Method for recognising obstacles and for predicting the change of position of known obstacles by means of signals from a plurality of sensors and for compressing and decompressing sensor signals used for the above purposes
A sensor signal and sensor technology, applied to identify obstacle objects based on signals from multiple sensors and predict changes in the position of known obstacle objects, and to compress and process sensor signals used for the above purposes In the field of decompression, it can solve problems that do not involve object recognition, object recognition of undescribed obstacles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
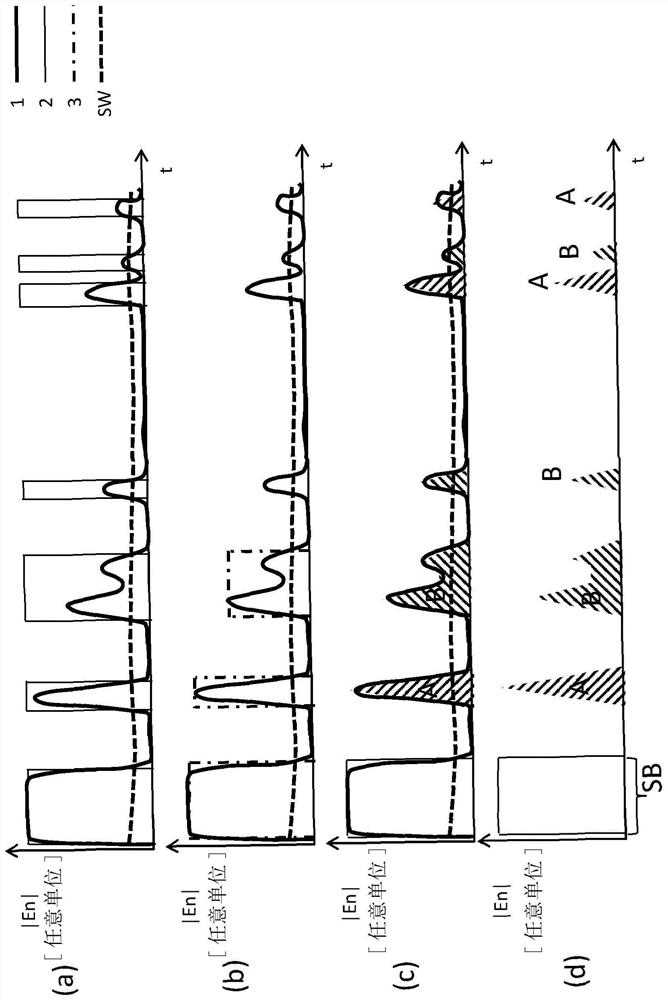
[0428] image 3 a shows the temporal profile of a conventional ultrasound echo signal 1 and its conventional evaluation in freely selectable units for the coordinate axes. It begins by sending out a transmit burst SB, carrying a threshold signal SW. Output 2 is set to logic 1 whenever the envelope signal of the ultrasound received signal (ultrasound echo signal 1 ) exceeds the threshold signal SW. Involves a time-analog interface with digital output levels. Then, a further evaluation takes place in the sensor's controller. Via this analog interface, which corresponds to the prior art, it is not possible to signal faults or control sensors.
[0429] image 3 b shows the time profile of a conventional ultrasound echo signal 1 and its conventional evaluation in freely selectable units for the coordinate axes. It begins by sending out a transmit burst SB, carrying a threshold signal SW. However, whenever the envelope signal of the ultrasound received signal (ultrasound echo ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com