Method for preparing polytetrafluoroethylene fiber by wet spinning
A polytetrafluoroethylene and polytetrafluoroethylene spinning technology, applied in wet spinning, fiber treatment, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., to achieve the effect of not easy to break, avoid sticking, and continuous spinning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
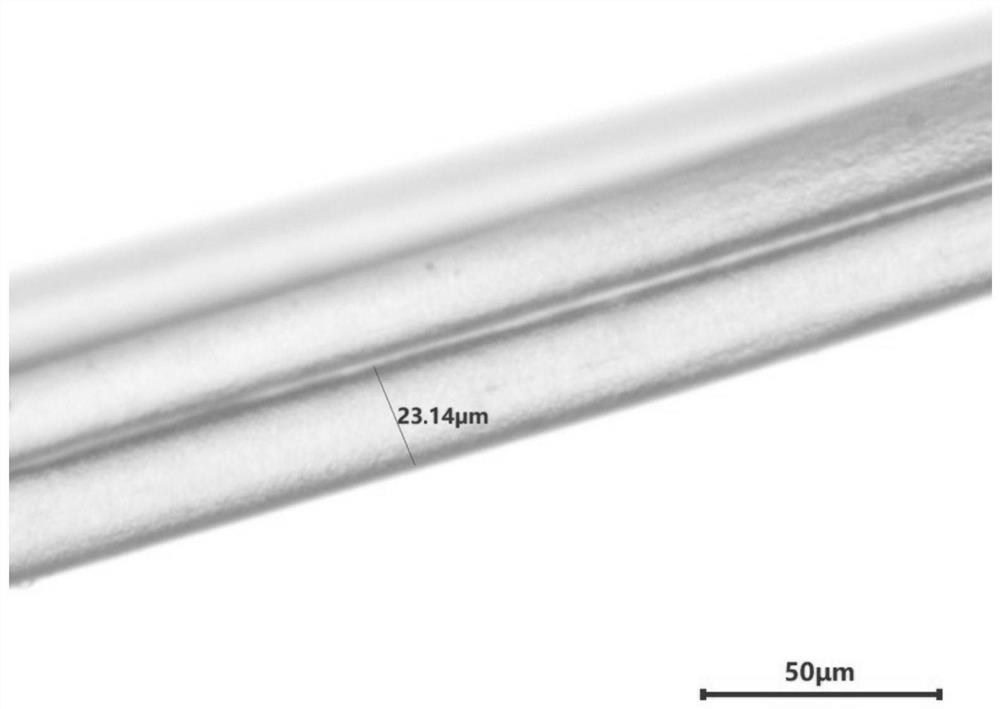
[0052] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polytetrafluoroethylene fibers by wet spinning.
[0053] (1) Dissolve 6g of sodium alginate with M:G ratio of 1:2 in 194g of deionized water at 70°C, cool to room temperature and add 0.1g of non-ionic silicone defoamer and polytetrafluoroethylene dispersion ( The massfraction of polytetrafluoroethylene dispersion liquid is 60%, promptly contains polytetrafluoroethylene (72g) 120g mixes in 120g, prepares the spinning solution that polytetrafluoroethylene mass concentration is 22.5%;
[0054] (2) The spinning solution is wet-spun with a spinning temperature of 25°C and a spinneret hole diameter of 70 μm, and then molded in a calcium chloride coagulation bath with a mass fraction of 1% ethanol at a temperature of 25°C to obtain a primary fiber;
[0055] (3) After washing the as-spun fiber, disperse it with an aluminum sulfate solution with a concentration of 2%, then wash it with ethanol, dry it at 100°C, and sinter it at 36...
Embodiment 2
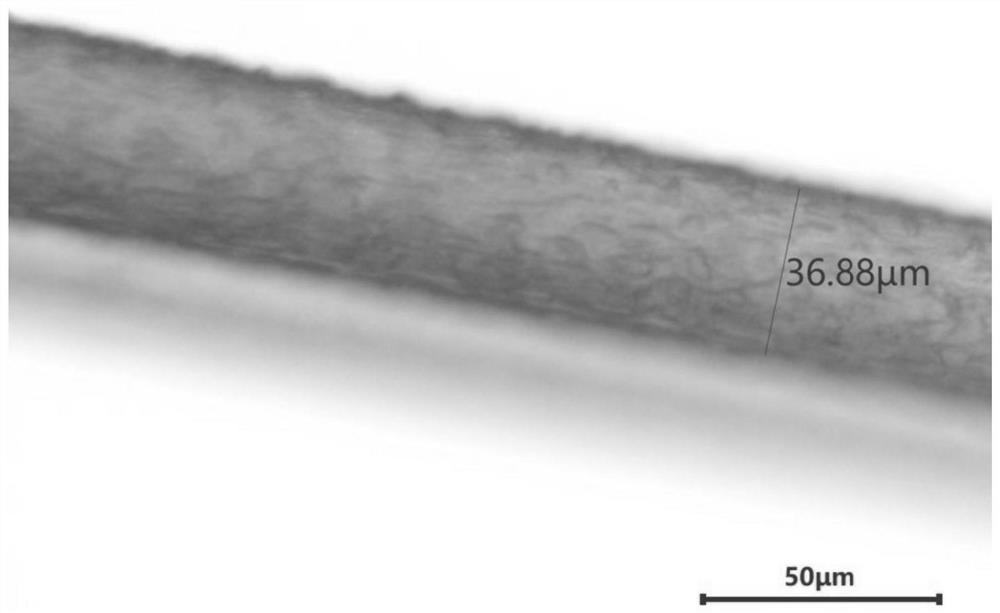
[0058] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polytetrafluoroethylene fibers by wet spinning.
[0059] The difference from Example 1 is that in this example, the dispersion is carried out with white oil.
[0060] figure 2 This is the metallographic optical microscope image of the polytetrafluoroethylene fiber obtained in this example. It can be seen from the figure that the diameter of the polytetrafluoroethylene fiber obtained in this example is 36.88 μm.
Embodiment 3
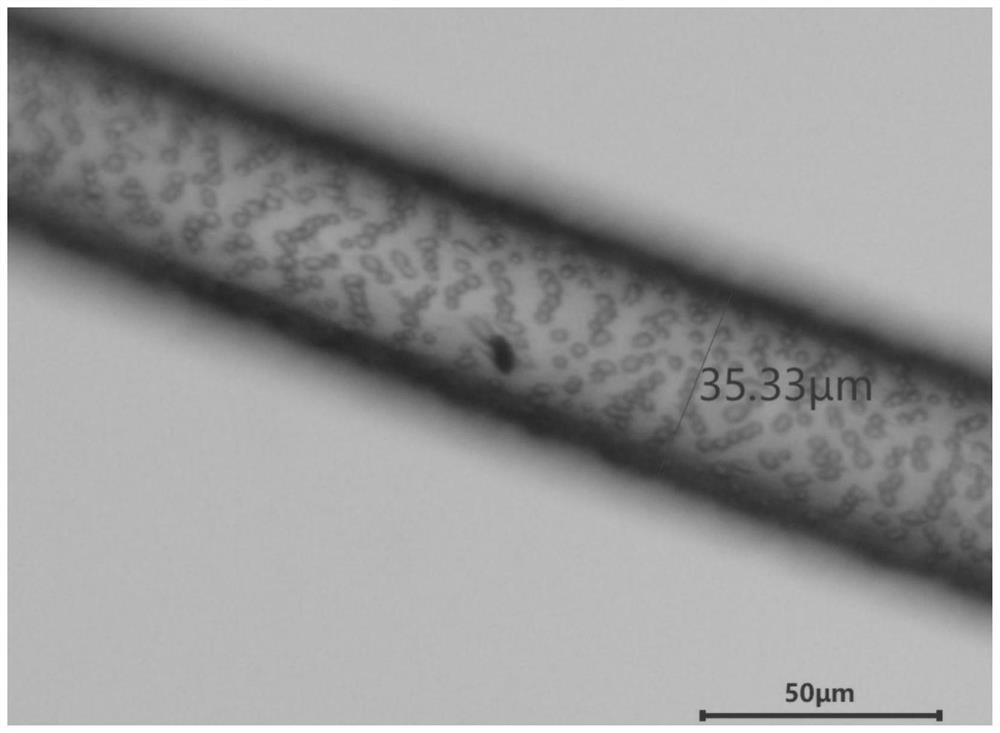
[0062] This embodiment provides a method for preparing polytetrafluoroethylene fibers by wet spinning.
[0063] The difference from Example 1 is that in this example, ethanol is not added to the coagulation bath.
[0064] In this example, when ethanol is not added to the coagulation bath, there will be a phenomenon of uneven sintering on the fiber surface. From the comparison of Example 1 and Example 3, it can be seen that adding ethanol to the coagulation bath can regulate the interfiber ions The exchange rate makes the exchange rate tend to be moderate, and the surface of the sintered fiber is more uniform.
[0065] image 3 This is the metallographic optical microscope image of the polytetrafluoroethylene fiber obtained in this example. It can be seen from the figure that the diameter of the polytetrafluoroethylene fiber finally obtained in this example is 35.33 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com