Distributed service migration method for mobile edge computing
A distributed service and edge computing technology, applied in the field of the Internet of Things, can solve problems such as unpredictable user mobility, unstable multi-user environment, frequent interaction, etc., to achieve increased convergence, migration costs, and average task completion time. The effect of improving sampling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
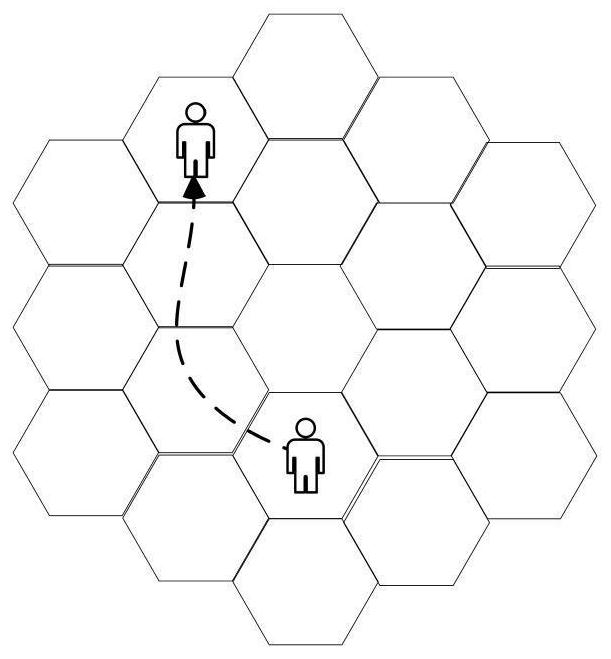
[0065] The method designed in this example uses Python to implement the proposed algorithm. Mobile devices move randomly within the coverage of multiple MEC servers, and their trajectories are based on a two-dimensional hexagonal random walk model, as shown in the attached figure 2 shown. Evaluate the latency and energy consumption of the algorithm through actual application scenarios. In addition, we compare the average latency and transfer energy consumption of similar algorithms under different parameters.
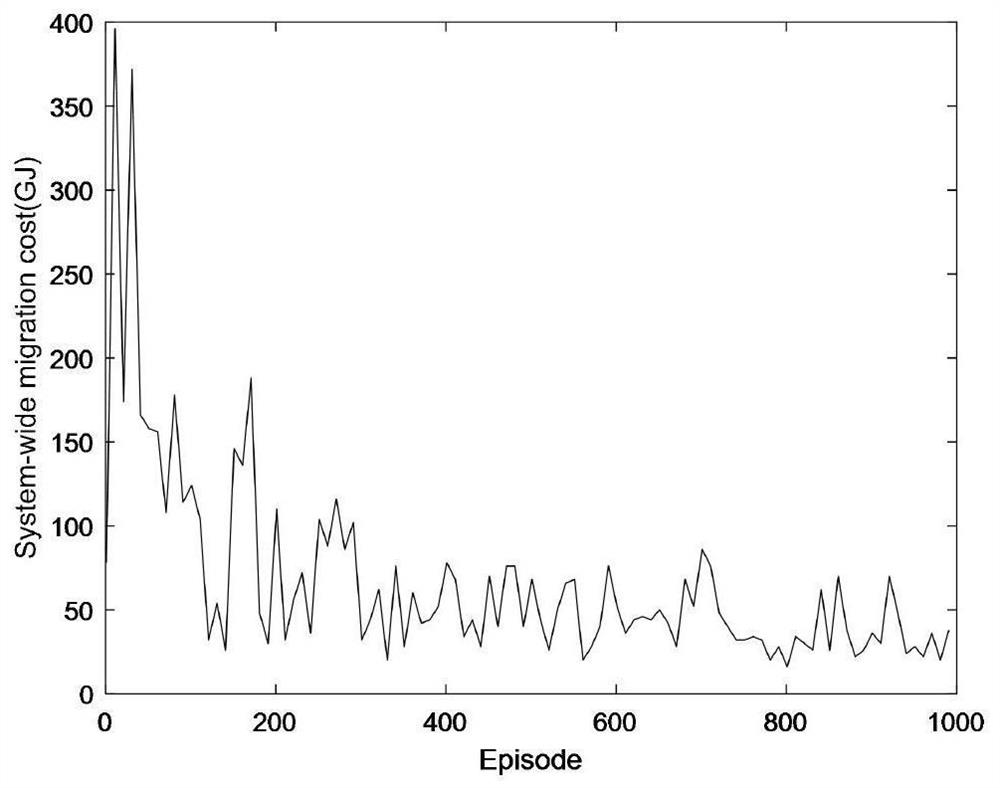
[0066] See attached Figure 10 , the distributed service migration method for mobile edge computing in this embodiment mainly includes the following key steps:
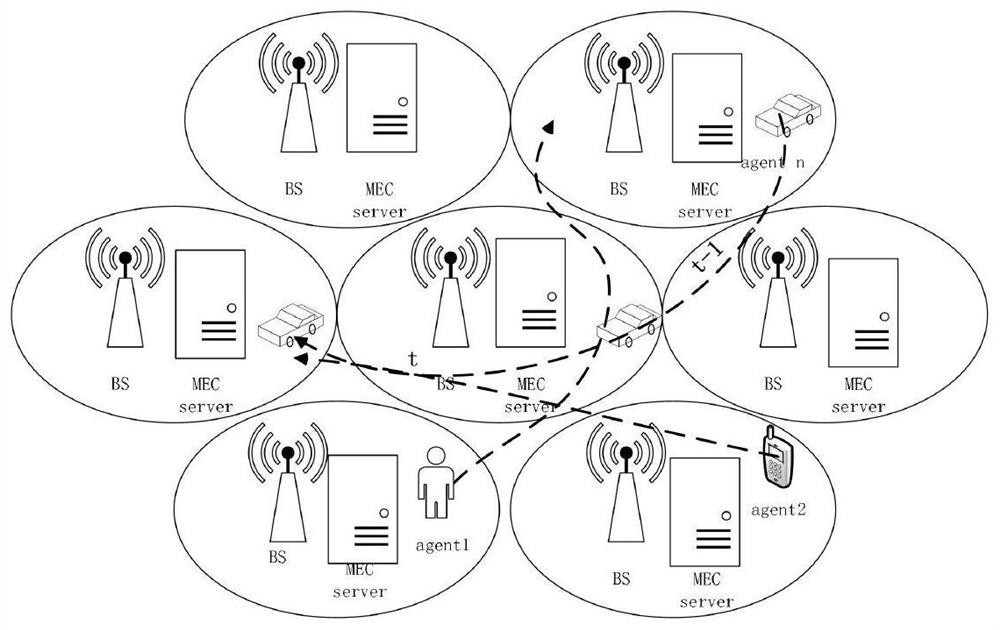
[0067] 1. Construction of the system model, the system model is as attached figure 1 Shown:
[0068] Section 1.1. Establish a backhaul delay model;
[0069] 1.2. Establish a communication delay model;
[0070] Section 1.3, establish a calculation delay model;
[0071] Section 1.4. Establish a migration ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com