Compositions for treating insulin deficiency conditions
A technology of insulin deficiency and composition, applied in the direction of drug combination, metabolic disease, endocrine system disease, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, lower quality of life of T1D patients, disability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0177] result
[0178] Beneficial metabolic effects of enhanced S100A9 in a mouse model of T1D
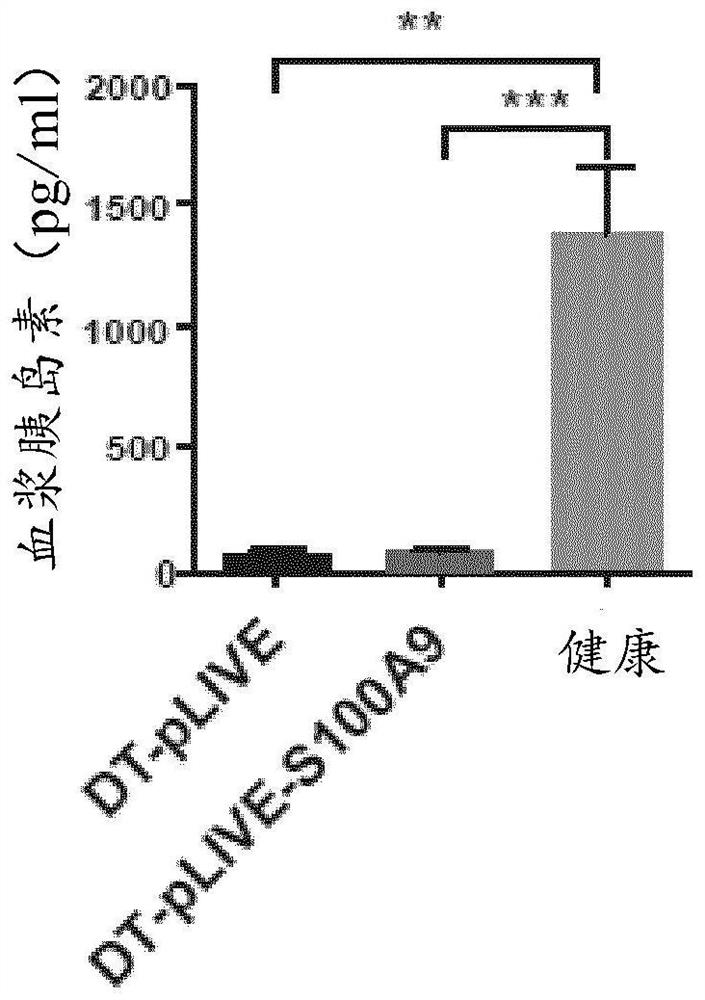
[0179] The inventors overexpressed S100A9 in insulin-deficient mice. The inventors performed hydrodynamic tail vein injection studies in RIP-DTR mice carrying the rat insulin promoter (RIP) upstream of the diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) sequence cloned into the X chromosome Hprt locus. After three consecutive intraperitoneal DT administrations, RIP-DTR mice almost completely lost pancreatic β cells. Indeed, in DT-injected RIP-DTR mice subjected to HTVI of pLIVE (DT-pLIVE) or pLIVE-S100A9 (DT-pLIVE-S100A9), nearly all pancreatic β-cells were ablated (data not shown). Consistent with β-cell loss, pancreatic proinsulin mRNA levels were barely measurable, and these defects resulted in barely detectable circulating insulin in DT-pLIVE and DT-pLIVE-S100A9 mice (Fig. 1a, Fig. 1b). To test whether S100A9 was increased in DT-pLIVE-S100A9 mice, we assessed plasma S100A9 levels and found ...
Embodiment 2
[0184] The presence of the C-terminal FLAG sequence did not interfere with the ability of S100A9 to ameliorate ID symptoms in mice.
[0185] To determine whether the addition of a FLAG tag sequence to S100A9 would affect the ability of S100A9 to ameliorate ID symptoms in mice, we overexpressed the full-length native S100a9 sequence (with or without a C-terminal FLAG tag) under the control of the albumin promoter using HTVI delivery. ) plasmid (pLIVE-n-S100A9 or pLIVE-S100A9-FLAG) or control empty vector (pLIVE). DT-treated RIP-DTR mice subjected to HTVI of pLIVE (DT-pLIVE) or pLIVE-n-S100A9 (DT-pLIVE-n-S100A9) or pLIVE-S100A9-FLAG (DT-pLIVE-S100A9-FLAG) 27 showed a similar degree of hypoinsulinemia ( image 3 a). While DT-pLIVE mice exhibited hyperglycemia and hyperketosis, DT-pLIVE-n-S100A9 mice and DT-pLIVE-S100A9-FLAG mice showed similar improvements in these parameters ( image 3 b to image 3 c). These data suggest that the fusion of S100A9 to the FLAG tag sequence doe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com