Forming method of CMOS image sensor transfer transistor
A transfer transistor and image sensor technology, applied in the field of image sensors, can solve the problems of poor negative pressure signal stability, large output signal noise, and increased process cost, etc., to reduce process cost, save area, and reduce dark current or white spots Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
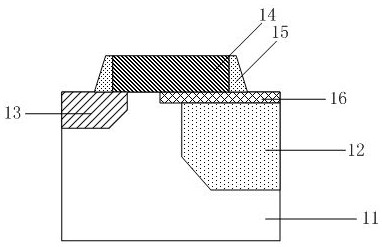
[0035] refer to figure 1 , the present embodiment provides a method for forming a transfer transistor of a CMOS image sensor, comprising: providing a substrate 11, forming a photodiode 12, a floating diffusion region 13, and forming at least one transfer transistor in the substrate 11;
[0036] P-type doped polysilicon 14 is correspondingly deposited on the photodiode 12 as the gate of the transfer transistor. When the charge accumulation state of the photodiode is applied, the voltage applied to the gate of the transfer transistor is greater than or equal to 0V.
[0037] Using p-type doped transfer transistor gate transfer transistor gate, when the photodiode is in the charge accumulation state, only need to apply a voltage of 0V or more to achieve the pinning effect, without the need to use large capacitors and additional circuit structures , save the area, reduce the process cost, and at the same time, the stability of the voltage signal is high.
[0038] The substrate 11 ...
Embodiment 2
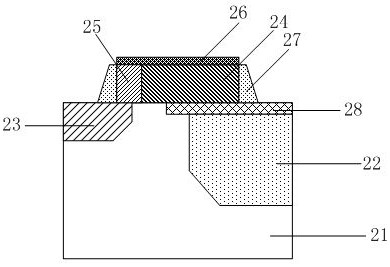
[0042] refer to figure 2 , the present embodiment provides a method for forming a transfer transistor of a CMOS image sensor, comprising: providing a semiconductor substrate 21, forming a photodiode 22, a floating diffusion region 23 and forming at least one transfer transistor in the substrate 21;
[0043] P-type doped polysilicon 24 is correspondingly deposited above the photodiode 22 as a part of the gate of the transfer transistor. When the charge accumulation state of the photodiode is applied, the voltage applied to the gate of the transfer transistor is greater than or equal to 0V.
[0044] The gate of the transfer transistor can be all p-type doped polysilicon, or partially p-type doped polysilicon. In this embodiment, the gate of the transfer transistor further includes n-type doped polysilicon 25 near the side of the floating diffusion region 23. When the charge accumulation state of the photodiode is applied, the voltage applied to the gate of the transfer transist...
Embodiment 3
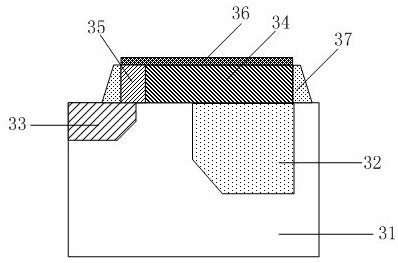
[0052] This embodiment provides a method for forming a transfer transistor of a CMOS image sensor. Its technical solution is similar to that of Embodiment 2. The difference from Embodiment 2 is that p-type doped polysilicon completely covers the carrier collection region of the photodiode. A pinning effect on the upper surface of the photodiode is achieved.
[0053] Specifically, refer to image 3 , providing a method for forming a CMOS image sensor transfer transistor, comprising: providing a semiconductor substrate 31, forming a photodiode 32, a floating diffusion region 33 and forming at least one transfer transistor in the substrate 31;
[0054] P-type doped polysilicon 34 is correspondingly deposited on the photodiode 32 as the gate or a part of the gate of the transfer transistor. When the charge accumulation state of the photodiode is applied, the voltage applied to the gate of the transfer transistor is greater than or equal to 0V.
[0055] In this embodiment, the p-t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com