Heart valve replacement prosthesis and threaded fastening heart apex pad thereof
A heart valve replacement and screw thread technology, which is applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as enlarged diameter and height of the apical pad, influence on the use effect, and weak mechanics, and achieve the effects of reduced production costs, convenient assembly, and convenient production and processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
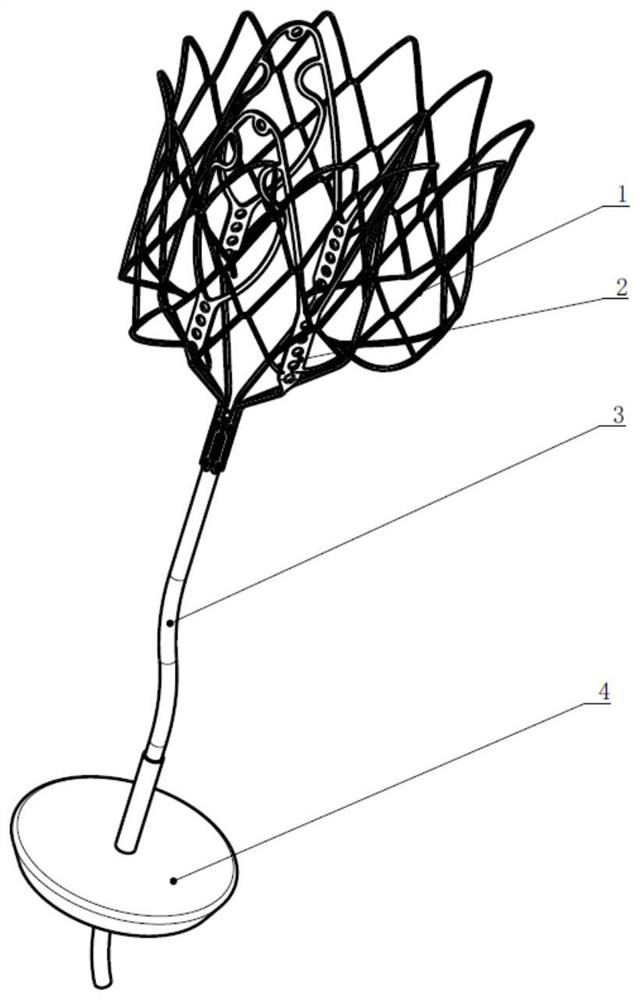
[0036] Refer to attached figure 1 As shown, the heart valve replacement prosthesis of this embodiment includes an outer stent 1 , an inner stent 2 , a tether 3 and an apical pad 4 . Among them, the outer bracket 1 and the inner bracket 2 are connected and assembled by plugging, the inner bracket 2 and the tether 3 are connected and assembled by crimping and suturing, and the apical pad 4 is used to fasten the tether 3 and is sealed in the suture. The outer side of the posterior apical membrane plays the role of fixing the internal and external stents and tethers, and blocking the apical membrane.
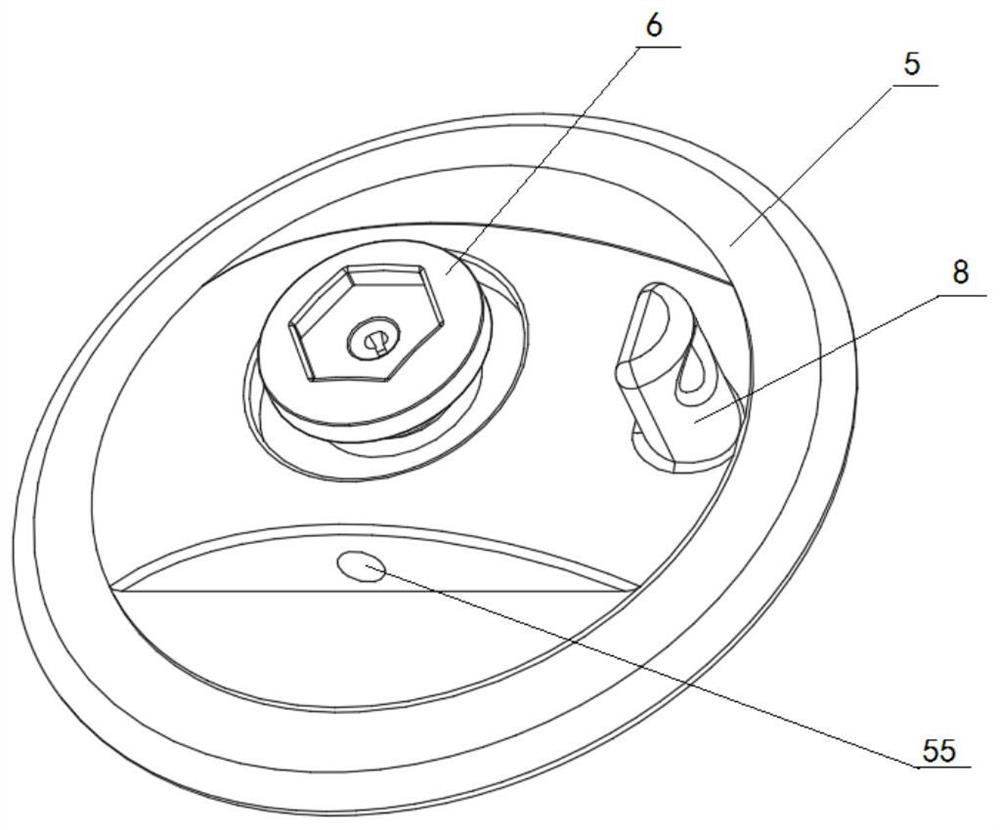
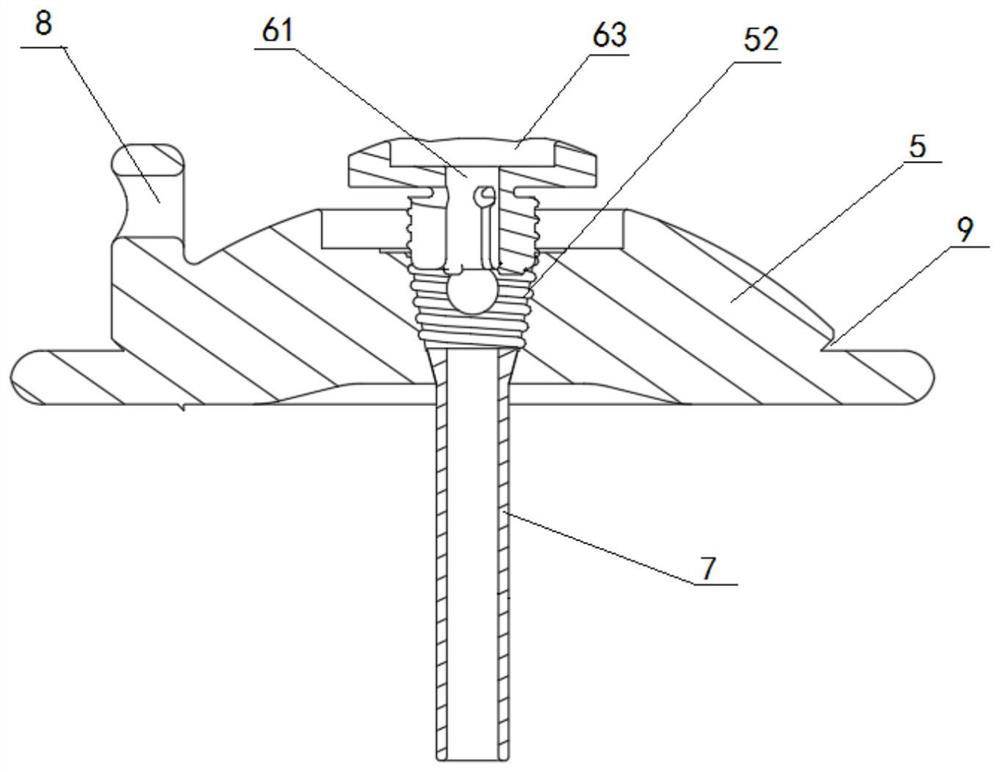
[0037] Refer to attached Figures 2 to 8 As shown, the threaded fastening apical pad 4 of the heart valve replacement prosthesis in this embodiment includes a plugging plate body 5 with a central through hole 51, a threaded locking nail 6 with a central hole 61 and a hollow column 7, the central through hole The hole 51, the central hole 61 and the internal through hole of the hol...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment above in that: refer to the attached Figures 9 to 10 As shown, the locking mechanism of the threaded locking nail 6 adopts a plurality of sharp edges 66 disposed on the inner side of the bottom end of each stud 64 . In this way, when the threaded locking nail 6 is screwed into the central through hole 51, when the sharp edge 66 is tightened with the inward deformation of the stud 64, it can be embedded in the clamped tether 3 to realize the tightening of the tether 3. Further fastening, improve the fastening effect.
[0051] Other parts of this embodiment are the same as those of the foregoing embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The third embodiment differs from the first embodiment above in that: refer to the attached Figures 11 to 12 As shown, the locking mechanism of the threaded locking nail 6 adopts a plurality of transverse annular grooves 67 arranged inside each stud 64 . In this way, when the threaded locking nail 6 is screwed into the central through hole 51, when the transverse ring groove 67 is tightened with the inward deformation of the stud 64, the clamped tether 3 can be engaged, and the same can be achieved for the tether. Improvement of the fastening effect of the rope 3.
[0054] In this embodiment, a plurality of transverse annular grooves 67 are distributed from top to bottom along the axial direction of the stud, and the number is between 1 and 10, forming sharp edges between the annular grooves, but not too sharp to prevent cutting of the tether , causing damage to the tether. Of course, the plurality of transverse ring grooves 67 can also be configured as an internal t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com