SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) site for detecting watermelon peripheral leaf shape, closely-linked molecular marker and application of SNP site and closely-linked molecular marker
A molecular marker, watermelon technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as unreported, and achieve the effect of good application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
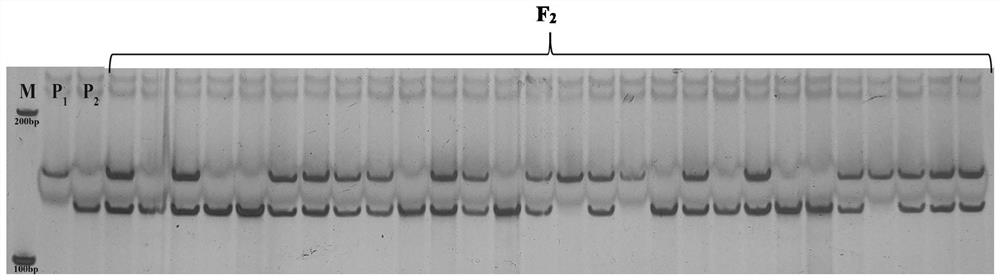
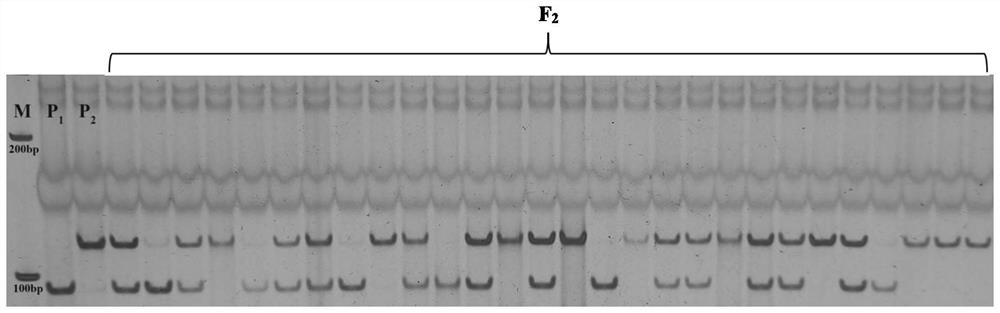
[0059] Example 1 Acquisition of SNP markers and closely linked dCAPS molecular markers co-segregated with the whole leaf shape gene of watermelon plants
[0060] This example mainly introduces the fine mapping process for the watermelon ClLL gene, including the construction of genetic segregation population, preliminary positioning, fine mapping and other processes (the analysis process is as follows: Figure 4 In this process, the development, design and inspection process of the final molecular markers dCAPS and SNP2 are involved. The relevant experimental process is briefly introduced as follows.
[0061] 1. Construction of genetically segregated populations
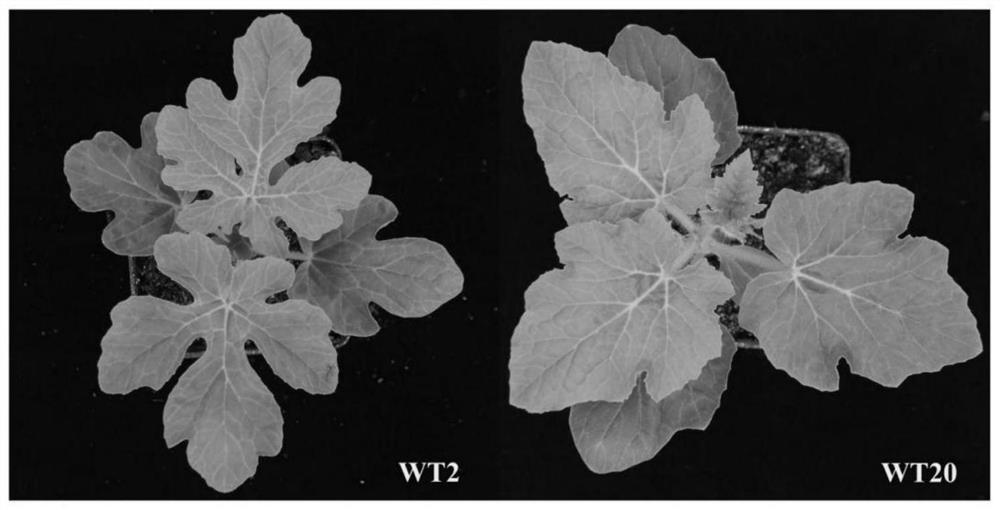
[0062] The watermelon whole leaf shape WT20 was used as the female parent, and the watermelon split leaf shape WT2 was used as the male parent (it needs to be explained that, during the experiment, considering the availability of materials and the convenience of operation, the inventors used WT2 as the male parent. O...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2 Identification of watermelon as whole leaf-shaped material using dCAPS molecular markers
[0113] 1. DNA extraction from watermelon tissue
[0114] The DNA of the watermelon sample tissue was extracted by the conventional CTAB method, and the RNA was removed, and the volume of the DNA sample was not less than 50 μL. The OD values of DNA samples at 260nm and 280nm were measured by UV spectrophotometer, and the DNA content and the ratio of OD260 / 280 were calculated. DNA sample purity OD260 / 280 value should be 1.8-2.0, and the concentration should be diluted to 100ng / μL.
[0115] 2. Primer selection
[0116] dCAPS2 uses the following primer sequences:
[0117] dCAPS2-F: 5'-AATGGGTATGATATTGTCCATCTC-3' (as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.1)
[0118] dCAPS2-R: 5'-AAAGTCTTGCATTGGCTAAAGA-3' (as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.2)
[0119] dCAPS3 uses the following primer sequences:
[0120] dCAPS3-F: 5'-AAAATTTGCATGTTTGGATTACAAAACTCA-3' (as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.3)
[0121] dCAPS3-R: 5'-T...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3 Identify whether watermelon is whole leaf-shaped material using SNP molecular markers
[0139] 1. DNA extraction from watermelon tissue
[0140] The DNA of the watermelon sample tissue was extracted by the conventional CTAB method, and the RNA was removed, and the volume of the DNA sample was not less than 50 μL. The OD values of DNA samples at 260nm and 280nm were measured by UV spectrophotometer, and the DNA content and the ratio of OD260 / 280 were calculated. DNA sample purity OD260 / 280 value should be 1.8-2.0, and the concentration should be diluted to 100ng / μL.
[0141] 2. Primer selection
[0142] SNP2 uses the following primer sequences:
[0143] SNP2-F: 5'-CCATTTTAGAATCACTCCCAAAC-3' (as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.9)
[0144] SNP2-R: 5'-AACTAAGCAAGAAGACATGTGACC-3' (as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.10)
[0145] The primers were synthesized by a biotechnology company and diluted to 10 μM before use.
[0146] 3. PCR reaction system
[0147] The PCR reaction program w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com