Distributed multi-platform underwater multi-target association and passive positioning method
A passive positioning and target association technology, applied in advanced technology, climate sustainability, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of low positioning accuracy and low accuracy rate of multi-target association, and achieve the effect of excellent positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0094] DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS 1. A distributed multi-platform underwater multi-target association and passive positioning method described in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
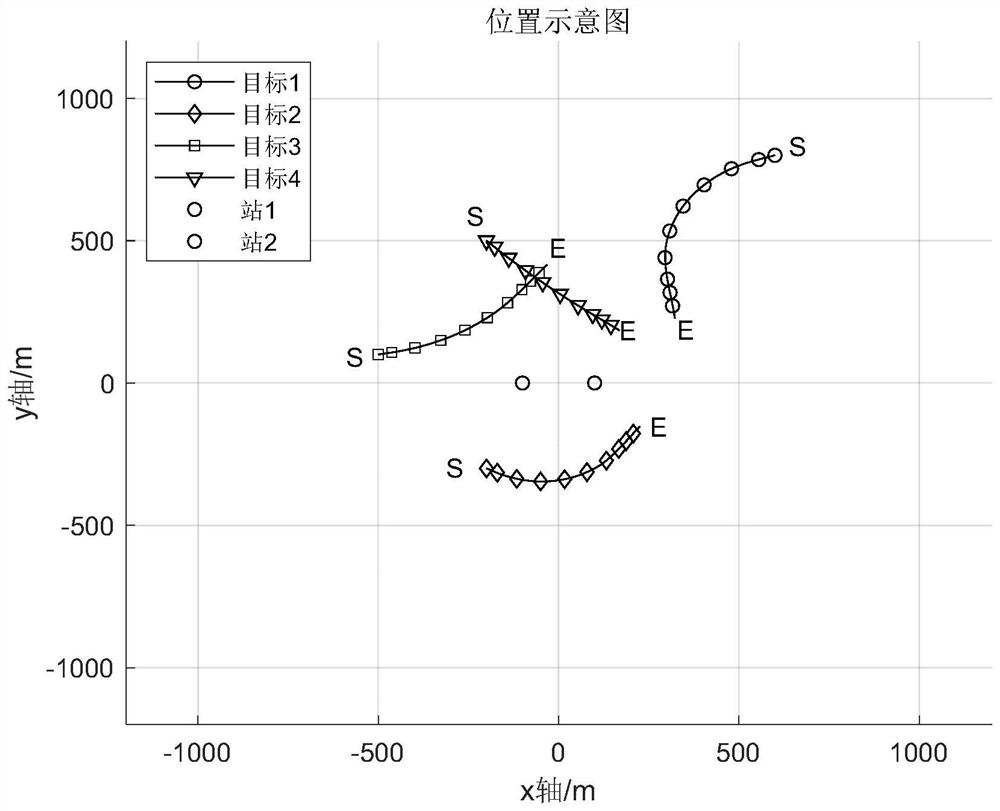
[0095] Step 1. Carry out target association according to the information vector estimation result of each target under the multi-platform, and obtain the target association result;
[0096] Step 2: Construct a TMA model composed of state equation and measurement equation;
[0097] Step 3: Based on the target association result in Step 1 and the TMA model in Step 2, use the forgetting factor-based fading and strong tracking filter to passively locate the azimuth-only maneuvering target under multiple platforms, and finally output each target. The positioning result of the target (including information such as position, speed, etc.).
[0098] The multi-platform in the present invention refers to two or more platforms, and the multi-target refers to two...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0099] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Step 1, a target association algorithm based on frequency feature multi-information vector fusion is used, and the specific process of Step 1 is:
[0100] Step 11. Input the estimation result of the target information vector under the multi-platform:
[0101] I mp (k)={θ mp (k),A mp (k),F mp(k),k=1,2,...,T},p=1,2,...,P,m=1,2,...,M
[0102] The target frequency feature information vector estimation result is extracted from the information vector estimation result of each target under multiple platforms:
[0103] J mp (k)={A mp (k),F mp (k),k=1,2,…,T} (1)
[0104] Among them, p represents the p-th target, p∈{1,2,…,P}, P is the total number of targets, m is the m-th platform, m∈{1,2,…,M}, M is the total number of platforms, k represents the sampling time k, T represents the total sampling time, A mp (k) represents the energy information of the p-th target observed by the m-th platfor...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0121] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the λ F (t k′ ) corresponding to the associated confidence value η F (t k′ )for:
[0122]
[0123] Among them, a 1 and a 2 is a constant;
[0124] the λ A (t k′ ) corresponding to the associated confidence value η A (t k′ )for:
[0125]
[0126] where b 1 and b 2 is a constant.
[0127] In this embodiment, the established test statistic rating standards are shown in Table 1 and Table 2:
[0128] Table 1 Rating standard of frequency test statistic
[0129]
[0130] Table 2 Rating criteria for energy test statistics
[0131]
[0132]
[0133] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com