Bionic cell membrane-inner core nanoparticle as well as preparation method and application thereof
A nanoparticle and cell membrane technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanomedicine, etc., can solve the problems of high preparation cost and limited application, and achieve the effect of improving effectiveness, reducing drug concentration, and simple and efficient preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
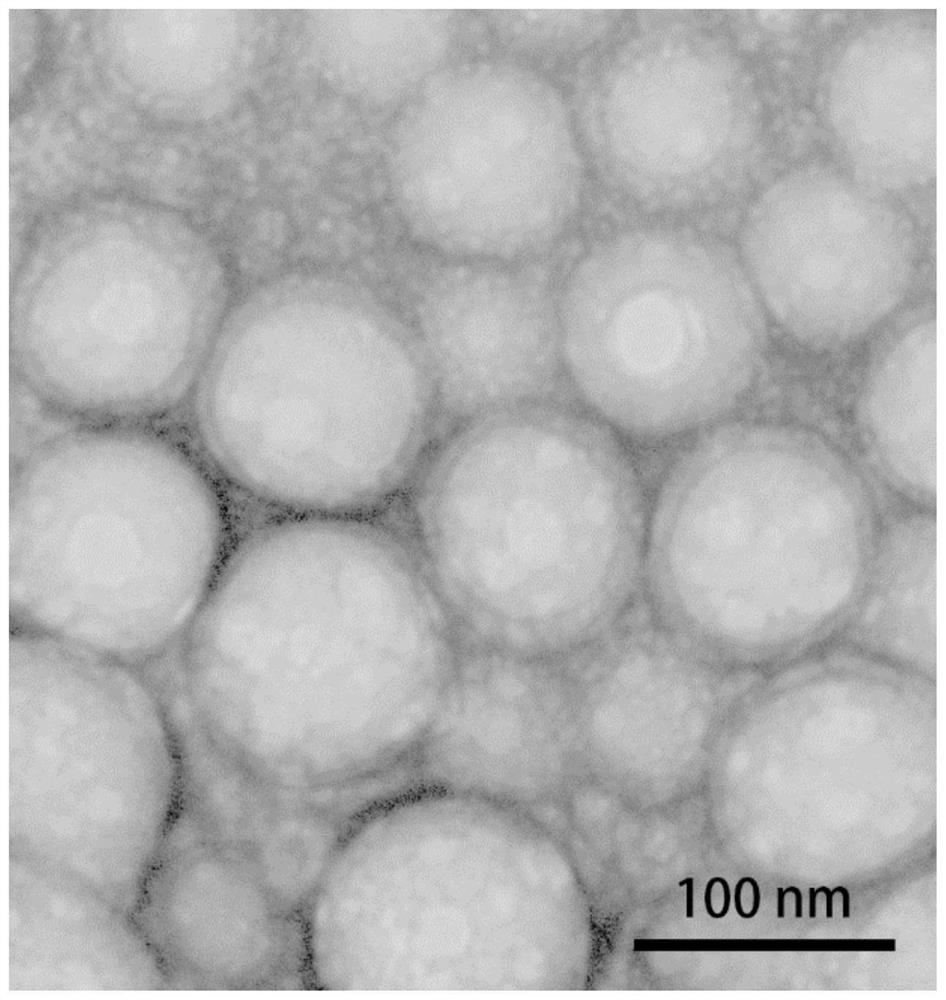
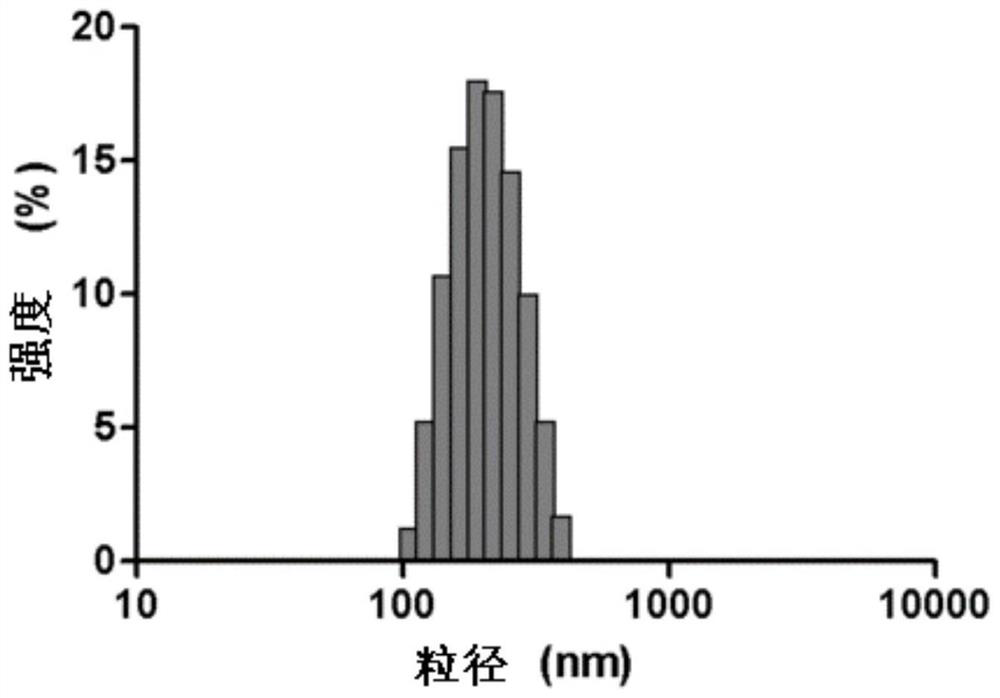
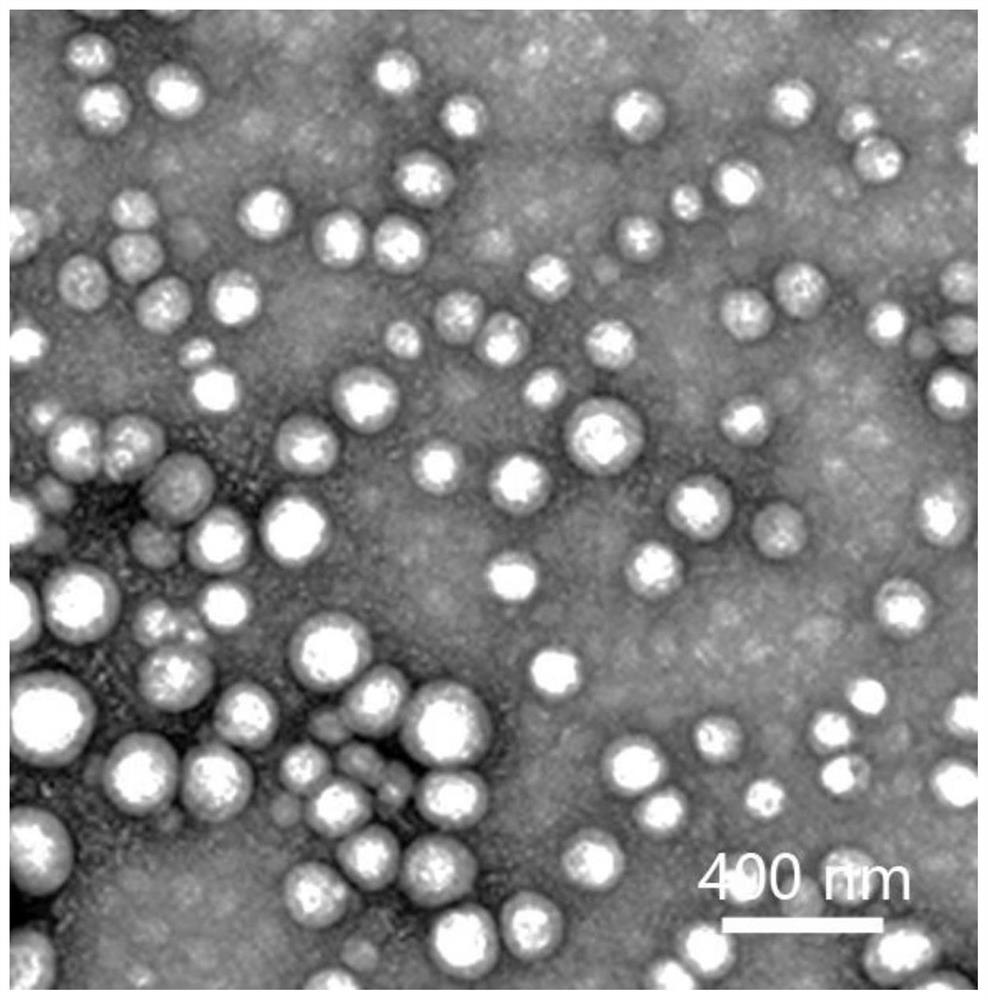
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0068] (1) Take fresh blood from Balb / c mice, add anticoagulant (anticoagulant: blood=3:7, v / v), centrifuge at 216g for 11min, separate red blood cell layer, and obtain platelet-rich plasma;
[0069] (2) Add platelet extraction buffer (1:1, v / v) to the platelet-rich plasma obtained in step (1), and centrifuge at 850g for 5min to obtain platelet precipitate;
[0070] (3) Add platelet purification buffer (1:1, v / v) to the platelet precipitate obtained in step (2), centrifuge at 1000 g for 5 min after resuspension, and obtain purified platelets;
[0071] (4) The purified platelets obtained in step (3) were repeatedly frozen and thawed at -80° C. to 4° C. for three times, with an interval of 10 minutes between freezing and thawing, centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 minutes, and resuspended to obtain platelet membranes.
preparation example 2
[0073] (1) Take fresh blood from Balb / c mice, add anticoagulant (anticoagulant: blood=1:5, v / v), centrifuge at 200g for 20min, separate red blood cell layer, and obtain platelet-rich plasma;
[0074] (2) Add platelet extraction buffer (2:1, v / v) to the platelet-rich plasma obtained in step (1), and centrifuge at 1200g for 2min to obtain platelet precipitates;
[0075] (3) Add platelet purification buffer (2:1, v / v) to the platelet precipitate obtained in step (2), and centrifuge at 800 g for 8 min after resuspending to obtain purified platelets;
[0076] (4) The purified platelets obtained in step (3) were repeatedly frozen and thawed four times at -80° C. to 4° C., with a freeze-thaw interval of 15 minutes, centrifuged at 5000 g for 20 minutes, and resuspended to obtain platelet membranes.
preparation example 3
[0078] (1) Take fresh blood from Balb / c mice, add anticoagulant (anticoagulant: blood=1:8, v / v), centrifuge at 230g for 5min, separate red blood cell layer, and obtain platelet-rich plasma;
[0079] (2) Add platelet extraction buffer (1:2, v / v) to the platelet-rich plasma obtained in step (1), and centrifuge at 600 g for 8 min to obtain platelet precipitates;
[0080] (3) Add platelet purification buffer (1:2, v / v) to the platelet precipitate obtained in step (2), centrifuge at 1500 g for 3 min after resuspension, and obtain purified platelets;
[0081] (4) The purified platelets obtained in step (3) were repeatedly frozen and thawed four times at -80° C. to 4° C., with a freeze-thaw interval of 15 minutes, centrifuged at 5000 g for 20 minutes, and resuspended to obtain platelet membranes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dispersion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com