Torque detection sensor
A technology of torque detection and sensors, which is applied in the direction of torque measurement, instruments, measuring devices, etc., and can solve the problems of large sensors and increased processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
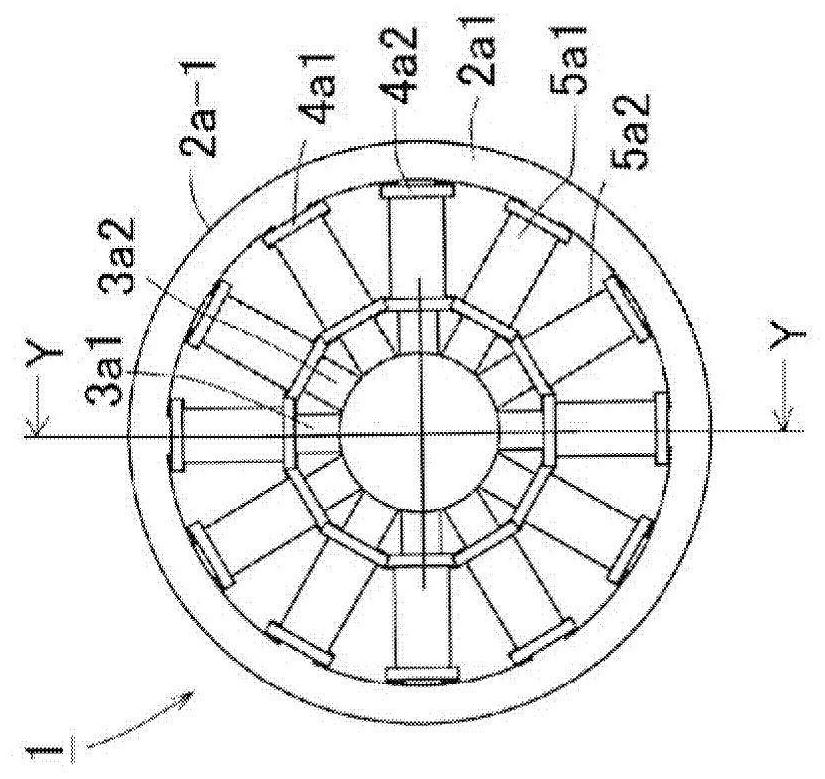
[0072] image 3 A magnetic circuit formed by energizing the first energization circuit 6 a 1 , the second energization circuit 6 a 2 , the third energization circuit 6 b 1 , and the fourth energization circuit 6 b 2 is shown as an example. In the figure, NA represents the pole tooth excited by coil A to N pole, SA represents the pole tooth excited by coil A to S pole, and in the same map, NB represents the pole tooth excited by coil B to N pole, and SB represents the pole tooth excited by coil B Become the pole teeth of the S pole. More precisely, the front end of the pole tooth facing the object S is excited to N pole or S pole. Whether to be excited to the N pole or to the S pole can be realized by reversing the winding directions of the coil A and the coil B (first coil 5a1, second coil 5a2, third coil 5b1, and fourth coil 5b2). In addition, the long frame E1 surrounding NA and SA and the long frame E2 surrounding NB and SB indicate the direction of the magnetic circuit w...
Embodiment 2
[0077] In addition, in Figure 4 Among them, the circumferentially adjacent first pole teeth 3a1 of the first core portion 2a-1, the circumferentially adjacent second pole teeth 3a2 of the second core portion 2a-2, and the third core portion 2b-1 may be The circumferentially adjacent third pole teeth 3b1 and the circumferentially adjacent fourth pole teeth 3b2 of the fourth core portion 2b-2 are excited to have different magnetic properties.
[0078] In this case, since the second pole tooth 3a2 and the fourth pole tooth 3b2, the first pole tooth 3a1 and the fourth pole tooth 3b1, which are located symmetrically with respect to the plane of symmetry M, are of the same magnetic pole, no crossover is formed. The magnetic circuit of the symmetry plane M of the first torque detection part 7a and the second torque detection part 7b, but a magnetic circuit is formed between the pole teeth adjacent in the circumferential direction among the first pole teeth 3a1 and the third pole tee...
Embodiment 3
[0080] In addition, if Figure 5 As shown, the first pole teeth 3a1 of the first core part 2a-1 located symmetrically with respect to the symmetry plane M of the first torque detection part 7a and the second torque detection part 7b are excited as S poles (or N poles). , the fourth pole teeth 3b2 of the fourth core portion 2b-2 are excited as N poles (or S poles). In addition, the second pole teeth 3a2 of the second core portion 2a-2 positioned symmetrically with respect to the symmetry plane M are excited as S poles (or N poles), and the third pole teeth 3b1 of the third core portion 2b-1 are excited as N pole (or S pole).
[0081] In this case, in the first pole tooth 3a1 and the third pole tooth 3b1, a magnetic path (NB→SA) (NA→SB) is formed between the pole teeth adjacent in the circumferential direction, and in addition, The distance between the second pole tooth 3a2 and the fourth pole tooth 3b2 is along the axial direction of the object to be detected ( Figure 5 Up an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com