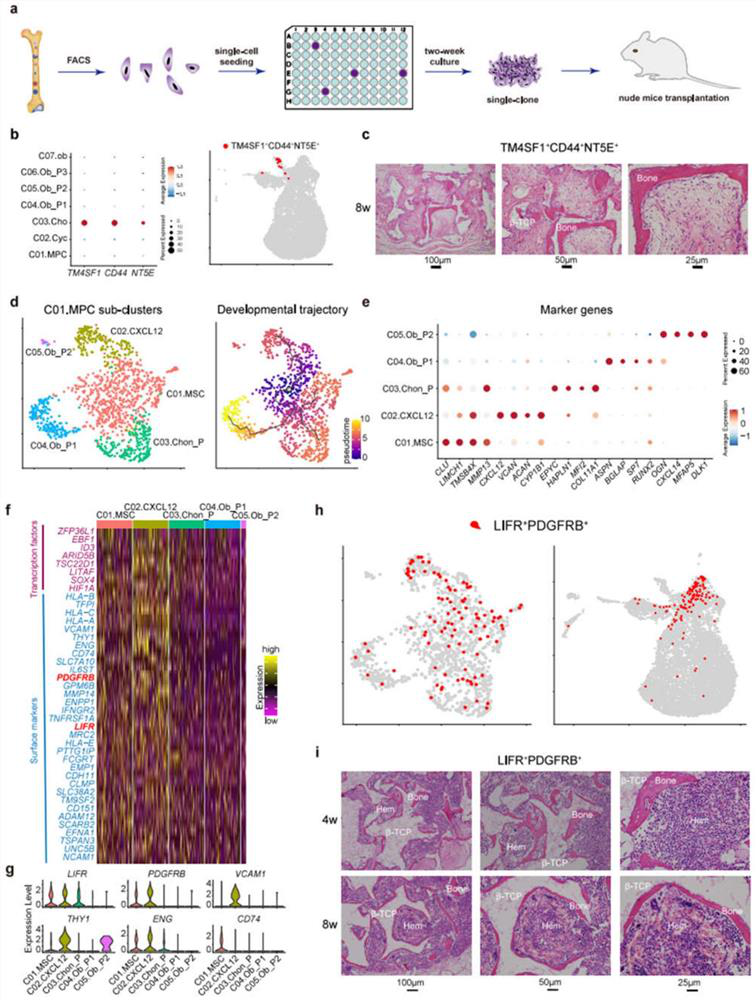
[0078] Example 2 - Heterogeneity of MSCs in Human Embryonic BM
[0079] A recent study elucidated that perinatal chondrocytes form the majority of new osteoblasts and gradually decrease with age 22 . Therefore, the inventors carried out an experimental test on the chondrocyte population by inoculating the sorted single cells in 96-well plates respectively, and then transplanting the expanded colonies subcutaneously on the dorsal side of nude mice with β-TCP vector ( figure 2 a).
[0080] like figure 2 As shown in b, the chondrocyte population specifically expresses the surface markers CD44, NT5E and TM4SF1. Subsequently, the inventors harvested CD44 by FACS sorting + CD73 + TM4SF1 + / CD45 - CD31 - CD235a - cell( Figure 8 a). STRT analysis further confirmed the accuracy of FACS ( Figure 8 b).
[0081] It was found that a single CD44 + CD73 + TM4SF1 + Cell-expanded colonies are able to efficiently form bone tissue ( figure 2 c). Therefore, the findings o...
Embodiment 3
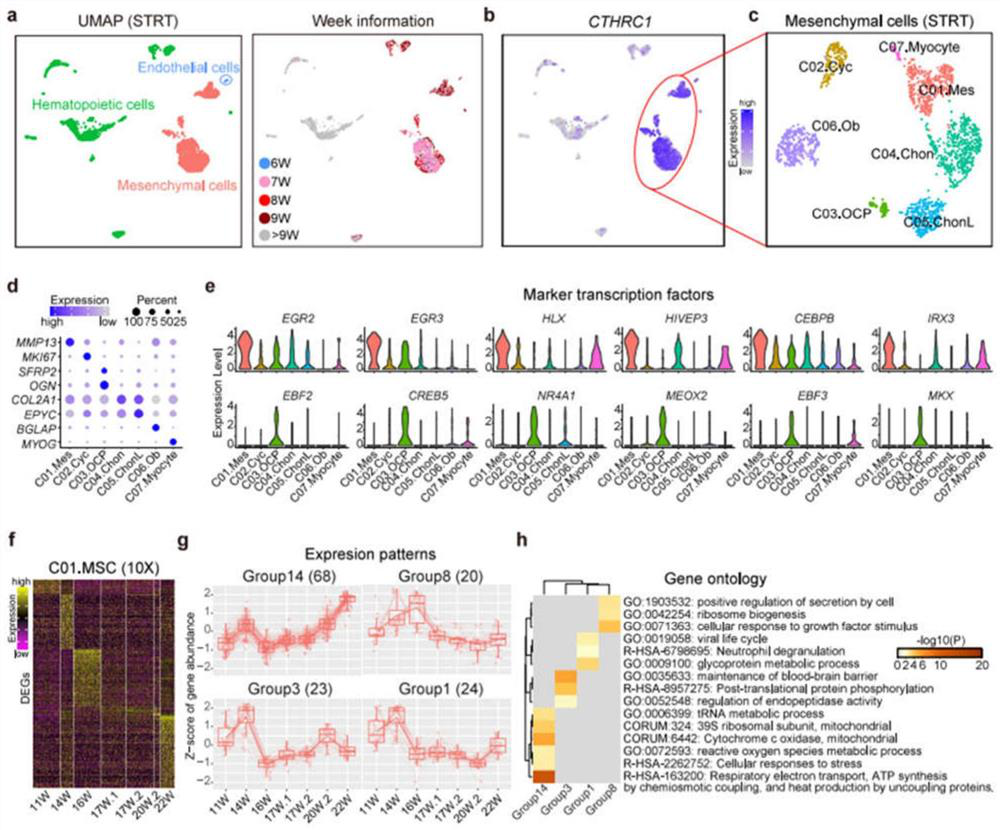
[0086] Example 3 - Differences between early and late stages of MSC development
[0087] To trace the origin of human embryonic MSCs, the inventors attempted to capture mesenchymal cells at an earlier developmental stage (6-9 weeks). However, due to the limited number of cells obtained early in development, the inventors did not use 10X genomics scRNA-seq technology, but collected cells by a random selection method and sequenced the cells using STRT scRNA-seq technology. The inventors obtained a total of 2,989 high-quality single-cell transcriptomes from cells derived from 17 embryos aged 6-24 weeks.
[0088] The inventors identified 3 main groups in the STRT dataset, namely, endothelial cells (specifically expressing CDH5), mesenchymal cells (highly expressing CTHRC1, collagen triple helical repeat protein-1) and hematopoietic cells (highly expressing PTPRC) and GYPA)( image 3 b, Figure 9 a-b). Notably, most of the sequenced cells at later stages of development (after...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com