Multi-disaster power distribution network elasticity evaluation method considering fault linkage
A distribution network and disaster technology, which is applied in the field of multi-disaster distribution network resilience assessment considering fault chaining, can solve the problems of complex distribution network structure, large scale, and inability to directly migrate distribution network resilience improvement strategies to prevent and the effect of suppressing the chain of failures and improving resilience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
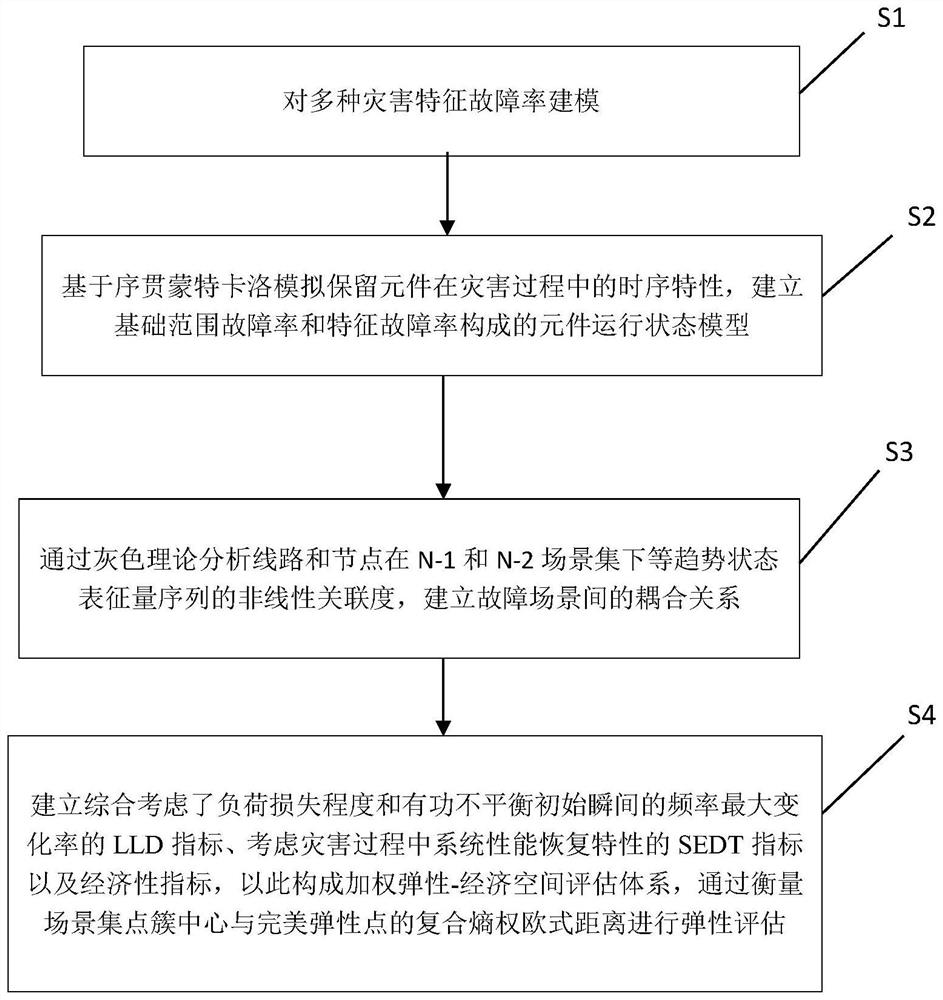
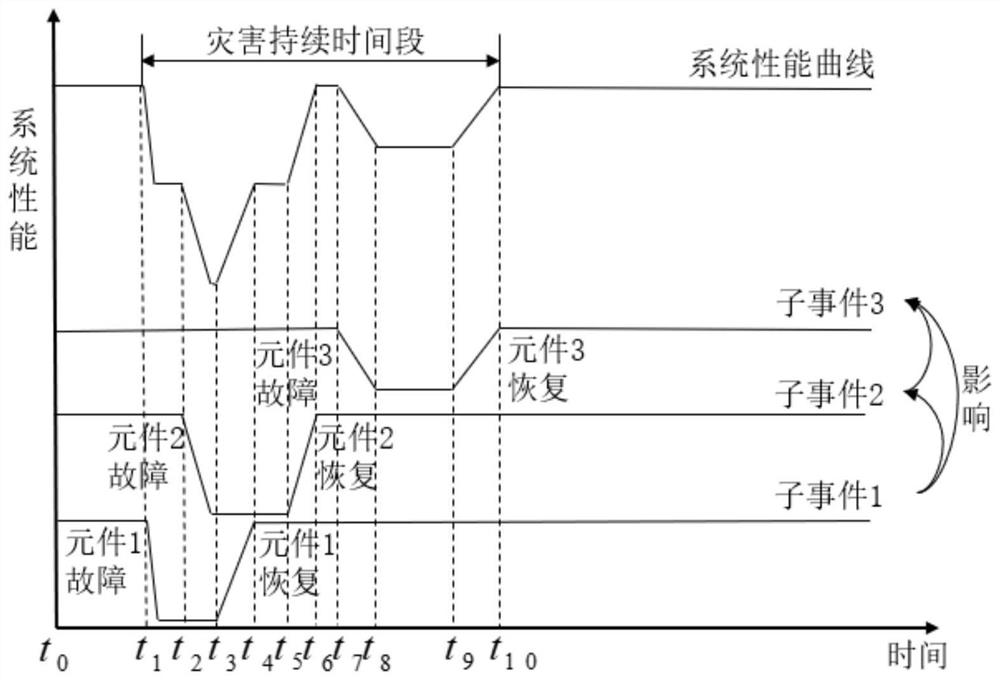
[0106] Example: such as figure 1 As shown in , a flow chart of a multi-disaster distribution network resilience assessment method considering fault cascading, including the following steps:
[0107] Step S1, modeling the characteristic failure rate of multiple disasters: the characteristics of multiple disasters include three disasters: typhoon, ice and snow, and lightning; respectively perform characteristic failure rate modeling for the three disasters of typhoon, ice and snow, and lightning;
[0108] The Batts model is used to simulate the wind speed and wind direction of each point within the influence range of the typhoon wind circle, the scattered points are generated in the topological coverage of the system and the range of typhoon action at different times is generated by k-means clustering, and the random The cluster center and the average distance of the scattered points are interpolated to obtain the trajectory of the typhoon center and the change of the radius of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com