Method for producing alginate lyase through co-fermentation of halophilic lactic acid bacteria and marine bacteria
A technology of alginate lyase and marine bacteria, which is applied in the field of marine biology, can solve the problems of high industrialization cost, complex production process, and long fermentation cycle, and achieve the effects of low cost, short fermentation time, and simple process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Pre-cultivation of the marine bacteria XS1412C strain: inoculate a single colony of the marine bacteria XS1412C strain into the culture medium, and shake and pre-cultivate it at 26° C. for 7 hours to obtain a highly active marine bacteria XS1412C strain.
[0040] The composition of the culture solution is: sodium alginate 2%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1%, ammonium chloride 0.2%, peptone 5%, and the treatment condition is: adding filtered seawater to dissolve.
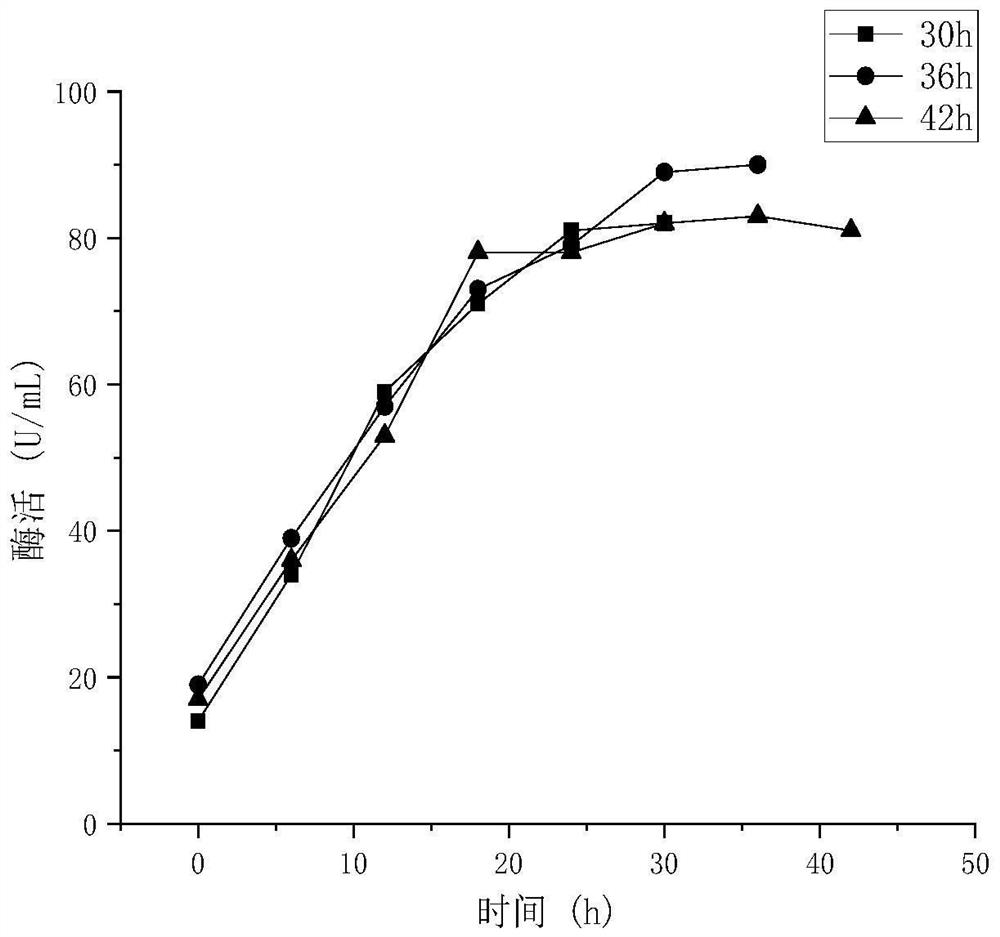
[0041](2) Preparation of marine bacterium XS1412C strain fermentation culture medium: inoculate the marine bacterium XS1412C strain cultivated in step (1) into the fermentation medium according to the inoculum size of 3%, and ferment at 30° C. for 36 hours to prepare marine bacterium XS1412C Strain fermentation broth.
[0042] The composition of the fermentation culture liquid is: peptone 5%, glucose 5%, sodium alginate 2%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1%, ammonium chloride 0.4%, magnesium sulfate ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The difference between this implementation method and Example 1 is that in step (2), the culture temperature of the fermentation broth of the marine bacteria XS1412C strain is 25° C., and the other steps are the same.
Embodiment 3
[0059] The difference between this implementation method and Example 1 is that in step (2), the culture temperature of the fermentation broth of the marine bacteria XS1412C strain is 35° C., and the other steps are the same.
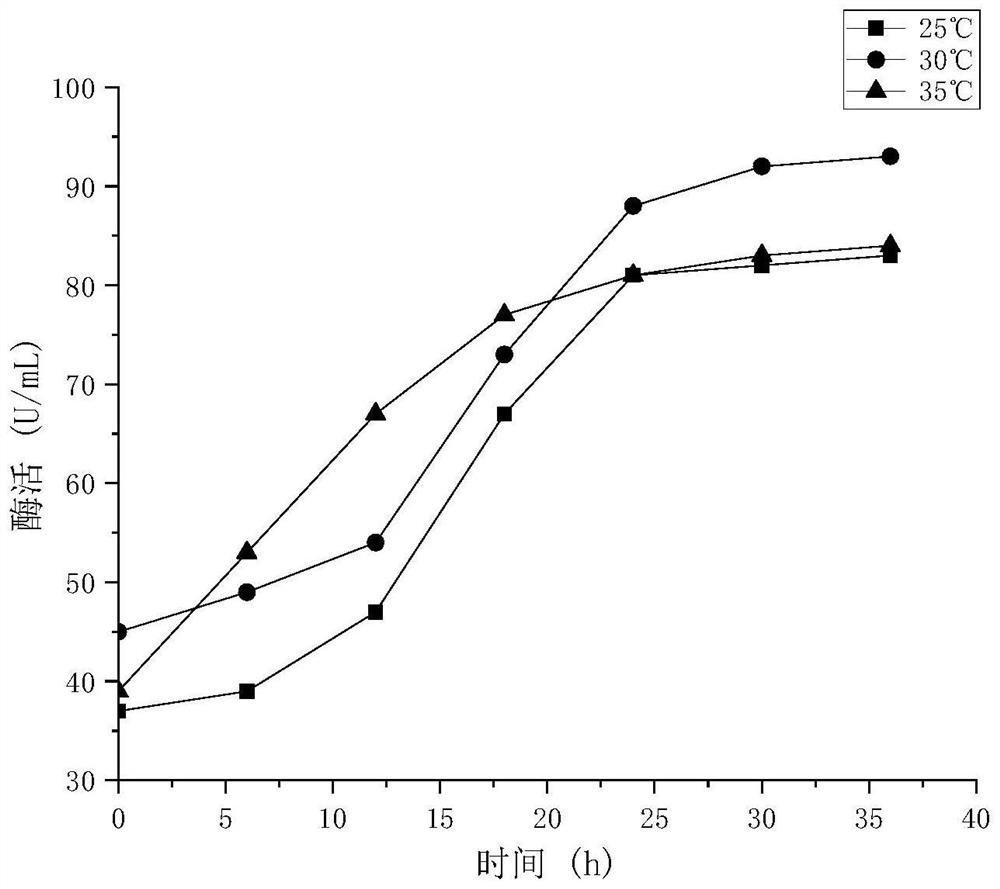
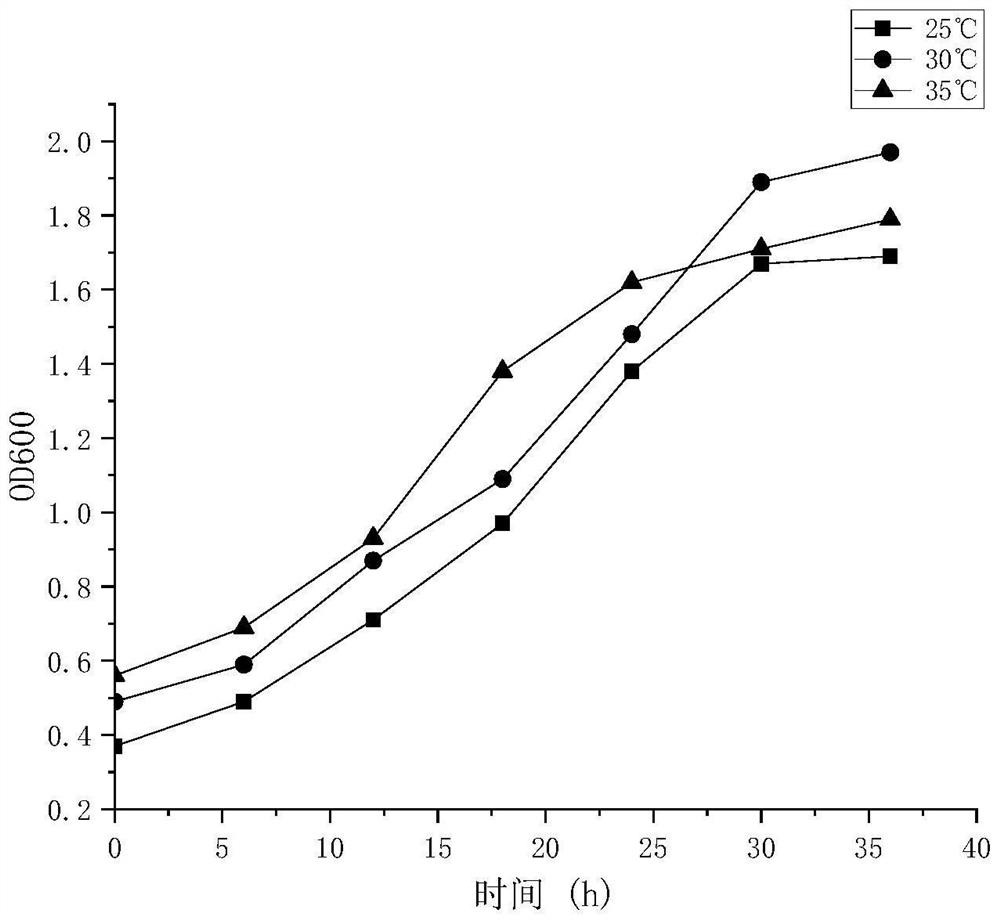
[0060] see figure 1 and figure 2 , are respectively the enzyme activity change diagram and the growth curve of the bacterial strain in the fermentation broth of the marine bacteria XS1412C bacterial strain under different culture temperatures, as can be seen from the above examples 1, 2, and 3, when the temperature is too low, the bacterial strain grows slowly and the enzyme activity Also lower, when the temperature is too high, although the bacterial strain grows faster in a short period of time, the continuous higher temperature inhibits the growth of the bacterial strain, which in turn affects its enzyme production. is 30°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com