Glass frosting liquid, frosted glass prepared from glass frosting liquid and preparation method of glass frosting liquid
A frosting liquid and glass technology, which is applied in the field of frosted glass preparation, can solve the problems of glass light pollution and achieve the effect of eliminating glare
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-8A
[0050] Embodiment 1-8AG glass frosting liquid
[0051] The frosting powder formulations of Examples 1-8 are shown in Table 1. The frosting liquid of Examples 1-8 is obtained by dispersing 100 g of frosting powder in 35 g of deionized water. The specific preparation method is: accurately weigh ammonium bifluoride according to the number of parts by mass , ammonium fluoride, oxalic acid dihydrate, sulfamic acid, white sugar, sucrose, barium sulfate, barium fluoride, calcium fluoride, sodium fluoride, potassium fluoride dihydrate, potassium chloride, aluminum fluorosilicate, twelve Sodium alkylsulfonate and magnesium fluorosilicate medicines are finely ground in a ceramic mortar (because many medicines are crystal blocks, so they need to be ground), and the grinding time is about 10 minutes (grinding until the medicine is dispersed) non-agglomerative powder, no agglomeration phenomenon), after the grinding is completed, transfer all the medicines in the mortar to a 1000mL beaker ...
Embodiment 1
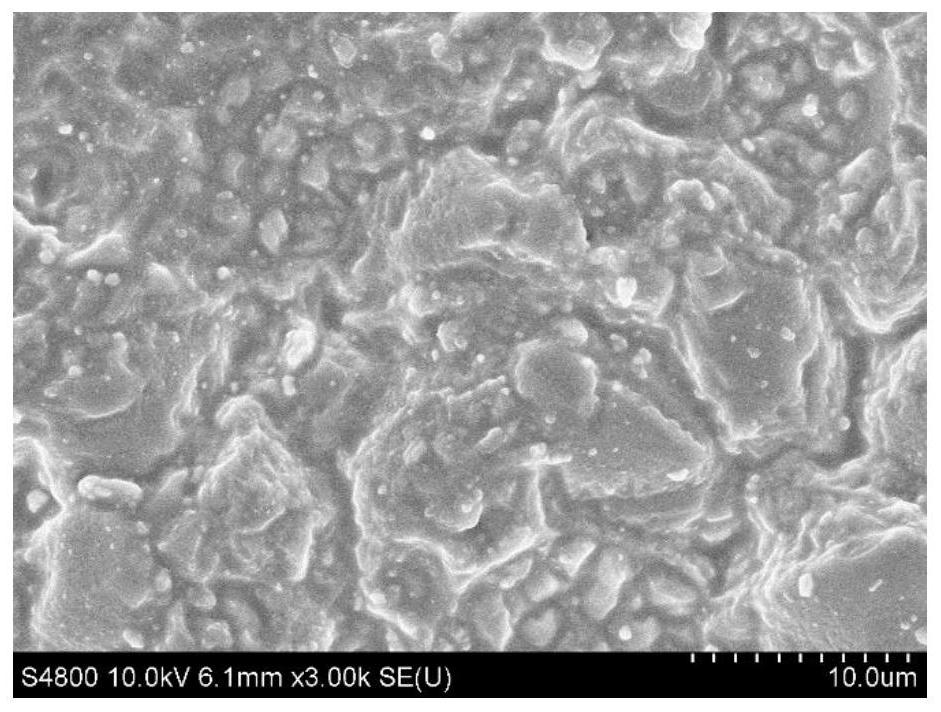
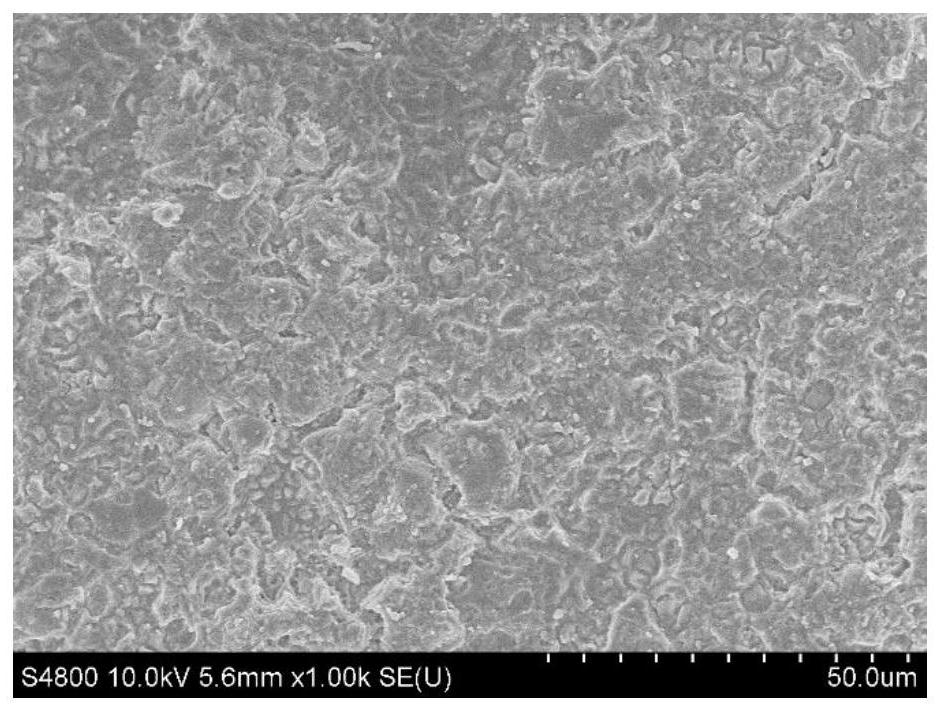
[0061] Compared with Example 1 and Example 2, the appearance of the AG powder frosted glass in Example 1 is very smooth, and the content of aluminum fluorosilicate increases, which improves the flatness of the frosted glass.
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown in the upper left corner, after the silicic acid in the glass is dissolved, aluminum fluorosilicate acts as a silicic acid gel accelerator to accelerate the polymerization of the silicic acid dissolved by ammonium bifluoride on the glass surface to form uniform gel particles. Aluminum fluorosilicate content reduces among the embodiment 2, causes figure 2 No homogeneous gel particles were observed in . Compared with Example 4, the ammonium bifluoride is slightly increased, causing the apparent roughness of the AG powder frosted glass to increase from an average of 0.359 to 0.532. Compared with Example 5, the content of aluminum fluorosilicate increased from 3.872% to 4.350%, which caused the apparent roughness of AG pow...
Embodiment 6
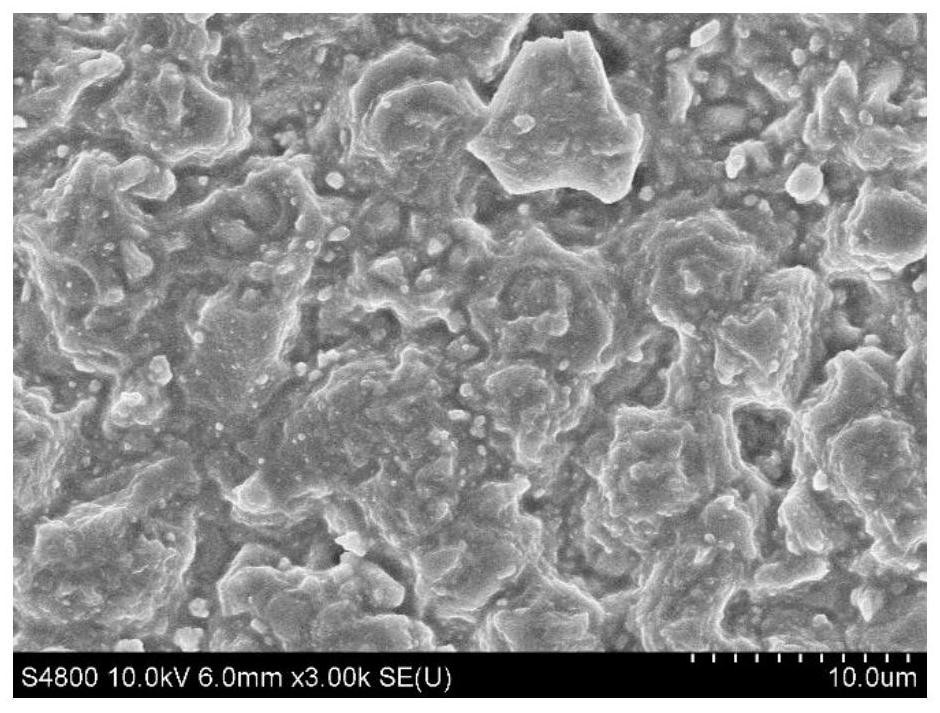
[0064] Examples 6-7 are different from Examples 1-5 and Example 8. Magnesium fluorosilicate is added to the AG powder frosting powder, and the roughness of the AG powder frosting glass is greatly improved. In Example 6, a large amount of magnesium fluorosilicate was added, and the roughness increased significantly, with an average roughness value of 0.970; while when the amount of magnesium fluorosilicate was only 0.5%, the average roughness value of Example 7 only increased to 0.810. Image 6 with Figure 7 The morphology scan of AG powder frosted glass also shows that due to the increase of magnesium fluorosilicate, magnesium fluorosilicate acts as an accelerator to promote the quick-setting of silicic acid sol, and the apparent roughness increases significantly. Moreover, the higher the magnesium fluorosilicate content, the lower the uniformity of the surface gel particles, Image 6 The coexistence of medium and large particles of gel and small particles of gel directly l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com