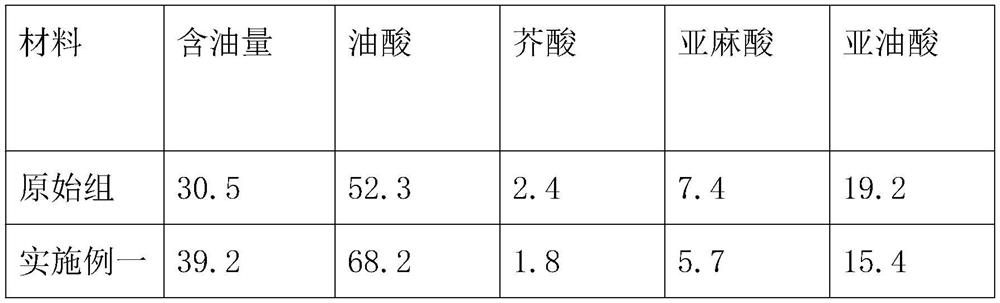
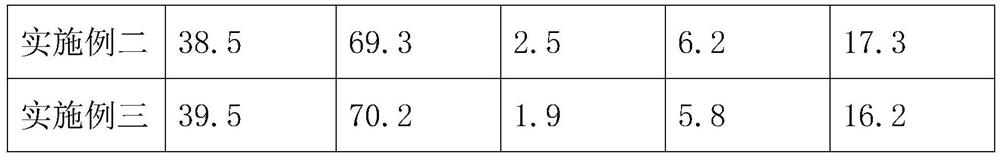
Rape mutation breeding method
A technology for mutation breeding and rapeseed, applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, plant regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of narrow genetic background, high quality, high yield, difficult to combine multiple resistances, etc., and achieves early maturity and bacteria resistance. Effects of Sclerotinia Enhancement, Yield and Oil Quality Improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for mutation breeding of rapeseed, characterized in that, comprising the steps:
[0025] Step 1. Take the clone test tube seedlings cultivated from the young embryos of rapeseed, expand and multiply to form a large number of bud clusters, sterilize them with a sodium hypochlorite solution with a volume percentage of 5% for 25 minutes, wash them once with distilled water, and finally soak them in distilled water. embryo 1 hour;
[0026] In the present embodiment, the young embryos in step 1 are young embryos of Brassica napus 15 days after pollination.
[0027] Step 2. Under aseptic conditions, a large number of bud clusters were firstly connected to MS as a medium and then added to a mutagenesis medium of 0.3% ethyl methanesulfonate for 15 hours of mutagenesis;
[0028] Step 3. Then add a selection agent that has been filtered and sterilized by suction for selection, select MS as the culture medium, and add auxin in different proportions, and treat it by light...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for mutation breeding of rapeseed, characterized in that, comprising the steps:
[0041] Step 1. Take the clone test tube seedlings cultivated from the immature embryos of rapeseed, expand and multiply to form a large number of bud clusters, disinfect with 5% sodium hypochlorite solution by volume for 28 minutes, then wash twice with distilled water, and finally soak with distilled water. embryo 2 hours;
[0042] In the present embodiment, the young embryos in step 1 are Brassica napus young embryos 18 days after pollination.
[0043] Step 2. Under aseptic conditions, a large number of bud clusters were firstly connected to MS as a medium and then added to the mutagenesis medium of 0.3% ethyl methanesulfonate and cultured for 18 hours;
[0044] Step 3. Then add a selection agent that has been filtered and sterilized for selection, select MS as a culture medium, and add auxin in different proportions, and treat it by lighting under a fluorescent lamp, the light...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A method for mutation breeding of rapeseed, characterized in that, comprising the steps:
[0057] Step 1. Take the clone test tube seedlings cultivated from the immature embryos of rapeseed, expand and multiply to form a large number of bud clusters, disinfect with 5% sodium hypochlorite solution by volume for 30 minutes, then wash with distilled water 3 times, and finally soak with distilled water. embryo 4 hours;
[0058] In the present embodiment, the young embryos in step 1 are the young embryos of Brassica napus 20 days after pollination.
[0059] Step 2. Under sterile conditions, a large number of bud clusters were firstly connected to MS as a medium and then added to the mutagenesis medium of 0.3% ethyl methanesulfonate for 20 hours of mutagenesis;
[0060] Step 3. Then add a selection agent that has been filtered and sterilized by suction for selection, select MS as the culture medium, and add auxin in different proportions, and treat it by lighting under a flu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com