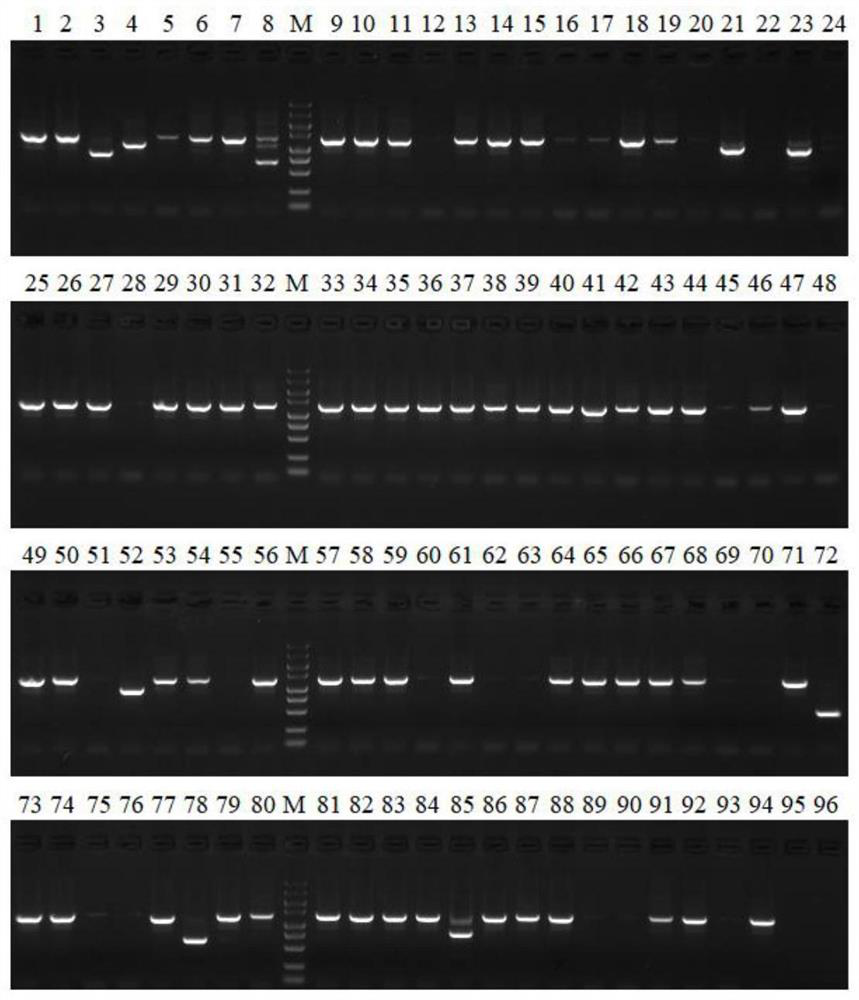
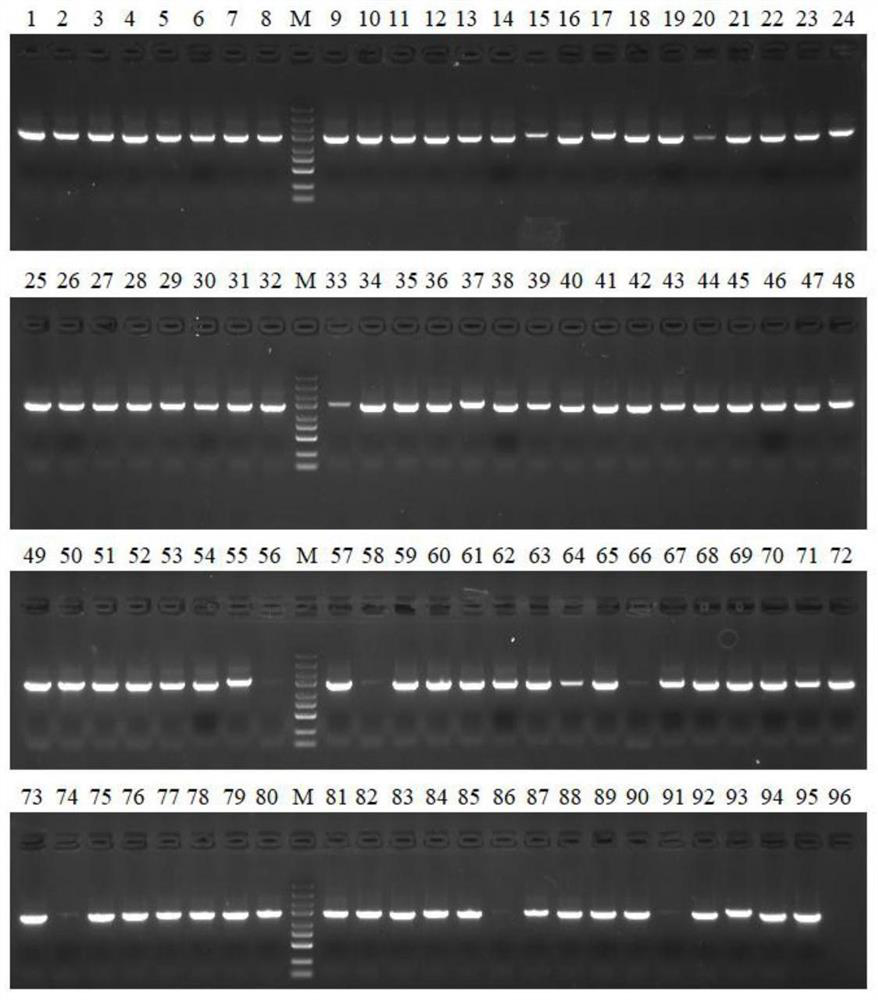
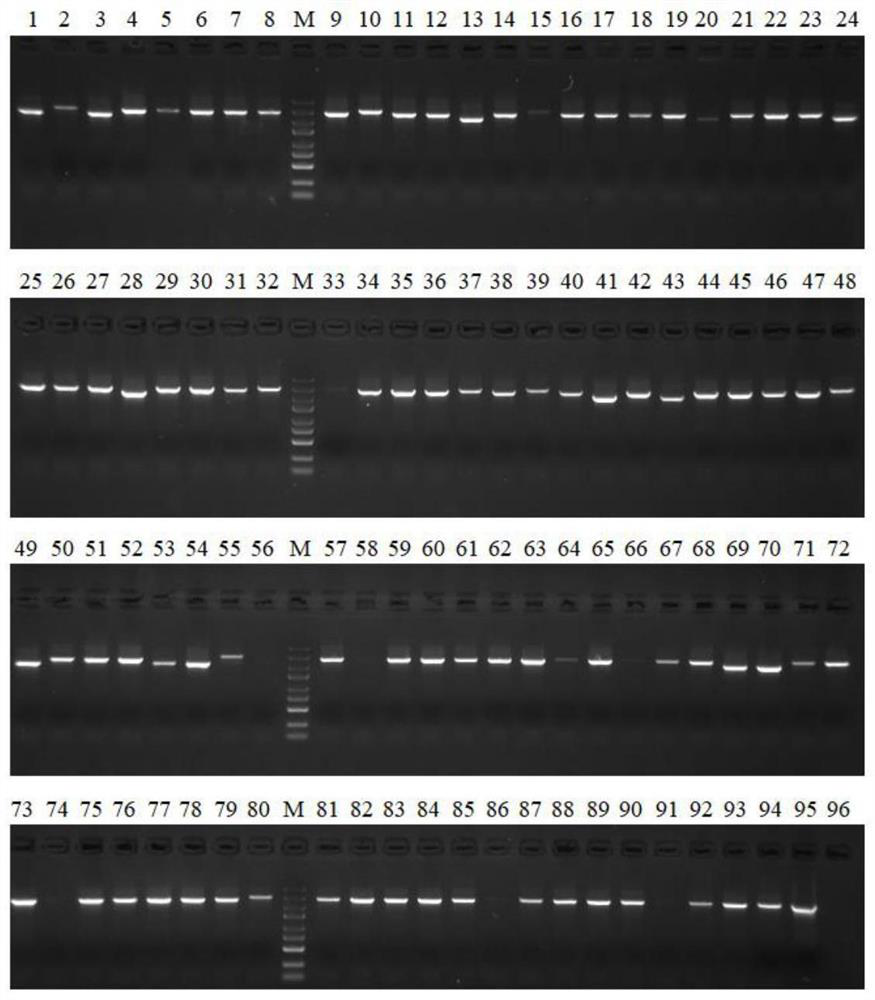
High-throughput screening tool for enabling escherichia coli to obtain effective NHEJ system and application of high-throughput screening tool
An Escherichia coli, high-throughput technology, applied in the field of gene editing, to achieve the effect of short time-consuming and high screening efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1 Construction of a high-throughput screening tool that enables Escherichia coli to obtain an effective NHEJ system
[0092] This embodiment provides a high-throughput screening tool for obtaining an effective NHEJ system for Escherichia coli, which includes:
[0093] pDual-Cas9-Parental plasmid vector: Rep101 gene, pSC101 replicon, kanamycin resistance gene, Cas9 gene, araC gene, 2 arabinose promoters, BsaI restriction enzyme recognition for cloning Ku gene connected in sequence site and the BbsI restriction enzyme recognition site for cloning the ligD gene;
[0094] And pDual-sgRNA-lacZ plasmid vector: the sgRNA sequence targeting the lacZ gene, the constitutively expressed strong promoter J23119 promoter, the replicon and the ampicillin resistance gene are connected in sequence.
[0095] The high-throughput screening tool for obtaining an effective NHEJ system for Escherichia coli is constructed by the following method:
[0096] (1) Gene synthesis of pDual-...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2 Construction of Ku+ligD plasmid library using pDual-Cas9-Parental as the backbone vector
[0109] In this example, pDual-Cas9-Parental is used as the backbone vector to construct a Ku+ligD plasmid library, including the following steps:
[0110] (1) Obtained five CDS coding sequences of Ku protein and ligD protein derived from microorganisms from NCBI, GenBank accession numbers are WP_010886496 (Bsu-Ku), GAS86454 (Mbr-Ku), YP_889815 (Msm-Ku), NP_215452 ( Mtb-Ku), ACV76561 (Nmu-Ku), NP_389223 (Bsu-ligD), ATD76462 (Bve-ligD), ALI25184 (Mfo-ligD), WP_011730625 (Msm-ligD) and NP_215453 (Mtb-ligD).
[0111] (2) Codon optimization was carried out on the CDS coding sequences of Ku protein and ligD protein for the E. coli host. The CDS coding sequences of the optimized Ku protein did not contain BbsI and BsaI recognition sequences, and the 5' end of the sequence was added with SEQ ID NO.22 The nucleotide sequence shown in the 3' end is added with the nucleotide seque...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Example 3 Screening of an effective NHEJ system in Escherichia coli from the Ku+ligD plasmid library
[0166] This embodiment screens the effective NHEJ system in Escherichia coli, including the following steps:
[0167] (1) The Ku+ligD plasmid library constructed in Example 2 was electrotransformed into MG1655 Escherichia coli competent cells, coated with kanamycin-resistant LB plates, and cultured overnight at 30°C.
[0168] (2) Scrape all the clones on the plate and inoculate the bacterial liquid into LB medium, cultivate it at 30°C and 220rpm, when the bacterial liquid OD 600 When the value reached 0.6, the competent cells were prepared according to the standard electroporation competent cell preparation method.
[0169] (3) Electrotransfer the pDual-sgRNA-lacZ plasmid to the electrotransfer competent cells prepared in step (2), spread the LB plate containing IPTG, X-gal, kanamycin and ampicillin, and culture overnight at 30°C.
[0170] (4) All the plates are whit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com