Efficient pre-hardening method for steel and steel workpiece
A high-efficiency, workpiece-friendly technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, furnace types, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of steel workpiece damage, inability to deal with surface shape steel workpieces, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
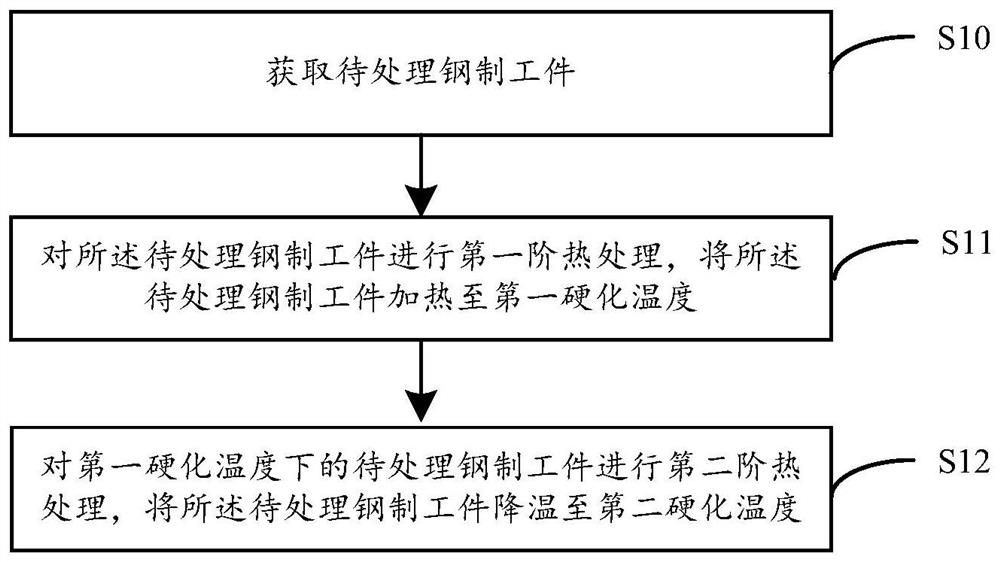
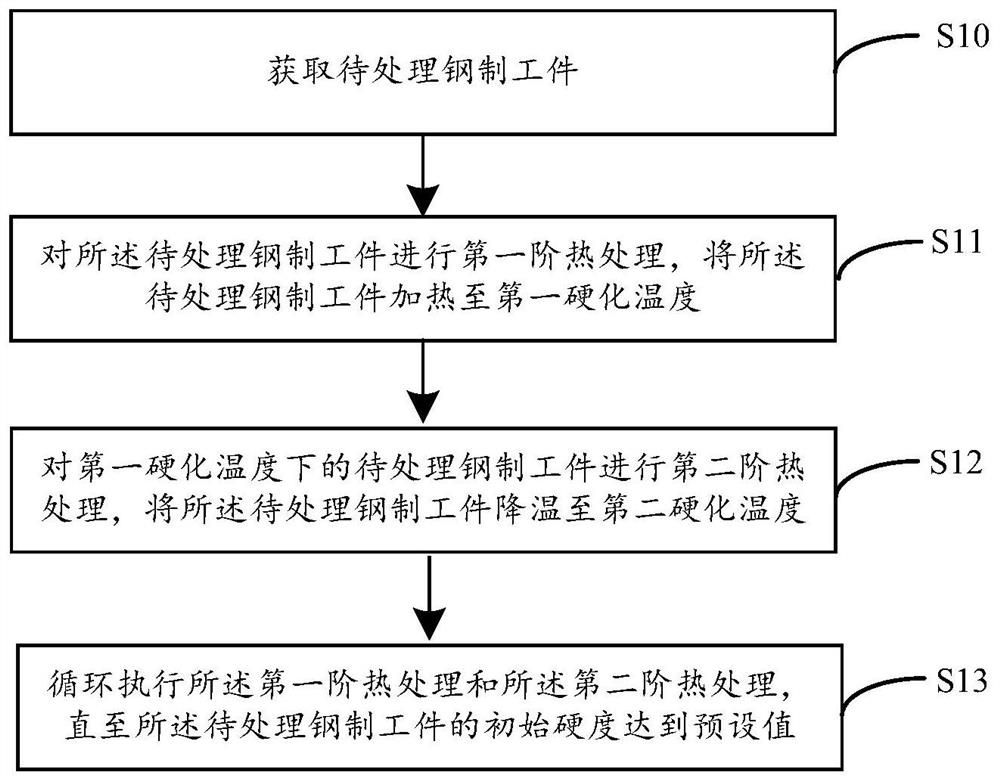
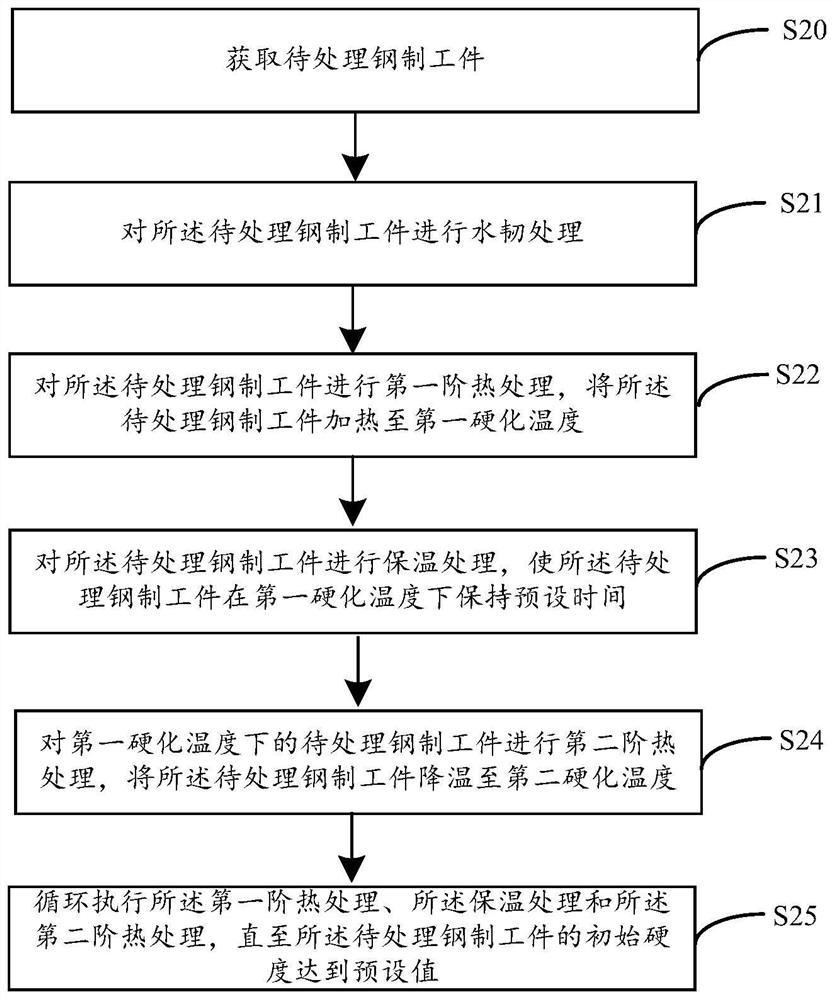
Image
Examples
example 1
[0093] In this example, the steel workpiece to be treated is made of ordinary high manganese austenitic steel material, the main chemical composition (wt.%) is C: 1.05, Si: 0.30, Mn: 13.05, and the rest is iron and other impurities. First, the steel workpiece to be treated is subjected to conventional water toughening process: after heating to 1050°C, water cooling to room temperature. At this time, the hardness of the high manganese steel is 220HV, the tensile strength of the matrix is 820MPa, and the elongation is 42%. Next, using induction heat treatment, the surface of the steel workpiece to be treated was heated to 500°C at a heating rate of 35°C / s, kept for 3s, and then water-cooled to room temperature with an average cooling rate of 80°C / s. After that, a heating and cooling process is performed in a cycle: the steel workpiece to be processed is heated until the surface temperature reaches 500°C, kept for 1s, and then cooled to room temperature with water, with an aver...
example 2
[0096] In this example, the steel workpiece to be treated is made of ordinary high manganese austenitic steel material, the main chemical composition (wt.%) is C: 1.05, Si: 0.30, Mn: 13.05, and the rest is iron and other impurities. First, the steel workpiece to be treated is subjected to conventional water toughening process: heating to 1050°C, cooling to room temperature by water cooling. At this time, the hardness of the high manganese steel is 220HV, the tensile strength of the matrix is 820MPa, and the elongation is 42%. Using direct current heating, the surface of the steel workpiece to be treated is heated to 700°C at a heating rate of 80°C / s, kept for 3s, and then cooled to room temperature by blowing helium, with an average cooling rate of 50°C / s. Afterwards, a heating and cooling process is performed in a cycle: the steel workpiece to be processed is heated until the surface temperature reaches 550°C, kept for 1s, and then water-cooled to room temperature, with an ...
example 3
[0099] In this example, the steel workpiece to be treated is made of alloyed high manganese austenitic steel material, the main chemical composition (wt.%) is C: 1.15, Si: 0.44, Mn: 11.8%, Cr: 0.6, and the rest is iron and other impurities. First, the steel workpiece to be treated is subjected to conventional water toughening process, heated to 1080°C, and cooled to room temperature by water cooling. At this time, the hardness of the high manganese steel is 240HV, the tensile strength of the matrix is 855MPa, and the elongation is 38%. Next, the flame heating method was used to heat the surface of the steel workpiece to be treated to 450°C at a heating rate of 110°C / s and keep it warm for 10s. After that, it was cooled to room temperature in ice water with an average cooling rate of 130°C / s. After the above process, refer to Figure 5 The microhardness curve of the steel workpiece to be processed is shown. The surface hardness of the steel workpiece to be processed is 290H...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com