Method for evaluating migration risk of antibiotic drug resistance gene
A technology for drug resistance genes and antibiotics, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc. achieve high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
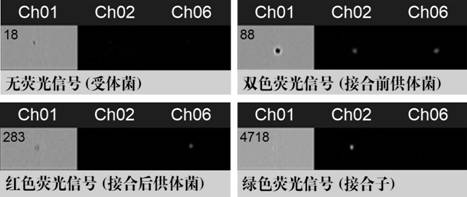
[0068] This example is a method for assessing the risk of antibiotic resistance gene transfer, as follows.
[0069] (1) Take out red fluorescent Escherichia coli K12 and green fluorescent Escherichia coli DH5α from the -80°C refrigerator, apply after activation, and check whether the fluorescent proteins of red fluorescent Escherichia coli and green fluorescent Escherichia coli are normally expressed.
[0070] (2) Select the above two strains of Escherichia coli and culture them to logarithmic growth phase in LB culture medium, in which the LB culture medium for cultivating Escherichia coli DH 5α contains 100 μg / mL ampicillin, 50 μg / mL kanamycin and 10 μg / mL tetracycline hydrochloride.
[0071] (3) Wash and dilute Escherichia coli K12 and Escherichia coli DH 5α with physiological saline or sterile phosphate buffer (0.1 mM) until the number of bacteria reaches 1010 CFU / mL respectively to obtain a preconjugated bacterial solution.
[0072] (4) Red Escherichia coli K12 was used ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com