Bacillus subtilis G-1 for producing organic acid and application thereof
A Bacillus subtilis, organic acid technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of endogenous infection of livestock and poultry, residues of livestock products and the environment, double infection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] 1.1 Isolation and purification of strains
[0051] Collect the whole plant corn, whole plant strawberry, and pine vanilla from the feed factory in Lianchi District, Baoding City, Hebei Province, package and ferment them for 3 to 5 days, take 10g of the fermented sample, add it to 100mL of sterile water, and place it at 37°C, Shake at 150 r / min for 1-2 hours, take out 1 mL of it and add it to a sterile test tube to dilute it, and then spread the plate and place it at 37°C for cultivation to obtain isolated strains. Finally, the isolated strains are purified to obtain purified strains.
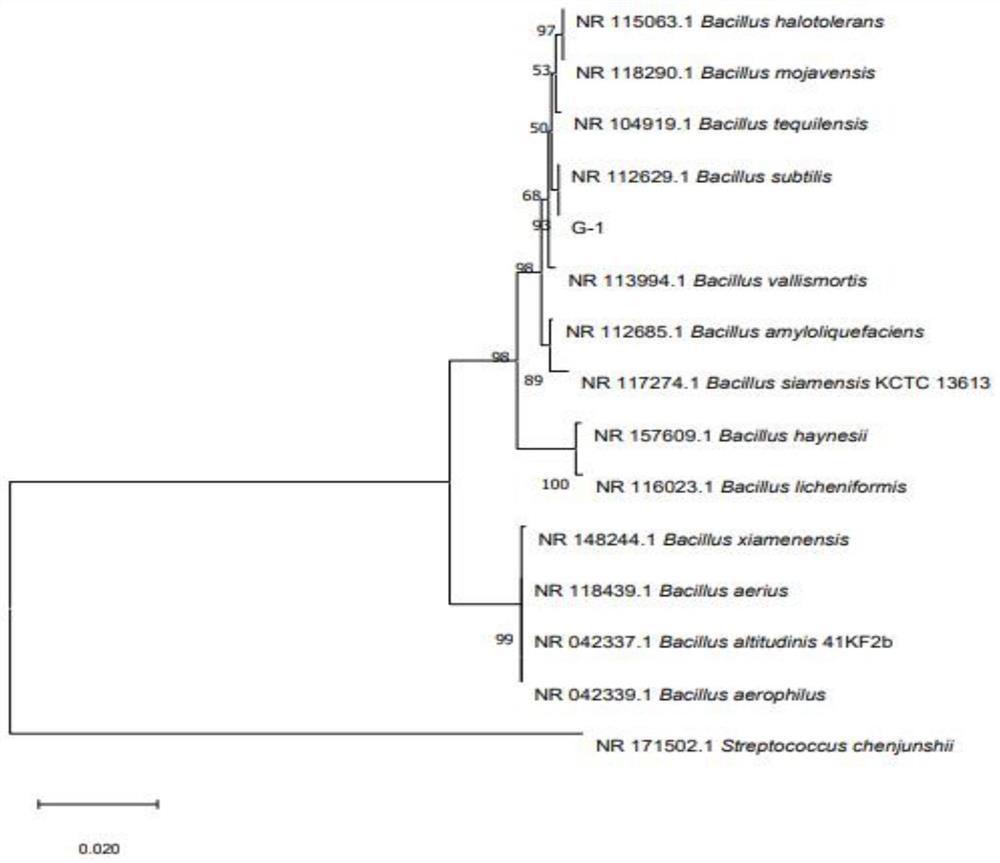
[0052] 1.2 Identification of strain G-1
[0053] The strain obtained by the above separation and purification was named G-1, and it was coated on the NA medium for observation of colony morphology. The strain formed on the solid medium with an irregular shape, milky white, opaque, small folds, and slightly folds in the middle. Raised colonies, gram stained purple, are gram positive; spor...
Embodiment 2
[0056] 2.1 Study on growth characteristics of strain G-1
[0057] The strain G-1 was inoculated from the slant medium to the NA solid medium for activation, and the activated single colony was inoculated into 100 mL of seed medium, and cultured with shaking at 37 °C and 150 r / min for 6 to 12 hours; cultured to OD 600 The value is 0.4 to 0.6, which is the logarithmic growth phase of the strain, and the seed liquid is obtained.
[0058] 2.1.1 The effect of different temperatures on the growth of strain G-1
[0059] The activated strain seed liquid was inserted into the fermentation medium at an inoculum of 6.0%, and 3 replicates were set for each, and cultured at 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, and 40°C respectively, and the growth of the strain was observed. , and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0060] Table 1 Growth characteristics of strain G-1 under different temperature conditions
[0061]
[0062] Note: "-" does not grow, "w" grows weakly, "+" grows, "++" grows better, a...
Embodiment 3
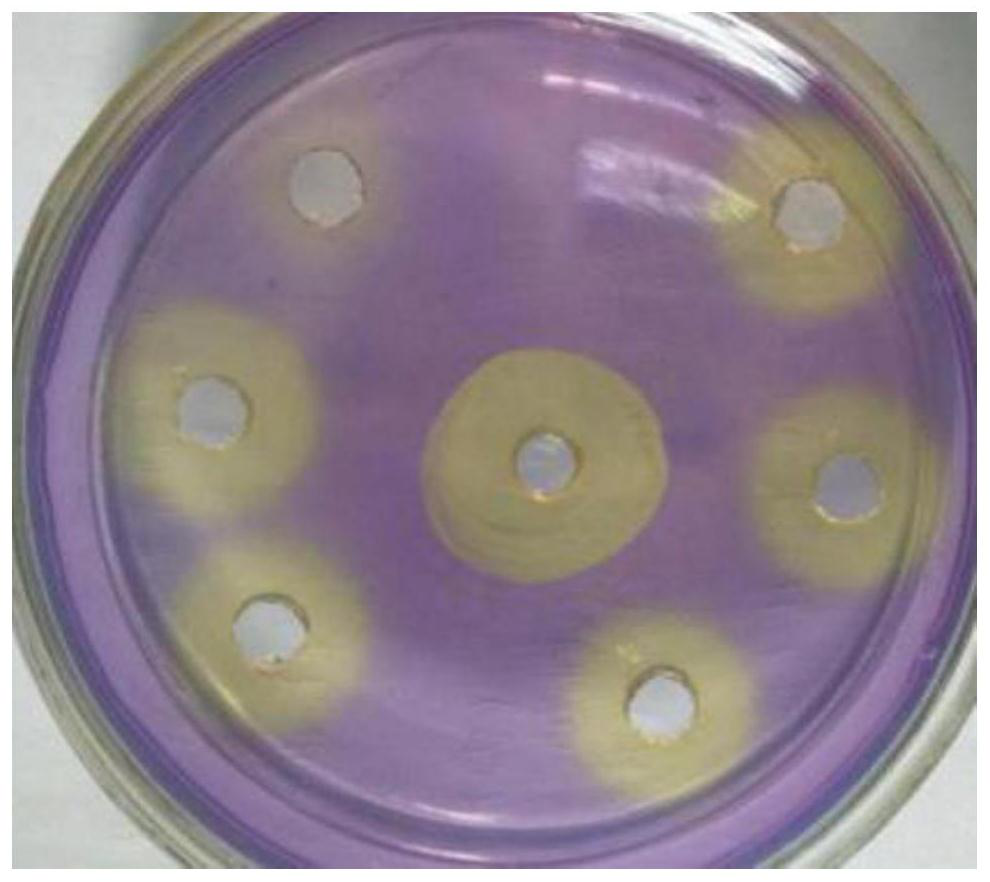
[0090] Effects of Strain G-1 on Whole Plant Corn Silage
[0091] The whole corn (Zheng Dan 958) planted in the experimental farm of Hebei Agricultural University was cut at the wax maturity stage, and transported to the forage processing base of Hebei Feed Microbial Technology Innovation Center, dried for half a day, and crushed with a silk rolling machine. The compound silage inoculant was added to the crushed whole corn, and the total amount of bacteria G-1 reached 1.0×10 9 CFU / kg (fresh weight), as a test group (T), silage was carried out in plastic bags with a size of 30cm×40cm, and the anaerobic fermentation was carried out by compaction for 45 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com