Method for detecting somatic mutation in plant genome
A plant genome and somatic cell mutation technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of high false positive rate of somatic cell mutation, inability to effectively evaluate false positive results, and neglect of genome information, and achieve efficient identification and screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
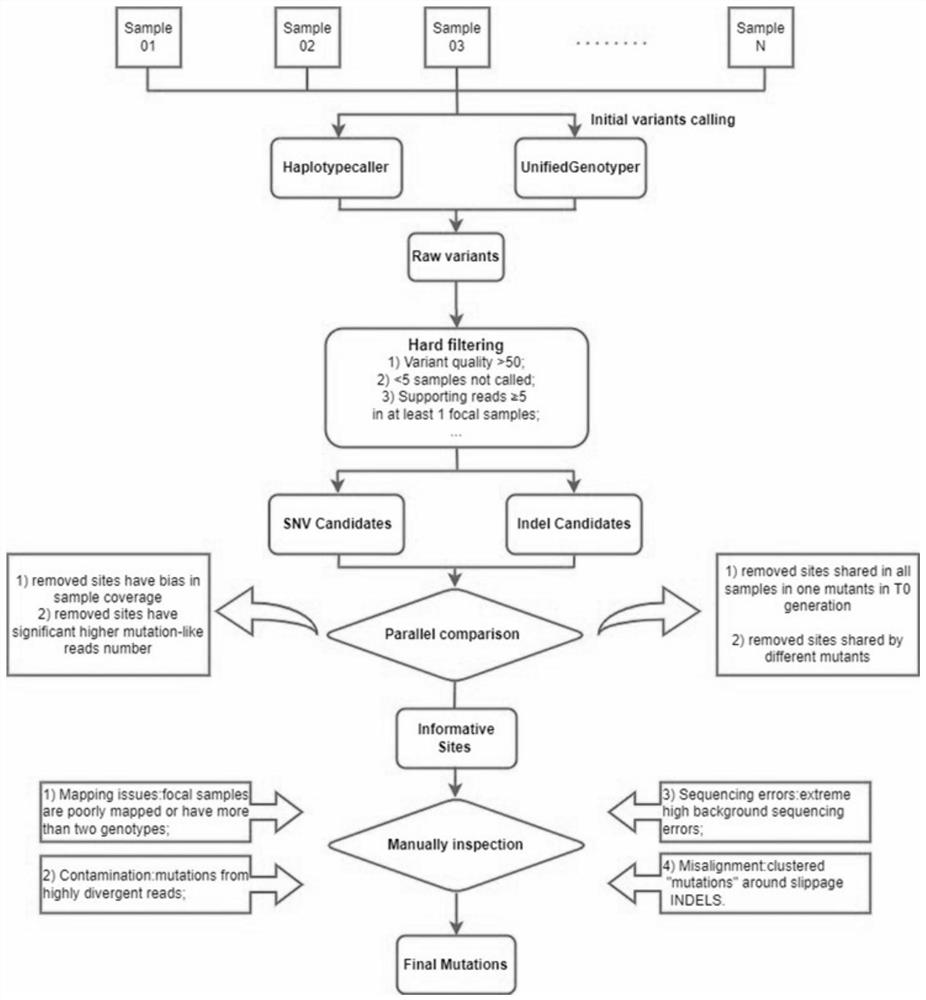
[0028] A method for detecting somatic mutations in plant genomes of the present invention ( figure 1 ), including the following steps:
[0029] (1) Evaluation of resequencing data: use software such as FastQC to perform quality inspection and evaluation on resequencing data, and filter to obtain clean data; pass MD5 value verification, and perform quality inspection on resequencing data according to GC content of sequencing data, sequencing depth, etc. , remove reads joints, reads with N ratio greater than 10%, and reads with low-quality bases accounting for more than 50% of the number of reads, and get clean data after filtering.
[0030] (2) Assembly of resequencing data: use the default parameters of BWA-mem to compare the clean data to the reference genome to obtain the original SAM file, sort and convert the SAM file to BAM format through the SortSam module of Picard; use the MarkDuplicates module to mark Abnormally amplified reads, and use GATK's RealignerTargetCreator...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Identification and screening of Arabidopsis msh6 mutant somatic mutations of the present invention
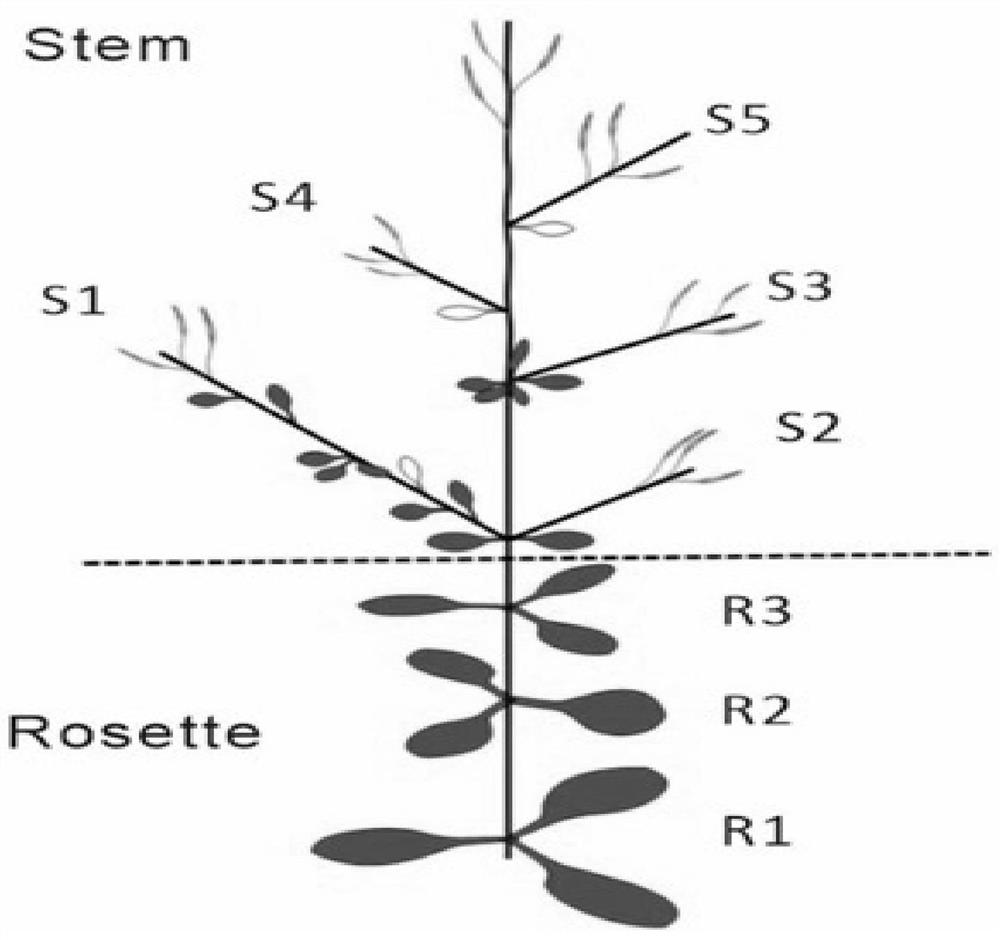
[0038] Resequencing of msh6 mutant leaf samples: Leaf spliced Arabidopsis T-DNA mutant msh6 ( figure 2 ), using the CTAB (Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) method to extract genomic DNA, and send it to Wuhan Huada Gene Technology Co., Ltd. for quality inspection, and select samples (21 samples in total) that meet the sequencing requirements for DNA testing for whole genome sequencing. The sequencing platform is the hiseq4000 platform, using conventional library construction, the size of the interrupted fragments is 350bp, and the fragment read length (reads) is 150bp. Using paired-end sequencing, the sequencing depth of each sample exceeds 30 times, ensuring that the sequencing quality is greater than 20 .
[0039] Evaluation of resequencing data: Perform quality inspection on the returned sequencing data, first check the MD5 value, and check whether the downloaded dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com